10,000 search results
(0.049 seconds)
- Elektrakution by Comicraft,
$19.00SHE'S DEAD, FRANK It's the year 1991, BC (Before Comicraft) when REM were still making records and Frank Miller’s memorable run on Marvel Comics’ DAREDEVIL was just over ten years old. Comicraft’s Richard Starkings found himself working in Anaheim, California for Graphitti Designs. Graphitti had produced the first hardcover edition of Miller’s Batman tale, DARK KNIGHT RETURNS and was now putting together the sequel to Miller’s DAREDEVIL — ELEKTRA LIVES AGAIN! Richard was not engaged to letter this book, the pages of Frank’s incredible original art that came through Graphitti’s studio were already lettered by Marvel Stalwart, Jim Novak. However, there were some cover elements that needed to be added, based on the logo originally rendered by Frank’s brother, Steve. Starkings set about the task of creating an alphabet that could be used to develop Steve’s idea for the trade dress -- the cover elements, the back cover copy and credits on the interior pages. This was long before Macintosh computers and font programs made this work considerably easier, so Rich sat down with a pencil and a sheet of vellum and rendered an alphabet that could be used as the basis for the text that was needed... Those sketches have languished in a drawer for nearly thirty years, but now, finally, Comicraft’s John Roshell has dusted off those old letterforms and Elektrakuted a font based on those designs, a font we HAD to call ELEKTRAKUTION! As for Elektra; she’s dead, Frank. Features: Ten weights (Light, Regular, Bold; Rough Light, Regular & Bold; Inline, Inline Rough, Outline & Outline Rough) with upper & lowercase characters, Western & Central European accents and Greek characters. - Blackhaus by Canada Type,
$25.00Almost a half of a millennium after being mistaken for the original 4th century Gothic alphabet and falsely labeled "barbaric" by the European Renaissance, the blackletter alphabet was still flourishing exclusively in early 20th century Germany, not only as an ode to Gutenberg and the country's rich printing history, but also as a continuous evolution, taking on new shapes and textures influenced by almost every other form of alphabet available. Blackletter would continue to go strong in Germany until just before the second World War, when it died a political death at the height of its hybridization. For almost 50 years after the war, blackletter was very rarely used in a prominent manner, but it continued to be seen sparely in a variety of settings, almost as a subliminal reminder of western civilization's first printed letters; on certificates and official documents of all kinds, religious publications, holiday cards and posters, to name a few. In the early 21st century, blackletter type has been appearing sporadically on visible media, but as of late 2005, it is not known how long the renewed interest will last, or even whether or not it will catch on at all. The last few years before World War II were arguably the most fascinating and creative in modern blackletter design. During those years, and as demonstrated with the grid-based Leather font, the geometric sans serif was influencing the blackletter forms, taking them away from their previous Jugendstil (Art Nouveau) hybridizations. Blackhaus is a digitization and elaborate expansion of a typeface called Kursachsen Auszeichnung, designed in 1937 by Peterpaul Weiss for the Schriftguss foundry in Dresden. This is one of very few designs from that time attempting to infuse more Bauhaus than Jugendstil into the Blackletter forms. This is why we used a concatenation of the words blackletter and Bauhaus to name this face. The result of injecting Bauhaus elements into blackletter turned out to be a typeface that is very legible and usable in modern settings, while at the same time harking back to the historical forms of early printing. The original 1937 design was just one typeface of basic letters and numbers. After digitizing and expanding it, we developed a lighter version, then added a few alternates to both weights. The Rough style came as a mechanically-grunged afterthought, due to current user demand for such treatment. Having the flexibility of 2 weights and many alternates of a blackletter typeface is not a very common find in digital fonts. More specifically, having the flexibility of 2 weights and alternates of a 20th century blackletter typeface is almost unheard of in digital fonts. So the Blackhaus family can be quite useful and versatile in an imaginative designer's hands. - PF Tempesta Five Compressed - Unknown license
- PF Tempesta Seven Condensed - Unknown license
- PF Tempesta Five Extended - Unknown license
- PF Tempesta Five Condensed - Unknown license
- PF Tempesta Seven Compressed - Unknown license
- PF Tempesta Seven Extended - Unknown license
- Slm by Antiochus,
$30.00We produce original printing press letter fonts, for example from the journal Southern Literary Messenger (circa 1830 - 1870). The only one in the world. What makes our fonts so attractive to the eye, are the myriad imperfections. It's not an approximation to the printing-press letters--- these are the actual letters, complete with all their manifold differences. If you look closely you will notice that the letter 'e' say, each time it is printed, is slightly different. These differences arise from the mechanical action of the inked-wooden press on the paper, and cannot be faked by artificial means. The eye subconsciously picks up this text as the actual printing press letters. Edgar Allan Poe published many of his great works in the Southern Literary Messenger, as did many other great nineteenth century writers, ie. Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Nathaniel Hawthorne &c. - Quardi - Unknown license
- ErasmusInline - Unknown license
- Erasmus - Unknown license
- Times Eighteen by Linotype,
$29.00In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Europa LT by Linotype,
$29.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten Paneuropean by Linotype,
$92.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Kingthings Spike Pro by CheapProFonts,
$10.00You gotta love this extreme take on the "gothic" blackletter traditions! Roger Nelsson edited a few letters, drastically improved the spacing - and then gave it the usual large CheapProFonts character set. Fun! Kevin King says: "Kingthings Spike was made because Buffy has one, I made Willow... Xander is yet to come. Oh and because I hate Engravers Old English! Pugin, eat my shorts! Sorry!" Kingthings Spikeless is a toned down version of Kingthings Spike. Kevin King says: "Kingthings Spikeless was requested by those who actually want to read text... well I call that tedious, but if you must, here it is no flourishes, just my small homage to black-letter." ALL fonts from CheapProFonts have very extensive language support: They contain some unusual diacritic letters (some of which are contained in the Latin Extended-B Unicode block) supporting: Cornish, Filipino (Tagalog), Guarani, Luxembourgian, Malagasy, Romanian, Ulithian and Welsh. They also contain all glyphs in the Latin Extended-A Unicode block (which among others cover the Central European and Baltic areas) supporting: Afrikaans, Belarusian (Lacinka), Bosnian, Catalan, Chichewa, Croatian, Czech, Dutch, Esperanto, Greenlandic, Hungarian, Kashubian, Kurdish (Kurmanji), Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Maori, Polish, Saami (Inari), Saami (North), Serbian (latin), Slovak(ian), Slovene, Sorbian (Lower), Sorbian (Upper), Turkish and Turkmen. And they of course contain all the usual "western" glyphs supporting: Albanian, Basque, Breton, Chamorro, Danish, Estonian, Faroese, Finnish, French, Frisian, Galican, German, Icelandic, Indonesian, Irish (Gaelic), Italian, Northern Sotho, Norwegian, Occitan, Portuguese, Rhaeto-Romance, Sami (Lule), Sami (South), Scots (Gaelic), Spanish, Swedish, Tswana, Walloon and Yapese. - Varisse by AVP,
$19.00Varisse spans over two centuries of type design and draws its inspiration from well-loved classics that are as fresh today as they were when they were created. The range stretches from a quintessential 18th century transitional serif to an uncompromising 20th century sans. Think Baskerville, think Gill. The idea was to create a family that shared similar forms and the same vertical metrics, allowing them to be mixed to provide impact and readability as required. With a generous x-height and a host of options, the Varisse family is ideally suited to branding, packaging, magazines and editorial. It also provides a wealth of opportunity in website presentation. The fonts are divided into five subfamilies by degree of ‘serification’. Varisse Sans Varisse Soft Sans Varisse (normal) Varisse Soft Serif Varisse Serif Each subfamily contains six weights and accompanying italics. - Musirte Antiqua by Intellecta Design,
$19.90 - Pennywhistle by Megami Studios,
$7.50 - DXOldStandard Condensed No2 by DXTypefoundry,
$25.00 - Noisetoy by Christie,
$10.00Noisetoy is an up-to-date font that can be used widely and successfully, as it is a simple, clear, minimal and funky and it clearly depicts 21st Century design. - ITC Pacella by ITC,
$29.99Pacella was designed by Vincent Pacella and fashioned in the tradiation of Century Schoolbook, Corona and Nimrod. Pacella maintains high legibilty and exhibits a character and personality all its own. - Labrat - Unknown license
- Stove Plate JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00An old printer's advertising cut for Red Star Oil Stoves yielded a typeface that was both vintage and somewhat techno at the same time. Originally drawn as a slanted logo, the individual letters had an array of chamfered, angled and flat sides combined with a bold outline. This font is available in both vertical and oblique versions. - SF Chromium 24 SC - Unknown license
- SF Espresso Shack Condensed - Unknown license
- SF Port McKenzie Extended - Unknown license
- SF Groove Machine ExtUpright - Unknown license
- SF Zero Gravity Condensed - Unknown license
- SF Burlington Script SC - Unknown license
- SF Arch Rival Extended - Unknown license
- SF Groove Machine Extended - Unknown license
- SF Groove Machine Upright - Unknown license
- Robo OS by OS CORP,
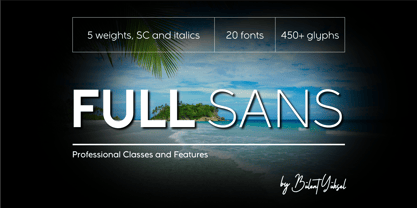
$9.00 - Full Sans by Bülent Yüksel,
$19.00Full Sans is a geometric sans in the tradition of Futura, Avant Garde and the like. It has a modern streak which is the result of a harmonization of width and height especially in the lowercase letters to support legibility. Full Sans is the younger brother of original Full Neue, Full Slab and Full Tools. Ideally suited for advertising and packaging, editorial and publishing, logo, branding and creative industries, poster and billboards, small text, wayfinding and signage as well as web and screen design. Full Sans provides advanced typographical support for Latin-based languages. An extended character set, supporting Central, Western and Eastern European languages, rounds up the family. The designation “Full Sans LC 50 Book” forms the central point. The first figure of the number describes the stroke thickness: 10 Thin to 90 Bold. Full Sans LC comes 5 weights and italics also Full Sans SC comes 5 weights and italics total 20 types. The family contains a set of 485 characters. Case-Sensitive Forms, Classes and Features, Small Caps from Letter Cases, Fractions, Superior, Inferior, Denominator, Numerator, Old Style Figures just one touch easy In all graphic programs. Full Sans is the perfect font for web use. You can enjoy using it. UPDATE: 08 March 2019 - Fixed extension of glyhps "y" and "g". - "LineGap" error has been fixed. - Fixed bug in "onum", "pnum", "tnum" and "tnum" software in OpenType feature. - Pamors by Alit Design,
$18.00PAMORS typeface is a bold and daring blackletter font that exudes a sense of strength and power. The mix of regular and italic styles provides versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of design applications. With 799 characters, Pamors typeface offers extensive multilingual support and includes PUA unicode for easy access to special characters. One of the standout features of this font is its use of ligatures and swashes, which add an extra touch of elegance and sophistication to any project. Whether used in headlines, logos, or body text, Pamors typeface is sure to make a bold statement that commands attention. Language Support : Latin, Basic, Western European, Central European, South European,Vietnamese. In order to use the beautiful swashes, you need a program that supports OpenType features such as Adobe Illustrator CS, Adobe Photoshop CC, Adobe Indesign and Corel Draw. but if your software doesn’t have Glyphs panel, you can install additional swashes font files. - Core Sans AR by S-Core,
$19.00Core Sans AR Family is a rounded version of Core Sans A that is clean, simple and highly readable. It is a part of the Core Sans Series such as Core Sans N, Core Sans M, Core Sans E, Core Sans A, Core Sans D, Core Sans G, Core Sans R and Core Sans B. Letters in this type family are designed with genuine neo-grotesque and neutral shapes without any decorative distractions. The spaces between individual letter forms are precisely adjusted to create the perfect typesetting. Core Sans AR family consists of 8 weights (Thin, Extra Light, Light, Regular, Medium, Bold, Extra Bold, Heavy) with their corresponding italics. Core Sans AR contains complete Basic Latin, Cyrillic, Central European, Turkish, Baltic character sets. Each font includes proportional figures, tabular figures, numerators, denominators, superscript, scientific inferiors, subscript, fractions and case features. We highly recommend it for use in books, web pages, screen displays, and so on. - Compatil Exquisit by Linotype,
$50.99Compatil from Linotype is the first comprehensive type system which enables all typographical elements to be used to full effect in order to reproduce the message conveyed by text information. Four different type styles with a total of 16 weights including italics have been merged into a unique typographical network. There are now no limits to the font user's creativity.The system is a product of technical innovation and constitutes a new design approach which meets the highest aesthetic standards. Compatil is a typeface family from the Platinum Collection. This series was created for the highest quality demanded by professional typography and includes complete families digitized using the newest technology, serving the specific needs of corporate design and similar projects. This Value Pack contains four different type styles of the Compatil type system: Linotype Compatil Exquisit Pro Regular, Italic, Bold and Bold Italic. These Pro fonts include the small caps and Adobe Central European character set for OpenType-supporting applications like Adobe InDesign.