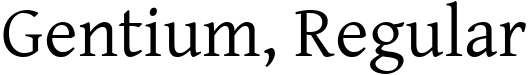9,882 search results
(0.06 seconds)
- nineveh - 100% free
- Gentium - 100% free
- Cartoonist - Personal use only
- Justus - Unknown license
- Averia Sans - Unknown license
- Averia - 100% free
- Aurulent Sans - Unknown license
- Nibby - 100% free
- Rambat Campotype - Personal use only
- Cyberspace - Personal use only
- Aurulent Sans Mono - Unknown license
- LT Makeup - 100% free
- LT Stopwatch - 100% free
- LT Sonoma - 100% free
- LT Wave - 100% free
- LT Superior - 100% free
- LT Superior Serif - 100% free
- LT Renovate - 100% free
- LT Beverage - 100% free
- TT Rounds Neue by TypeType,
$39.00We have updated TT Rounds Neue! TT Rounds Neue was released as a logical continuation of the TT Rounds and TT Rounds Condensed fonts, more modern and technically advanced. In the update, we have preserved the visual nature of the font, the proportions of the letters and the balance between bold and thin faces. We have made the typeface even more functional and convenient by fixing technical flaws, expanding the character set and adding a full-fledged variable font. In the new version of TT Rounds Neue, you will find additional extended Latin and Cyrillic characters, updated kerning and hinting. The font can be used for headings or for text typesetting. The typeface is optimized for web, print and packaging design. Thanks to its soft character and rounded shapes, it is suitable for decorating baby food and eco-products. TT Rounds Neue consists of 3 subfamilies: Compressed, Condensed and Normal. There are 55 faces in the font: 27 upright, 27 italic, and 1 variable font. Variability is across all three axes, thickness, slope, and width. Each style has 684 glyphs. The font has 29 OpenType features, including ligatures, a set of alternative characters, old-style figures, and many others. ?Please note that we are removing the TT Rounds and TT Rounds Condensed fonts from the marketplace, but you can still get them by contacting TypeType's commercial department directly commercial@typetype.org TT Rounds Neue OpenType features: aalt, ccmp, locl, subs, sinf, sups, numr, dnom, frac, ordn, tnum, onum, lnum, pnum, case, salt, liga, dlig, calt, ss01, ss02, ss03, ss04, ss05, ss06, ss07, ss08, ss09, ss10 TT Rounds Neue language support: English, Albanian, Basque, Catalan, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Hungarian, Icelandic, Irish, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Luxembourgish, Moldavian (lat), Montenegrin (lat), Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Serbian (lat), Slovak, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish, Swiss German, Valencian, Azerbaijani, Kazakh (lat), Turkish, Acehnese, Banjar, Betawi, Bislama, Boholano, Cebuano, Chamorro, Fijian, Filipino, Hiri Motu, Ilocano, Indonesian, Javanese, Khasi, Malay, Marshallese, Minangkabau, Nauruan, Nias, Palauan, Rohingya, Salar, Samoan, Sasak, Sundanese, Tagalog, Tahitian, Tetum, Tok Pisin, Tongan, Uyghur, Afar, Asu, Aymara, Bemba, Bena, Chiga, Embu, Gikuyu, Gusii, Kabuverdianu, Kalenjin, Kamba, Kikuyu, Kinyarwanda, Kirundi, Kongo, Luganda, Luo, Luyia, Machame, Makhuwa-Meetto, Makonde, Malagasy, Mauritian Creole, Meru, Morisyen, Ndebele, Nyankole, Oromo, Rombo, Rundi, Rwa, Samburu, Sango, Sangu, Sena, Seychellois Creole, Shambala, Shona, Soga, Somali, Sotho, Swahili, Swazi, Taita, Tsonga, Tswana, Vunjo, Xhosa, Zulu, Maori, Alsatian, Aragonese, Arumanian, Belarusian (lat), Bosnian (lat), Breton, Colognian, Cornish, Corsican, Faroese, Frisian, Friulian, Gaelic, Gagauz (lat), Galician, Interlingua, Judaeo-Spanish, Karaim (lat), Kashubian, Ladin, Leonese, Manx, Occitan, Rheto-Romance, Romansh, Scots, Silesian, Sorbian, Vastese, Volapu?k, Vo?ro, Walloon, Walser, Karakalpak (lat), Kurdish (lat), Talysh (lat), Tsakhur (Azerbaijan), Turkmen (lat), Zaza, Aleut (lat), Cree, Haitian Creole, Hawaiian, Innu-aimun, Karachay-Balkar (lat), Karelian, Livvi-Karelian, Ludic, Tatar, Vepsian, Guarani, Nahuatl, Quechua,, Russian, Belarusian (cyr), Bosnian (cyr), Bulgarian (cyr), Macedonian, Serbian (cyr), Ukrainian, Gagauz (cyr), Moldavian (cyr), Kazakh (cyr), Kirghiz, Tadzhik, Turkmen (cyr), Uzbek (cyr), Lezgian, Abazin, Agul, Archi, Avar, Dargwa, Ingush, Kabardian, Kabardino-Cherkess, Karachay-Balkar (cyr), Khvarshi, Kumyk, Lak, Nogai, Ossetian, Rutul, Tabasaran, Tsakhur, Buryat, Komi-Permyak, Komi-Yazva, Komi-Zyrian, Shor, Siberian Tatar, Tofalar, Touva, Bashkir, Chechen (cyr), Chuvash, Erzya, Kryashen Tatar, Mordvin-moksha, Tatar Volgaic, Udmurt, Uighur, Rusyn, Karaim (cyr), Montenegrin (cyr), Romani (cyr), Dungan, Karakalpak (cyr), Shughni, Mongolian, Adyghe, Kalmykk - Fleischmann Gotisch PT by preussTYPE,
$29.00Johann Michael Fleischmann was born June 15th, 1707 in Wöhrd near Nuremberg. After attending Latinschool he started an apprenticeship as punchcutter in the crafts enterprise of Konstantin Hartwig in Nuremberg, which ought to last six years. For his extraordinary talent Fleischmann completed his apprenticeship after four and a half years, which was very unusual. 1727 his years of travel (very common in these days) began, during which he perfected his handcraft by working in different enterprises as journeyman. First location was Frankfurt/Main where he worked for nearly a year at the renowned type foundery of Luther and Egenolff. Passing Mainz he continued to Holland, where he arrived in November 1728 and stayed till he died in 1768. In Amsterdam he worked for several type founderies, among others some weeks for Izaak van der Putte; in The Hague for Hermanus Uytwerf. Between 1729 and 1732 he created several exquisite alphabets for Uytwerf, which were published under his own name (after his move to Holland Fleischmann abandoned the second n in his name), apparently following the stream of the time. After the two years with Uytwerf, Fleischmann returned to Amsterdam, where he established his own buiseness as punchcutter; following an advice of the bookkeeper and printer from Basel Rudolf Wetstein he opened his own type foundery 1732, which he sold in 1735 to Wetstein for financial reasons. In the following Fleischmann created several types and matrices exclusively for Wetstein. In 1743 after the type foundery was sold by Wetstein’s son Hendrik Floris to the upcoming enterprise of Izaak and Johannes Enschedé, Fleischmann worked as independent punchcutter mostly for this house in Haarlem. Recognizing his exceptional skills soon Fleischmann was consigned to cutting the difficult small-sized font types. The corresponding titling alphabets were mostly done by Jaques-Francois Rosart, who also cut the main part of the ornaments and borders used in the font examples of Enschedé. Fleischmann created for Enschedé numerous fonts. The font example published 1768 by Enschedé contains 3 titling alphabets, 16 antiquacuts, 14 italic cuts, 13 textura- and 2 scriptcuts, 2 greek typesets (upper cases and ligatures), 1 arabic, 1 malayan and 7 armenian font systems, 5 sets of musicnotes and the poliphonian musicnotesystem by Fleischmann. In total he brought into being about 100 alphabets - the fruits of fourty years of creative work as a punchcutter. Fleischmann died May 27th, 1768 at the age of 61. For a long time he was thought one of the leading punchcutters in Europe. A tragedy, that his creating fell into the turning of baroque to classicism. The following generations could not take much pleasure in his imaginative fonts, which were more connected to the sensuous baroque than to the bare rationalism of the upcoming industrialisation. Unfortunately therefore his masterpieces did not survive the 19th century and person and work of Fleischmann sank into oblivion. The impressive re-interpretation of the Fleischmann Antiqua and the corresponding italics by Erhard Kaiser from Leipzig, which were done for the Dutch Type Library from 1993 to 1997, snatched Fleischmann away from being forgotten by history. Therefore we want to place strong emphasis on this beautiful font. Fleischman Gotisch The other fonts by Fleischmann are only known to a small circle of connoisseurs and enthusiasts. So far they are not available in adequat quality for modern systems. Same applies the "Fleischman Gotisch", which has been made available cross platform to modern typeset-systems as CFF Open Type font through the presented sample. The Fleischman Gotisch has been proved to be one of the fonts, on which Fleischmann spent a good deal of his best effort; this font simply was near to his heart. Between 1744 and 1762 he created 13 different sizes of this font. All follow the same principles of forms, but their richness of details has been adapted to the particular sizes. In later times the font was modified more or less sensitive by various type founderies; letters were added, changed to current taste or replaced by others; so that nowadays a unique and binding mastercopy of this font is missing. Likewise the name of the font underwent several changes. Fleischmann himself probably never named his font, as he did with none of his fonts. By Enschedé this textura was named Nederduits, later on Nederduitsch. When the font was offered by the german type foundery Flinsch in Frankfurt/Main, the more convenient name of Fleischmann-Gotisch was chosen. In his "Masterbook of the font" and his "Abstract about the Et-character" Jan Tschichold refered to it as "Duyts" again. To honour the genious of Johann Michael Fleischmann we decided to name the writing "Fleischmann Gotisch PT" (unhyphenated). Developing the digital Fleischman Gotisch I decided not to use one of the thirteen sizes as binding mastercopy, but corresponding to the typical ductus of the font to re-create an independent use of forms strongly based on Fleischmann´s language of forms. All ascenders and descenders were standardised. Some characters, identified as added later on, were eliminated (especially the round lower case-R and several versions of longs- respectively f-ligatures) and others were adjusted to the principles of Fleischmann. Where indicated the diverse characters were integrated as alternative. They can be selected in the corresponding menu. All for the correct german black letter necessary longs and other ligatures were generated. Through the according integration into the feature-code about 85% of all ligatures in the type can be generated automatically. Problematic combinations (Fl, Fk, Fh, ll, lh, lk, lb) were created as ligatures and are likewise constructed automatically. A historically interesting letter is the "round r", which was already designated by Fleischmann; it is used after preceding round letters. Likewise interesting is the inventive form of the &-character, which is mentioned by Tschichold in his corresponding abstract. Nevertheless despite all interpretation it was very important to me to maintain the utmost fidelity to the original. With this digital version of a phantastic texturfont of the late baroque I hope to contribute to a blossoming of interest for this genious master of his kind: Johann Michel Fleischmann. OpenType features: - Unicode (ISO 10646-2) - contains 520 glyphes - Basic Latin - Latin-1 Supplement - Latin Extended-A - Latin Extended-B - Central European Glyhps - Ornaments - Fractions - Standard ligatures - Discretionary ligatures - Historical ligatures - Kerning-Table - LT Oksana - Personal use only
- spinwerad - Unknown license
- Renny Hybrid - 100% free
- B de bonita shadow - Personal use only
- Mirkwood Chronicle - 100% free
- !CRASS ROOTS OFL - Unknown license
- Anfalas - 100% free
- B de bonita - Personal use only
- Exo - 100% free
- kawoszeh - 100% free
- Hollow Roachian Futhark - 100% free
- SF Old South Arabian by Sultan Fonts,
$9.99Historical Background Old South Arabian Script (OSA) was used before the Islamic era not only in the southwest corner of the Arabian Peninsula, but actually in the entire Peninsula. In addition, samples of OSA have been found as far as Uruk in Mesopotamia, Delos in Greece, and Giza in Egypt. Archaeological finds show that as far back as the 8th century BCE, OSA was used in trade, religious writing, and in civil records. Following the spread of Islam in Yemen, the decline of OSA began in the 7th century CE as it was gradually supplanted by Arabic script. OSA was typically known by the name of the then-dominant peoples in the Southern Peninsula. At various times, it was known as Sabaean, Qatabani, or Hadramite, among others. Although it was used for a variety of languages, OSA is most strongly associated with Sabaean. Many Peninsular languages borrowed OSA before introducing further changes of their own. Prime examples are the Thamudic, Safaitic, and Lihyanite scripts which eventually developed into independent scripts. The westward migration of the Sabaean people into the Horn of Africa introduced the South Arabian consonantal alphabet into the region. The transplanted script formed the roots of the Geez script of Ethiopia, which, in time and under presumably external influences, developed into a rich syllabary unlike any other Semitic script in history. Even a cursory examination of the letter forms of Modern Ethiopic writing reveal a striking similarity to South Arabian Script. OSA inscriptions typically reveal a dominant right-to-left directionality, although there are also many cases of alternating directions, known as boustrophedon writing. Figure 1 is a fine example of this style of writing. OSA inscriptions were discovered early in the 19th century. Soon thereafter, two orientalists, Gesenius and Rödiger, made great strides towards deciphering the script. Styles of Writing Old South Arabian inscriptions have survived primarily on stone, ceramic, and metallic surfaces. Hundreds of artifacts have been found and, to this day, continue to be discovered. Some of the best examples number of inscriptions on softer materials, such as wood and leather, have also been discovered. Although there is a significant difference between the styles of letters on the hard surfaces and those on the soft. Old South Arabian (Musnad) is composed of 29 letters , that is one letter more than the Arabic alphabet, which is between “S” and “Sh”, and names “Samekh”. Aspects of difference between Musnad and the present Arabic writing is that Musnad is written in separate letters, and the shape of the letters do not change according to its place in the word. However, some letters change according to the beginning of the writing. Musnad is either prominent, or deep. Prominent writings are for important writings and deep writings are for ordinary. The material on which the Musnad was written were stones, rocks, wood, and metal. In the course of its development the Musnad use appeared in the “Lehyanite’, “Thamudic”, “Safaitic”, pen to which many changes and amendments were made. And from it “Habashi’ writing was born. As regards his place among the Arabs of the Peninsula , when we look at the internet and its role in cultural dialogue , the Arabs of the Peninsula considered Musnad inscription which was indisputably their national writing until the dawn of Islam. It was used by people in all parts of Arabia in their homeland and abroad . It was their means of chronology and record of their glories and history.2- Features of Musnad Script: 1. It is written from right to left and vice versa. 2. Its letters are not joined. 3. Shape of letters are uniform despite their positions in the word. 4. Words are separated by vertical lines. 5. A letter is doubled in case of assertion. 6. No points and punctuations. 7. Easy to be learned by beginners. My OSA Musnad Font My design and technical work is only a treatment of the OSA Musnad as a symbol of writing. And it is possible to use in computer.. My design is not aimed at demonstrating the linguistic and intellectual structure of the Old South Arabian (Musnad). It is so simple that it could be easy to learn by learners and those who are interested in the OSA Musnad letters in computer. The basis of such importance is that it spares a lot of time and effort for researchers and students in this field. Formerly they used to write the Musnad texts either by handwriting or scan them , But now they can easily write its texts in OSA Musnad by using keyboard directly, so that they can change , amend and fulfill easily and accurately . So, we made use of speed, easiness and accuracy. And anyone interested in the South Arabian history in any part of the world can due to this design read and write OSA Musnad letters most easily. This design will also be used by historians and archeologists. , as well as specialist linguistics . The design also demonstrates the aesthetics of the Himyarit writing. About this font family Old South Arabian is An Arabic, Old South Arabian and Latin typeface for desktop applications ,for websites, and for digital ads. Old South Arabian font family contains two types: Old South Arabian and Old South Arabian serif. The font includes a design that supports Arabic, Old South Arabian and Latin languages. Old South Arabian typeface comes with many opentype features. - TT Tsars by TypeType,
$39.00TT Tsars useful links: Specimen | Graphic presentation | Customization options The TT Tsars font family is a collection of serif display titling fonts that are stylized to resemble the fonts of the beginning, the middle and the end of the XVIII century. The project is based on title fonts, that is, the fonts that were used to design book title pages. The idea for the project TT Tsars was born after a small study of the historical development of the Cyrillic type and is also based on Abram Shchitsgal’s book "Russian Civil Type". At the very beginning of the project, we had developed a basic universal skeleton for the forms of all characters in all subfamilies of the family, and later on, we added styles, visual features, artifacts and other nuances typical of the given period onto the skeleton. Yes, from the historical accuracy point of view it might be that such an approach is not always justified, but we have achieved our goal and as a result, we have created perfectly combinable serifs that can be used to style an inscription for a certain time period. The TT Tsars font family consists of 20 fonts: 5 separate subfamilies, each of which consists of 4 fonts. Each font contains 580 glyphs, except for the TT Tsars E subfamily, in which each font consists of 464 characters. Instead of lowercase characters in the typeface, small capitals are used, which also suggests that the typeface is rather a display than text one. In TT Tsars you can find a large number of ligatures (for Latin and Cyrillic alphabets), arrows and many useful OpenType features, such as: frac, ordn, sinf, sups, numr, dnom, case, onum, tnum, pnum, lnum, salt (ss01), dlig. Time-related characteristics of the subfamilies are distributed as follows: • TT Tsars A—the beginning of the 18th century (Latin and Cyrillic) • TT Tsars B—the beginning of the 18th century (Latin and Cyrillic) • TT Tsars C—the middle of the 18th century (Latin and Cyrillic) • TT Tsars D—the end of the 18th century (Latin and Cyrillic) • TT Tsars E—conditionally the beginning of the 18th century (only Latin) TT Tsars A and TT Tsars B families (both the beginning of the 18th century) have different starting points: for TT Tsars A it is Latin, for TT Tsars B it is Cyrillic. The development of the TT Tsars A family began in Latin, the font is based on the royal serif Romain du Roi. The Cyrillic alphabet is harmoniously matched to the Latin. The development of the TT Tsars B family began in Cyrillic, which is based on a Russian civil type. Characteristic elements are the curved one-sided serifs of triangular characters (A, X, Y), drops appear in the letter ?, the middle strokes ? and P are adjacent to the main stroke. Latin was drawn to pair with Cyrillic. It is still based on the royal serif, but somewhat changed: the letters B and P are closed and the upper bar of the letter A rose. This was done for the visual combination of Cyrillic and Latin and at the same time to make a distinction between TT Tsars A and TT Tsars B. TT Tsars C is now the middle of the 18th century. Cyrillic alphabet itself did not stand still and evolved, and by the middle of the 18th century, its forms have changed and become to look the way they are shown in this font family. Latin forms are following the Cyrillic. The figures are also slightly modified and adapted to the type design. In TT Tsars C, Cyrillic and Latin characters are created in parallel. A distinctive feature of the Cyrillic alphabet in TT Tsars C is the residual influence of the flat pen. This is noticeable in such signs as ?, ?, K. The shape of the letters ?, ?, ?, ? is very characteristic of the period. In the Latin alphabet, a characteristic leg appears at the letter R. For both languages, there is a typical C characterized by an upper serif and the appearance of large, even somewhat bolding serifs on horizontals (T, E, ?, L). TT Tsars D is already the end of the 18th century when with the development of printing, the forms of some Cyrillic characters had changed and turned into new skeletons of letters that we transposed into Latin. The figures were also stylized. In this font, both Cyrillic and Latin are stylistically executed with different serifs and are thus logically separated. The end of the century is characterized by the reduction of decorative elements. Straight, blueprint-like legs of the letters ?, R, K, ?. Serifs are very pronounced and triangular. E and ? are one-sided on the middle horizontal line. A very characteristic C with two serifs appears in the Latin alphabet. TT Tsars E is a steampunk fantasy typeface, its theme is a Latinized Russian ?ivil type (also referred to as Grazhdansky type which emerged after Peter the Great’s language reform), which includes only the Latin alphabet. There is no historical analog to this typeface, it is exclusively our reflections on the topic of what would have happened if the civil font had developed further and received a Latin counterpart. We imagined such a situation in which the civil type was exported to Europe and began to live its own life. - DeLouisville - 100% free
- Antique by Storm Type Foundry,
$26.00The concept of the Baroque Roman type face is something which is remote from us. Ungrateful theorists gave Baroque type faces the ill-sounding attribute "Transitional", as if the Baroque Roman type face wilfully diverted from the tradition and at the same time did not manage to mature. This "transition" was originally meant as an intermediate stage between the Aldine/Garamond Roman face of the Renaissance, and its modern counterpart, as represented by Bodoni or Didot. Otherwise there was also a "transition" from a slanted axis of the shadow to a perpendicular one. What a petty detail led to the pejorative designation of Baroque type faces! If a bookseller were to tell his customers that they are about to choose a book which is set in some sort of transitional type face, he would probably go bust. After all, a reader, for his money, would not put up with some typographical experimentation. He wants to read a book without losing his eyesight while doing so. Nevertheless, it was Baroque typography which gave the world the most legible type faces. In those days the craft of punch-cutting was gradually separating itself from that of book-printing, but also from publishing and bookselling. Previously all these activities could be performed by a single person. The punch-cutter, who at that time was already fully occupied with the production of letters, achieved better results than he would have achieved if his creative talents were to be diffused in a printing office or a bookseller's shop. Thus it was possible that for example the printer John Baskerville did not cut a single letter in his entire lifetime, for he used the services of the accomplished punch-cutter John Handy. It became the custom that one type founder supplied type to multiple printing offices, so that the same type faces appeared in various parts of the world. The type face was losing its national character. In the Renaissance period it is still quite easy to distinguish for example a French Roman type face from a Venetian one; in the Baroque period this could be achieved only with great difficulties. Imagination and variety of shapes, which so far have been reserved only to the fine arts, now come into play. Thanks to technological progress, book printers are now able to reproduce hairstrokes and imitate calligraphic type faces. Scripts and elaborate ornaments are no longer the privilege of copper-engravers. Also the appearance of the basic, body design is slowly undergoing a change. The Renaissance canonical stiffness is now replaced with colour and contrast. The page of the book is suddenly darker, its lay-out more varied and its lines more compact. For Baroque type designers made a simple, yet ingenious discovery - they enlarged the x-height and reduced the ascenders to the cap-height. The type face thus became seemingly larger, and hence more legible, but at the same time more economical in composition; the type area was increasing to the detriment of the margins. Paper was expensive, and the aim of all the publishers was, therefore, to sell as many ideas in as small a book block as possible. A narrowed, bold majuscule, designed for use on the title page, appeared for the first time in the Late Baroque period. Also the title page was laid out with the highest possible economy. It comprised as a rule the brief contents of the book and the address of the bookseller, i.e. roughly that which is now placed on the flaps and in the imprint lines. Bold upper-case letters in the first line dramatically give way to the more subtle italics, the third line is highlighted with vermilion; a few words set in lower-case letters are scattered in-between, and then vermilion appears again. Somewhere in the middle there is an ornament, a monogram or an engraving as a kind of climax of the drama, while at the foot of the title-page all this din is quietened by a line with the name of the printer and the year expressed in Roman numerals, set in 8-point body size. Every Baroque title-page could well pass muster as a striking poster. The pride of every book printer was the publication of a type specimen book - a typographical manual. Among these manuals the one published by Fournier stands out - also as regards the selection of the texts for the specimen type matter. It reveals the scope of knowledge and education of the master typographers of that period. The same Fournier established a system of typographical measurement which, revised by Didot, is still used today. Baskerville introduced the smoothing of paper by a hot steel roller, in order that he could print astonishingly sharp letters, etc. ... In other words - Baroque typography deserves anything else but the attribute "transitional". In the first half of the 18th century, besides persons whose names are prominent and well-known up to the present, as was Caslon, there were many type founders who did not manage to publish their manuals or forgot to become famous in some other way. They often imitated the type faces of their more experienced contemporaries, but many of them arrived at a quite strange, even weird originality, which ran completely outside the mainstream of typographical art. The prints from which we have drawn inspiration for these six digital designs come from Paris, Vienna and Prague, from the period around 1750. The transcription of letters in their intact form is our firm principle. Does it mean, therefore, that the task of the digital restorer is to copy meticulously the outline of the letter with all inadequacies of the particular imprint? No. The type face should not to evoke the rustic atmosphere of letterpress after printing, but to analyze the appearance of the punches before they are imprinted. It is also necessary to take account of the size of the type face and to avoid excessive enlargement or reduction. Let us keep in mind that every size requires its own design. The longer we work on the computer where a change in size is child's play, the more we are convinced that the appearance of a letter is tied to its proportions, and therefore, to a fixed size. We are also aware of the fact that the computer is a straightjacket of the type face and that the dictate of mathematical vectors effectively kills any hint of naturalness. That is why we strive to preserve in these six alphabets the numerous anomalies to which later no type designer ever returned due to their obvious eccentricity. Please accept this PostScript study as an attempt (possibly futile, possibly inspirational) to brush up the warm magic of Baroque prints. Hopefully it will give pleasure in today's modern type designer's nihilism. - Areplos by Storm Type Foundry,
$53.00To design a text typeface "at the top with, at the bottom without" serifs was an idea which crossed my mind at the end of the sixties. I started from the fact that what one reads in the Latin alphabet is mainly the upper half of the letters, where good distinguishableness of the individual signs, and therefore, also good legibility, is aided by serifs. The first tests of the design, by which I checked up whether the basic principle could be used also for the then current technology of setting - for double-sign matrices -, were carried out in 1970. During the first half of the seventies I created first the basic design, then also the slanted Roman and the medium types. These drawings were not very successful. My greatest concern during this initial phase was the upper case A. I had to design it in such a way that the basic principle should be adhered to and the new alphabet, at the same time, should not look too complicated. The necessary prerequisite for a design of a new alphabet for double-sign matrices, i.e. to draw each letter of all the three fonts to the same width, did not agree with this typeface. What came to the greatest harm were the two styles used for emphasis: the italics even more than the medium type. That is why I fundamentally remodelled the basic design in 1980. In the course of this work I tried to forget about the previous technological limitations and to respect only the requirements then placed on typefaces intended for photosetting. As a matter of fact, this was not very difficult; this typeface was from the very beginning conceived in such a way as to have a large x-height of lower-case letters and upper serifs that could be joined without any problems in condensed setting. I gave much more thought to the proportional relations of the individual letters, the continuity of their outer and inner silhouettes, than to the requirements of their production. The greatest number of problems arose in the colour balancing of the individual signs, as it was necessary to achieve that the upper half of each letter should have a visual counterbalance in its lower, simpler half. Specifically, this meant to find the correct shape and degree of thickening of the lower parts of the letters. These had to counterbalance the upper parts of the letters emphasized by serifs, yet they should not look too romantic or decorative, for otherwise the typeface might lose its sober character. Also the shape, length and thickness of the upper serifs had to be resolved differently than in the previous design. In the seventies and at the beginning of the eighties a typeface conceived in this way, let alone one intended for setting of common texts in magazines and books, was to all intents and purposes an experiment with an uncertain end. At this time, before typographic postmodernism, it was not the custom to abandon in such typefaces the clear-cut formal categories, let alone to attempt to combine the serif and sans serif principles in a single design. I had already designed the basic, starting, alphabets of lower case and upper case letters with the intention to derive further styles from them, differing in colour and proportions. These fonts were not to serve merely for emphasis in the context of the basic design, but were to function, especially the bold versions, also as independent display alphabets. At this stage of my work it was, for a change, the upper case L that presented the greatest problem. Its lower left part had to counterbalance the symmetrical two-sided serif in the upper half of the letter. The ITC Company submitted this design to text tests, which, in their view, were successful. The director of this company Aaron Burns then invited me to add further styles, in order to create an entire, extensive typeface family. At that time, without the possibility to use a computer and given my other considerable workload, this was a task I could not manage. I tried to come back to this, by then already very large project, several times, but every time some other, at the moment very urgent, work diverted me from it. At the beginning of the nineties several alphabets appeared which were based on the same principle. It seemed to me that to continue working on my semi-finished designs was pointless. They were, therefore, abandoned until the spring of 2005, when František Štorm digitalized the basic design. František gave the typeface the working title Areplos and this name stuck. Then he made me add small capitals and the entire bold type, inducing me at the same time to consider what to do with the italics in order that they might be at least a little italic in character, and not merely slanted Roman alphabets, as was my original intention. In the course of the subsequent summer holidays, when the weather was bad, we met in his little cottage in South Bohemia, between two ponds, and resuscitated this more than twenty-five-years-old typeface. It was like this: We were drinking good tea, František worked on the computer, added accents and some remaining signs, inclined and interpolated, while I was looking over his shoulder. There is hardly any typeface that originated in a more harmonious setting. Solpera, summer 2005 I first encountered this typeface at the exhibition of Contemporary Czech Type Design in 1982. It was there, in the Portheim Summer Palace in Prague, that I, at the age of sixteen, decided to become a typographer. Having no knowledge about the technologies, the rules of construction of an alphabet or about cultural connections, I perceived Jan Solpera's typeface as the acme of excellence. Now, many years after, replete with experience of revitalization of typefaces of both living and deceased Czech type designers, I am able to compare their differing approaches. Jan Solpera put up a fight against the digital technology and exerted creative pressure to counteract my rather loose approach. Jan prepared dozens of fresh pencil drawings on thin sketching paper in which he elaborated in detail all the style-creating elements of the alphabet. I can say with full responsibility that I have never worked on anything as meticulous as the design of the Areplos typeface. I did not invent this name; it is the name of Jan Solpera's miniature publishing house, in which he issued for example an enchanting series of memoirs of a certain shopkeeper of Jindrichuv Hradec. The idea that the publishing house and the typeface might have the same name crossed my mind instinctively as a symbol of the original designation of Areplos - to serve for text setting. What you can see here originated in Trebon and in a cottage outside the village of Domanín - I even wanted to rename my firm to The Trebon Type Foundry. When mists enfold the pond and gloom pervades one's soul, the so-called typographic weather sets in - the time to sit, peer at the monitor and click the mouse, as also our students who were present would attest. Areplos is reminiscent of the essential inspirational period of a whole generation of Czech type designers - of the seventies and eighties, which were, however, at the same time the incubation period of my generation. I believe that this typeface will be received favourably, for it represents the better aspect of the eighties. Today, at the time when the infection by ITC typefaces has not been quite cured yet, it does absolutely no harm to remind ourselves of the high quality and timeless typefaces designed then in this country.In technical terms, this family consists of two times four OpenType designs, with five types of figures, ligatures and small capitals as well as an extensive assortment of both eastern and western diacritics. I can see as a basic text typeface of smaller periodicals and informative job-prints, a typeface usable for posters and programmes of various events, but also for corporate identity. Štorm, summer 2005 - Affair by Sudtipos,
$99.00Type designers are crazy people. Not crazy in the sense that they think we are Napoleon, but in the sense that the sky can be falling, wars tearing the world apart, disasters splitting the very ground we walk on, plagues circling continents to pick victims randomly, yet we will still perform our ever optimistic task of making some little spot of the world more appealing to the human eye. We ought to be proud of ourselves, I believe. Optimism is hard to come by these days. Regardless of our own personal reasons for doing what we do, the very thing we do is in itself an act of optimism and belief in the inherent beauty that exists within humanity. As recently as ten years ago, I wouldn't have been able to choose the amazing obscure profession I now have, wouldn't have been able to be humbled by the history that falls into my hands and slides in front of my eyes every day, wouldn't have been able to live and work across previously impenetrable cultural lines as I do now, and wouldn't have been able to raise my glass of Malbeck wine to toast every type designer who was before me, is with me, and will be after me. As recently as ten years ago, I wouldn't have been able to mean these words as I wrote them: It’s a small world. Yes, it is a small world, and a wonderfully complex one too. With so much information drowning our senses by the minute, it has become difficult to find clear meaning in almost anything. Something throughout the day is bound to make us feel even smaller in this small world. Most of us find comfort in a routine. Some of us find extended families. But in the end we are all Eleanor Rigbys, lonely on the inside and waiting for a miracle to come. If a miracle can make the world small, another one can perhaps give us meaning. And sometimes a miracle happens for a split second, then gets buried until a crazy type designer finds it. I was on my honeymoon in New York City when I first stumbled upon the letters that eventually started this Affair. A simple, content tourist walking down the streets formerly unknown to me except through pop music and film references. Browsing the shops of the city that made Bob Dylan, Lou Reed, and a thousand other artists. Trying to chase away the tourist mentality, wondering what it would be like to actually live in the city of a billion tiny lights. Tourists don't go to libraries in foreign cities. So I walked into one. Two hours later I wasn't in New York anymore. I wasn't anywhere substantial. I was the crazy type designer at the apex of insanity. La La Land, alphabet heaven, curves and twirls and loops and swashes, ribbons and bows and naked letters. I'm probably not the very first person on this planet to be seduced into starting an Affair while on his honeymoon, but it is something to tease my better half about once in a while. To this day I can't decide if I actually found the worn book, or if the book itself called for me. Its spine was nothing special, sitting on a shelf, tightly flanked by similar spines on either side. Yet it was the only one I picked off that shelf. And I looked at only one page in it before walking to the photocopier and cheating it with an Argentine coin, since I didn't have the American quarter it wanted. That was the beginning. I am now writing this after the Affair is over. And it was an Affair to remember, to pull a phrase. Right now, long after I have drawn and digitized and tested this alphabet, and long after I saw what some of this generation’s type designers saw in it, I have the luxury to speculate on what Affair really is, what made me begin and finish it, what cultural expressions it has, and so on. But in all honesty it wasn't like that. Much like in my Ministry Script experience, I was a driven man, a lover walking the ledge, an infatuated student following the instructions of his teacher while seeing her as a perfect angel. I am not exaggerating when I say that the letters themselves told me how to extend them. I was exploited by an alphabet, and it felt great. Unlike my experience with Ministry Script, where the objective was to push the technology to its limits, this Affair felt like the most natural and casual sequence of processions in the world – my hand following the grid, the grid following what my hand had already done – a circle of creation contained in one square computer cell, then doing it all over again. By contrast, it was the lousiest feeling in the world when I finally reached the conclusion that the Affair was done. What would I do now? Would any commitment I make from now on constitute a betrayal of these past precious months? I'm largely over all that now, of course. I like to think I'm a better man now because of the experience. Affair is an enormous, intricately calligraphic OpenType font based on a 9x9 photocopy of a page from a 1950s lettering book. In any calligraphic font, the global parameters for developing the characters are usually quite volatile and hard to pin down, but in this case it was particularly difficult because the photocopy was too gray and the letters were of different sizes, very intertwined and scan-impossible. So finishing the first few characters in order to establish the global rhythm was quite a long process, after which the work became a unique soothing, numbing routine by which I will always remember this Affair. The result of all the work, at least to the eyes of this crazy designer, is 1950s American lettering with a very Argentine wrapper. My Affair is infused with the spirit of filete, dulce de leche, yerba mate, and Carlos Gardel. Upon finishing the font I was fortunate enough that a few of my colleagues, great type designers and probably much saner than I am, agreed to show me how they envision my Affair in action. The beauty they showed me makes me feel small and yearn for the world to be even smaller now – at least small enough so that my international colleagues and I can meet and exchange stories over a good parrilla. These people, whose kindness is very deserving of my gratitude, and whose beautiful art is very deserving of your appreciation, are in no particular order: Corey Holms, Mariano Lopez Hiriart, Xavier Dupré, Alejandro Ros, Rebecca Alaccari, Laura Meseguer, Neil Summerour, Eduardo Manso, and the Doma group. You can see how they envisioned using Affair in the section of this booklet entitled A Foreign Affair. The rest of this booklet contains all the obligatory technical details that should come with a font this massive. I hope this Affair can bring you as much peace and satisfaction as it brought me, and I hope it can help your imagination soar like mine did when I was doing my duty for beauty. - Waschkueche - 100% free
- Berlin Email - 100% free