10,000 search results
(0.033 seconds)
- SF Proverbial Gothic Extended - Unknown license
- SF Square Root Shaded - Unknown license
- SF Pale Bottom Condensed - Unknown license
- SF Intoxicated Blues Extended - Unknown license
- SF Archery Black SC - Unknown license
- SF Pale Bottom Extended - Unknown license
- SF Square Root Extended - Unknown license
- SF Archery Black SC Shaded - Unknown license
- SF Wonder Comic Blotch - Unknown license
- SF Minced Meat Shaded - Unknown license
- SF Chrome Fenders Extended - Unknown license
- SF Proverbial Gothic Condensed - Unknown license
- SF Archery Black Shaded - Unknown license
- SF Intoxicated Blues Shaded - Unknown license
- SF Minced Meat Extended - Unknown license
- SF Diego Sans Shaded - Unknown license
- SF Shai Fontai Extended - Unknown license
- Marisco by estudioCrop,
$19.90 - Antique by Storm Type Foundry,
$26.00The concept of the Baroque Roman type face is something which is remote from us. Ungrateful theorists gave Baroque type faces the ill-sounding attribute "Transitional", as if the Baroque Roman type face wilfully diverted from the tradition and at the same time did not manage to mature. This "transition" was originally meant as an intermediate stage between the Aldine/Garamond Roman face of the Renaissance, and its modern counterpart, as represented by Bodoni or Didot. Otherwise there was also a "transition" from a slanted axis of the shadow to a perpendicular one. What a petty detail led to the pejorative designation of Baroque type faces! If a bookseller were to tell his customers that they are about to choose a book which is set in some sort of transitional type face, he would probably go bust. After all, a reader, for his money, would not put up with some typographical experimentation. He wants to read a book without losing his eyesight while doing so. Nevertheless, it was Baroque typography which gave the world the most legible type faces. In those days the craft of punch-cutting was gradually separating itself from that of book-printing, but also from publishing and bookselling. Previously all these activities could be performed by a single person. The punch-cutter, who at that time was already fully occupied with the production of letters, achieved better results than he would have achieved if his creative talents were to be diffused in a printing office or a bookseller's shop. Thus it was possible that for example the printer John Baskerville did not cut a single letter in his entire lifetime, for he used the services of the accomplished punch-cutter John Handy. It became the custom that one type founder supplied type to multiple printing offices, so that the same type faces appeared in various parts of the world. The type face was losing its national character. In the Renaissance period it is still quite easy to distinguish for example a French Roman type face from a Venetian one; in the Baroque period this could be achieved only with great difficulties. Imagination and variety of shapes, which so far have been reserved only to the fine arts, now come into play. Thanks to technological progress, book printers are now able to reproduce hairstrokes and imitate calligraphic type faces. Scripts and elaborate ornaments are no longer the privilege of copper-engravers. Also the appearance of the basic, body design is slowly undergoing a change. The Renaissance canonical stiffness is now replaced with colour and contrast. The page of the book is suddenly darker, its lay-out more varied and its lines more compact. For Baroque type designers made a simple, yet ingenious discovery - they enlarged the x-height and reduced the ascenders to the cap-height. The type face thus became seemingly larger, and hence more legible, but at the same time more economical in composition; the type area was increasing to the detriment of the margins. Paper was expensive, and the aim of all the publishers was, therefore, to sell as many ideas in as small a book block as possible. A narrowed, bold majuscule, designed for use on the title page, appeared for the first time in the Late Baroque period. Also the title page was laid out with the highest possible economy. It comprised as a rule the brief contents of the book and the address of the bookseller, i.e. roughly that which is now placed on the flaps and in the imprint lines. Bold upper-case letters in the first line dramatically give way to the more subtle italics, the third line is highlighted with vermilion; a few words set in lower-case letters are scattered in-between, and then vermilion appears again. Somewhere in the middle there is an ornament, a monogram or an engraving as a kind of climax of the drama, while at the foot of the title-page all this din is quietened by a line with the name of the printer and the year expressed in Roman numerals, set in 8-point body size. Every Baroque title-page could well pass muster as a striking poster. The pride of every book printer was the publication of a type specimen book - a typographical manual. Among these manuals the one published by Fournier stands out - also as regards the selection of the texts for the specimen type matter. It reveals the scope of knowledge and education of the master typographers of that period. The same Fournier established a system of typographical measurement which, revised by Didot, is still used today. Baskerville introduced the smoothing of paper by a hot steel roller, in order that he could print astonishingly sharp letters, etc. ... In other words - Baroque typography deserves anything else but the attribute "transitional". In the first half of the 18th century, besides persons whose names are prominent and well-known up to the present, as was Caslon, there were many type founders who did not manage to publish their manuals or forgot to become famous in some other way. They often imitated the type faces of their more experienced contemporaries, but many of them arrived at a quite strange, even weird originality, which ran completely outside the mainstream of typographical art. The prints from which we have drawn inspiration for these six digital designs come from Paris, Vienna and Prague, from the period around 1750. The transcription of letters in their intact form is our firm principle. Does it mean, therefore, that the task of the digital restorer is to copy meticulously the outline of the letter with all inadequacies of the particular imprint? No. The type face should not to evoke the rustic atmosphere of letterpress after printing, but to analyze the appearance of the punches before they are imprinted. It is also necessary to take account of the size of the type face and to avoid excessive enlargement or reduction. Let us keep in mind that every size requires its own design. The longer we work on the computer where a change in size is child's play, the more we are convinced that the appearance of a letter is tied to its proportions, and therefore, to a fixed size. We are also aware of the fact that the computer is a straightjacket of the type face and that the dictate of mathematical vectors effectively kills any hint of naturalness. That is why we strive to preserve in these six alphabets the numerous anomalies to which later no type designer ever returned due to their obvious eccentricity. Please accept this PostScript study as an attempt (possibly futile, possibly inspirational) to brush up the warm magic of Baroque prints. Hopefully it will give pleasure in today's modern type designer's nihilism. - Sansumi - Unknown license
- Earth's Mightiest 3D - Unknown license
- SF Quartzite - Unknown license
- SF Juggernaut - Unknown license
- Minya Nouvelle - Unknown license
- SF Technodelight - Unknown license
- Wolf's Bane Expanded - Unknown license
- SF Gothican - Unknown license
- Landmark by Oporto Design,
$29.90 - French Plug by HiH,
$8.00Frank H. Atkinson was a popular Art Nouveau sign painter in Chicago, Illinois. He designed signs for the Cadillac Motor Car Co., Chicago Academy of Fine Arts and the department store Marshall Field. Oddly enough, he even designed signs for other sign painters. In 1908 he published a book, Sign Painting, which sold well. French Plug, a bold, rounded, all-cap design in an American Art Nouveau style from that book. It has a relaxed, easy-going informality that is useful for ads and flyers. It also would have fit very nicely with many French posters of the period. - Veronika Luxurious by Great Studio,
$19.00Veronika Luxurious is a Glamour Luxury typeface. with beautiful letters and a touch of elegant appearance. plant it firmly in a modern design. It is a careful collaboration between beauty and function. Designed specifically for logo-themed projects, the font itself features many alternative and binding options, perfect for creating elegant, chic lifestyle designs, such as logos, titles, branding, web design and book designs. Veronika Luxurious displays both uppercase and lowercase letters, supports Latin-based languages. It holds two weights, Regular and Bold. each offers something different and they are all made to work together in harmony. - Replica Rough SG by Spiece Graphics,
$39.00Here’s an edge-tattered, slightly distorted typeface that was developed from hand stamping using ink. You’ll find it ideal for both display and text situations where legibility is a big concern. This version holds up in very small sizes. Replica Rough SG Regular and Bold are now available in the OpenType format. This OpenType version includes stylistic alternates, discretionary ligatures, small caps, petite caps, ornaments and oldstye figures. Advanced features currently work in Adobe Creative Suite InDesign, Creative Suite Illustrator, and Quark XPress. Check for OpenType advanced feature support in other applications as it gradually becomes available with upgrades. - Stiana by WDC Fonts,
$30.00Stiana font is a venetian serif in modern design. The general idea was inspired by beautiful masterpieces of Nicolas Jensen and William Morris. Stiana holds fine, balanced readability of venetian serif, and both 21st century trends. Letterforms are expressive and bold enough to use font as display, but it also fits nicely for text. Stiana supports Western Europe, Cyrillic and Greek languages. Stiana is surely a good choice both for screen applications and print media. Its multipurpose spreads over package design, logos, headlines, body texts, stationary and back labels. Also very good for books and magazines. - Play Day - Personal Use - Personal use only
- LTC Bixler Ornaments by Lanston Type Co.,
$24.95LTC Bixler Ornaments One includes all designs found in the metal Bixler Type Handypacks #1–6 from P22 that were created using actual Lanston mats to cast these metal type sets. The 14 designs found in the metal type are presented in this digital version—each rotated and optimized to align easily and tightly for digital layouts.? LTC Bixler Ornaments Two incudes all designs found in the metal Bixler Type Handypacks #7–14 from P22 that were created using actual Lanston mats to cast these metal type sets. The 17 designs found in the metal type are presented in this digital version—each rotated and optimized to align easily and tightly for digital layouts. - Beautiful Ink - Unknown license
- EDB Indians - Unknown license
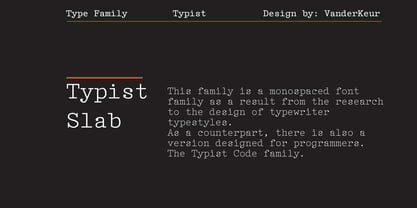
- Typist Slab Mono by VanderKeur,
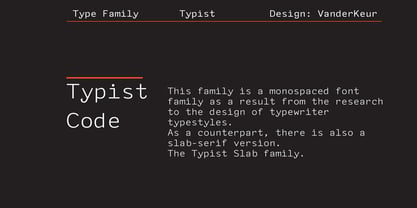
$25.00The typeface Typist originated during an extensive research on the origin and development of typewriter typestyles. The first commercially manufactured typewriter came on the market in 1878 by Remington. The typestyles on these machines were only possible in capitals, the combination of capitals and lowercase came available around the end of the nineteenth century. Apart from a few exceptions, most typestyles had a fixed letter width and a more or less unambiguous design that resembled a thread-like structure. A lot of this mechanical structure was due to the method the typestyles were produced. Looking at type-specimens for print before the first typewriters were good enough to came on the market we can see that in 1853 and in 1882 Bruce’s Type Foundry already had printing type that had a structure of the typewriter typestyles. Of course printing types were proportional designed as typewriter typestyles had a fixed width. So it is possible that except from the method of production for typewriter typestyles, the design of printing types were copied. In the design of the Typist, the purpose was – next to the monospace feature – to include some of the features of the early typewriter typestyles. Features such as the ball terminals and the remarkable design of the letter Q. This new typeface lacks the mechanical and cold look of the early typewriter typestyles. The Typist comes in six weights with matching italics in two versions. One that resembled the early typewriter typestyles (Typist Slab) and a version designed with coding programmers in mind (Typist Code). - Typist Code Mono by VanderKeur,
$25.00The typeface Typist originated during an extensive research on the origin and development of typewriter typestyles. The first commercially manufactured typewriter came on the market in 1878 by Remington. The typestyles on these machines were only possible in capitals, the combination of capitals and lowercase came available around the end of the nineteenth century. Apart from a few exceptions, most typestyles had a fixed letter width and a more or less unambiguous design that resembled a thread-like structure. A lot of this mechanical structure was due to the method the typestyles were produced. Looking at type-specimens for print before the first typewriters were good enough to came on the market we can see that in 1853 and in 1882 Bruce’s Type Foundry already had printing type that had a structure of the typewriter typestyles. Of course printing types were proportional designed as typewriter typestyles had a fixed width. So it is possible that except from the method of production for typewriter typestyles, the design of printing types were copied. In the design of the Typist, the purpose was – next to the monospace feature – to include some of the features of the early typewriter typestyles. Features such as the ball terminals and the remarkable design of the letter Q. This new typeface laks the mechanical and cold look of the early typewriter typestyles. The Typist comes in six weights with matching italics in two versions. One that resembled the early typewriter typestyles (Typist Slab) and a version designed with coding programmers in mind (Typist Code). - Helsa Display by ParaType,
$39.00Helsa is a slim and eccentric serif for headings and short texts. It’s a modern interpretation of the narrow Elseviers of the early 20th century. The letterforms are based on Dutch samples, and in the details there are references to both American type catalogs and letters from the foundries of Wolf and Herbeck. Due to the compact proportions of characters and the high contrast of strokes, Helsa doesn’t take up much space in the line and allows you to increase the type size freely, drawing the viewer's attention to the text. The typeface is suitable for branding museums and exhibitions, alternative music bands, independent clothing and perfume brands, and for any topic related to design or history. Helsa’s character set has more than 1600 characters. It supports hundreds of languages, including extended Cyrillic, Greek, and Vietnamese, as well as many OpenType features: fractions, ligatures, old style and tabular numerals, titular letter alternates, and more. There are variants of dashes and other punctuation marks specifically for uppercase typing. In addition to letters, the typeface contains arrows, numbers in circles (in fact, in ovals), symbols of various types of plastic, card suits and much more. Helsa typeface was made at Paratype in 2020-2022. - Sukothai by Linotype,
$155.99Sukothai is a traditional Thai design based on early metal type. The classic and distinct forms make it excellent for setting text at small sizes or in large passages. Originally released by Linotype for digital photocomposition, now both the Light and Bold weights are available in OpenType format. This makes it possible to dynamically and precisely position the various levels of superscript and subscript vowel signs and tonal marks. In addition to this, the complete Unicode page range for Thai is covered to ensure flawless conversion between other OpenType fonts using Unicode. The accompanying Latin design matches well in scale and texture and supports most Western European languages making it ideal for setting bilingual texts.