10,000 search results
(0.18 seconds)
- AndironOutline - Unknown license
- WC Wunderbach Bta - Unknown license
- Bionic Comic - Personal use only
- Jonny Quest Classic - Unknown license
- Jumbo Outline - 100% free
- Star Series - Unknown license
- Robotaur - Unknown license
- Notice - Unknown license
- Arbuckle - Unknown license
- RaveParty Narrow - Unknown license
- Crosspatchers delight - Unknown license
- Pakenham - Unknown license
- Omicron Zeta - Unknown license
- PR8 London Ads - Unknown license
- Brothers of Metal - Unknown license
- RNS BARUTA BLACK - 100% free
- Lumio - Unknown license
- HIPTRONIC - 100% free
- Kovacs - Unknown license
- American Dream - Unknown license
- Staggering Bob - Unknown license
- Prussian Brew - Unknown license
- NeverSayDie - Unknown license
- Heavy Rotation - Unknown license
- Cal Neuland Shadow by Posterizer KG,
$16.00 - Rail Service JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Goudy Handtooled by Bitstream,
$29.99Goudy Handtooled was done in 1922 and is a shaded version of Goudy Bold. Some authorities credit the design to Charles A. Becker and others to Morris Fuller Benton and Wadsworth Packer. - Century Oldstyle by Bitstream,
$29.99Century Oldstyle is Linn Boyd Benton’s and Morris Fuller Benton’s renovation of Phemister’s Miller & Richard Old Style for ATF forty-five years later, using the Century name for marketing purposes. - Store Clerk JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00The cover of the 1929 sheet music from the First National/Vitaphone picture “The Girl from Woolworth’s” had its title (“Someone”) hand lettered. This single word title was the model for Store Clerk JNL, which is available in both regular and oblique versions as well as solid and solid oblique versions (without an inline). A bold, casual sans serif with rounded ends and an inline, Store Clerk JNL is perfectly suited for projects where a strong, yet playful title is necessary to grab the reader’s attention. For those old enough to remember, Woolworth’s was a leading “Five and Dime” store chain, especially in the days when a nickel or a dime actually could purchase something. - Volvoreta RG LG by LGF Fonts,
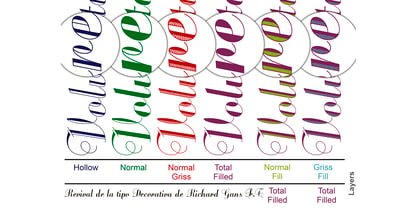
$17.00Bolboreta Hollow is a revival of "Decorativa" font of Richard Gans Foundry .We've expanded the family with padded versions, striped versions (gray on other Gans fonts, in keeping with the days of lead fonts), and those same fills in separate font files, for graphic designer layered play. In addition to Bold versions. - Ashby - Unknown license
- Console - Unknown license
- Hazelnut Milk Tea by Fikryal,
$18.00Introducing this very simple sans serif font that is Hazelnut Milk Tea font. I created this font with the inspiration of simplicity and it is very friendly to look at, with four versions, namely regular, italic, bold, bold italic. Very suitable to be applied in various aspects of design, Also it’s perfect for logo, branding, title, social media posts, advertisements, product packaging, product designs, label, photography, watermark, special event, magazine, web designs, etc. Features : Hazelnut Milk Tea Regular ( Uppercase, Lowercase ) Hazelnut Milk Tea Regular Italic ( Uppercase, Lowercase ) Hazelnut Milk Tea Bold ( Uppercase, Lowercase ) Hazelnut Milk Tea Bold Italic ( Uppercase, Lowercase ) Symbols multilingual support If you have any questions please don’t hesitate to contact me follow my Instagram: @fkryall Thank you - Rock It by Fenotype,
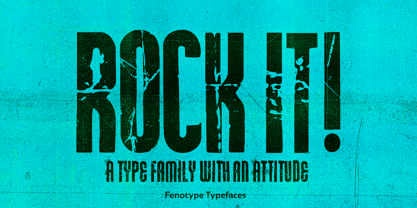
$29.95Rock it! is a type family that let's you create instant graphic design for any ROCK, PUNK, HARDCORE, HORROR and so on -gig, poster, logo, and whatever you need. Just type your texts and combine all the tree versions for authentic look! Rock It! includes three ultra condensed sans fonts with different eroded textures and partially different letter shapes. Different versions of Rock It! are set as "Light," "Regular," and "Bold", where Light and Regular have eroded holes in them whereas Bold has "dirty print stains" all over the characters. - Italiko by Luca Bolognese,
$11.00Italiko is a calligraphic font. The letters have been hand-drawn individually to extract the common strokes. The strokes have then been re-composed to give the font a more unified appearance. It comes in Black, Bold, Regular, and Thin. The Thin version is different as the extreme contrast in the font makes the thinner lines disappear. It is likely best used as a display font. There are ligatures for the combination of letters that can be written more quickly by using a single stroke and letters that are slightly different from the ‘Italic canon.’ You can select which one to use in your application (i.e., Word) using combinations of italic/bold: No selection -> Regular Bold -> Bold Italic -> Thin Bold Italic -> Black If you end up using the font, get in touch at https://github.com/lucabol/Italiko. Feel free to suggest improvements or let me know if you encounter problems. - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer."