4,463 search results
(0.061 seconds)
- Tighten is a compressed sans serif font family , notable for its elegance derived from an exaggerated vertical proportion. His style is a fusion between art-deco and futurism, which gives him an unm...
- As of my last update in April 2023, Saintharpy is not a widely recognized or standardized font in mainstream typography repositories or discussions. However, let me paint a picture of what a font wit...
- Ah, Equestrian by Darrian, a font that prances gracefully across the page like a well-groomed stallion at the Kentucky Derby. This isn't your average, run-of-the-mill typeface. Oh no, it carries the ...
- Alright, let's dive into the font HoMicIDE EFfeCt. Just from the name, you can tell this isn't your average, everyday font. It suggests a vibe that's edgy, perhaps a bit dark, yet undeniably eye-catc...
- Ah, the mighty Tabarra Shadow! Picture this: If fonts were characters at a grand costume party thrown by Typography itself, Tabarra Shadow would arrive fashionably late, decked out in its enigmatic g...
- The "Pure Evil 2" font, designed by Chris Hansen, is a testament to the creative potency embodied in font design, particularly when it aims to evoke a specific atmosphere or emotion. This font stands...
- The "Fabrics" font by CloutierFontes, a design entity known for creating distinctive and thematic typefaces, stands out as a unique addition to the digital typography landscape. This font captures th...
- Close your eyes. Wait, don’t—then you won’t be able to read this. Imagine, in a world where letters not only talk but strut down the catwalk with unmatched elegance, there lives a font: Ordinatum Med...
- Sailor '87 is a captivating typeface that beckons with the romance and adventure of the open sea, invoking the nostalgic spirit of the 1980s. Its design elegantly merges the robustness of traditional...
- As of my last update, there is no widely recognized or specific font known as "Can Control" within the standard typographic or design communities. However, the name itself evokes a particular style t...
- As of my last update in April 2023, SERIESB is not a widely recognized or standard typeface within the vast library of fonts available to designers and typographers. This suggests that SERIESB might ...
- The font "Kallot" by Junkohanhero is a striking typeface that intriguingly blends contemporary design elements with a touch of vintage charm. Designed by the talented artist behind the moniker Junkoh...
- Ah, the Confinental FREE font by Inspiratype – a name that evokes the elegance of a continental breakfast in Paris but with the 'FREE' tag dangling like a cherry on top that says, "Bonjour, mon ami! ...
- Oh, the Kanna-W4 font by Flop Design is like the chameleon of the design world, smoothly blending into its surroundings while still managing to stand out, much like a ninja in a tuxedo at a high scho...
- The Sex Pistols font captures the raw energy and rebellious spirit of the punk rock movement, much like the iconic band it's named after. This typeface is more than just a collection of letters; it e...
- Elektrogothik is a typeface that encapsulates the spirit of two seemingly disparate worlds: the dark allure of gothic culture and the energized pulse of electronic music. This font is designed to bri...
- Pabellona (C) Tríplex is a distinctive font fashioned by the talented designer Fernando Haro, known professionally as deFharo, a versatile Spanish typographer and graphic designer. This font is part ...
- Marsh Gas, crafted by the talented Levi Halmos, is a font that seems to rise from the depths of fantasy and enchantment, encapsulating the essence of mystery and peculiar charm. At first glance, Mars...
- The Iphegenia™ font, masterfully created by the talented designer David F. Nalle, embodies a unique blend of artistic inventiveness and refined classicism, making it a remarkable typeface in the font...
- Malambo by Sudtipos,
$59.00The master of the dancing brush, Angel Koziupa, and the node-obsessed perfectionist, Alejandro Paul, offer up another bucket of fun with Malambo. This time Koziupa allows his brush to jitter one whole millimeter, and Paul digitizes with two eyes instead of his usual three. Follow your heart, but consume an ounce of peroxide first. Full of energy and cheeky mischief, Malambo tells the eye amusing stories of mirrorless shaving accidents, wine mistakenly poured over the morning cereal, and someone who trips over his own shadow on the dance floor, yet keeps on dancing. And dancing is what this typeface is all about. Malambo is a traditional Argentine dance performed by the gauchos (the Argentine equivalent of 19th century North American cowboys?). The gauchos are still around in the less than touristic areas of Argentina. And although they dance quite passionately and make the heartiest parrillas, most of them probably don't know what a font is. But you know, and we know. And that's something. Malambo was selected as the Best in show display font at the Biennial Letras Latinas. - Peridot Latin by Foundry5,
$8.00Peridot is not just another typeface – it's a multifaceted sans serif type system crafted with passion and precision by Foundry5. Painstakingly developed through long hours and a keen focus on every minute detail, this typeface boasts a high-quality 10 weight family with matching italics in 6 widths, and the highly versatile variable format. Brimming with character, Peridot invites you to experiment with its various stylistic variants, allowing you to tailor the typographic tone to fit your creative vision perfectly. The diverse range of widths and styles in Peridot offers a dynamic typographic toolbox, ready to inspire and captivate even the most innovative designers. Peridot Latin covers over 320 languages, including Vietnamese. It includes all required localised variants, tabular numerals and currencies, fractions, clever discretionary ligatures and many more features. Peridot performs in varied environments – from branding, display, corporate use, editorial, advertising, poster, web, screen usage etc. Think of any other use case as well, and Peridot will perform. Peridot comprises 120 static fonts, family packages, and variable support. It is the gem you ought to have in your collection. - Wonderful Branding by Din Studio,
$29.00Is your branding missing something wonderful that makes people going crazy impressed? Have you thought about how you can add that touch of that something to your branding and projects? Want to transport your audience to a world of gorgeous, elegant, wonderful, versatile, yet modern? Then, we have the solution for you. Introducing Wonderful Branding-A Handwritten Brush Font Giving you a simple, yet wonderful solution to your branding. This font is more than just another handwritten brush font. It encapsulates the essence of modernity and elegance. With elegance and passion edged into every curve and twist of this brush font - you’ll be sure to boost your sales and make the best impressions. Use it for headings, logos, business cards, printed quotes, invitations of all sorts, cards, packaging, and your website or social media branding. Wonderful Branding includes Multilingual Options to make your branding globally acceptable. Features: Beautiful Ligatures Stylistic Sets Multilingual Support (84 languages) PUA Encoded Numerals and Punctuation Thank you for downloading premium fonts from Din Studio - Ouido by Hanken Design Co.,
$30.00The Ouido typeface has tastefully narrow characters with enough default spacing for comfortable reading at small sizes. Equipped with features like letter-spaced small caps and conservatively drawn italics for emphasizing words that maintain the reading speed—providing the reader a pleasant overall experience. Ouido (pronounced as “widow”) is derived from the Portuguese word OUVIR which means to hear or to listen. Ouido refers to the ability to play a song on any musical instrument after listening to it a couple of times and without reading the notes. The Ouido typeface is a modernized nostalgia for music enthusiasts, a whimsical revamp of the classic serif font. It bears resemblance with printed classical music scores, characterized by each letter’s rounded strokes like how one drew clefs with passion. Each dot is a twin of the quarter note minus the stem, so weaving sentences together could feel like composing a melody. Inspired by the astounding phenomenon of absolute pitch, the visual appeal of this typeface may hone your imaginative ability to embellish your creation without needing a reference. - Darling Suttine by Aldedesign,
$18.00Darling Suttine is a font is both awesome and classy. It comes with a natural feeling and so many ligatures. We kept this font looks classy, readable, elegant, stylish, catchy and absolutely easy to use. Darling Suttine is the great choice for watermark on branding, design, wedding, photography, signature, logo design, album cover, business card, quotes, and many other design project. This font is for those who want to show something smooth and modern. Use this font if you want to attract modern buyers. The font design seems to show that you have a passion in the business and give your love to the products and services you are offered to customers. Because it is an eye-catching signature font, you can use it for a variety of purposes including wedding invitation, signature, logo, branding, poster, and more. Each font has: - Stylish handwritten style - Many special ligatures - Multilingual support - PUA Encoded Characters - Fully accessible without additional design software. - How to access alternate glyphs? you can see it here: http://goo.gl/1vy2fv - Milonguita by Sudtipos,
$49.00Milonga is one of the most characteristic dances of Argentina and it is usually compared to Tango. However, couples perform shorter and more energetic movements when dancing to the beat of Milonga. In addition, while Tango evokes the idea of nostalgia and reminiscence, Milonga conjures up more light-hearted memories in people's minds. Milonguita was designed so that readers can experience the passion and spontaneity of this dancing style through words. Users can play with the upwards and downwards patterns of the letters creating different images and textures and thus, making texts flow smoothly and naturally, just as a warm piece of Milonga would. The irregularity of the strokes conveys emotions and establishes a bond between the font and the sensitivity of the writer. The result will be a typographic combination of elegance, energy and rhythm which will surely reach the heart of the reader. Milonguita comes in all font formats, including a Opentype version plenty of built-in alternates and a simulated random code. Digitized by Alejandro Paul. - Love Story by Latinotype,
$29.00Love story is a display hairline typeface for use in big sizes and short texts. It’s inspired by different kinds of love and specially designed for Valentine’s day. Its soft curves and sweet style give it a lovely personality. Designed by Luciano Vergara and his wife Guisela Mendoza who has been studying ornaments since 2007 and has done her best for each project. You can see in her dingbats specially Printa and Abel designed for generate patterns. Now she integrated her passion to the ornament in a clean set which includes dingbats, ornaments and patterns. Luciano Vergara has designed very strong fonts with a particular work in the lines study and close to the geometry since 2005, getting a structure style, you can see in his fonts specially Regia and Kahlo. Now he integrated his study of lines, in a hairline font delicate, continuous and beautiful. In this story both designers have been merged their worlds creating a gorgeous product. This is a romantic type story, a love story. - Psycho Poetry is a font that truly captivates the imagination, inviting its audience into a universe where typography and creativity merge in a dance of poetic madness. Imagine each letter crafted wi...
- Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - HS Alwajd by Hiba Studio,
$50.00Hs Alwajd is an Arabic display typeface, under “titles” category. It is useful for book titles, creative designs and modern logos. Also, it is used when a contemporary and simple look is desired that can fit with the characteristics of Kufi fatmic where horizontal parts are equal than vertical ones. It is a new style based on HS Almajd but without swirling round forms terminating in ball. The font is based on Kufi Fatmic calligraphy along with some derived ideas of decorative fonts, maintaining the beauty of the Arabic font and its fixed rates. Undoubtedly, the insertion of curved ornament in some parts adds more beauty and fascinating diversity in the flow line between sharp, soft and curved parts. This font supports Arabic, Persian, Pashtu, Kurdish Sorani, Kurdish Kirmanji and Urdu, consisting only one weight which can add to the library of Arabic Kufic fonts contemporary models that meet with the purposes of various designs for all purposes and all tastes. - Fancy Glow by Nathatype,
$29.00Are you ready to rock your design project? Now you can make stunning design project with Fancy Glow. A touch of sophisticated yet fancy style font. The perfect way to brighten up your project. Fancy Glow is a script font that resembles actual handwriting. This one is suited to any sizes of text. The curves of the characters convey a sense of elegance and will not go out of style. In addition, it has more fascinating features that allows you maximize your design. Features: Stylistic Sets Ligatures Multilingual Supports Numerals and Punctuations PUA Encoded It can be used for many design projects, such as poster, logo, book cover, branding, heading, printed product, merchandise, quotes, social media campaign, etc. Learn more about how to use it by seeing the font preview. Thank you for purchasing our fonts. Please don’t hesitate to contact us, if you have any further question or issues. We’re happy to help. Happy Designing. - Mr De Haviland Pro by Sudtipos,
$45.00The Charles Bluemlein Script Collection is an intriguing reminder of the heady days of hand lettering and calligraphy in the United States. From the early 1930s through World War II, there were about 200 professional hand letterers working in New York City alone. This occupation saw its demise with the advent of photo lettering, and after digital typography, became virtually extinct. The odd way in which the Bluemlein scripts were assembled and created - by collecting different signatures and then building complete alphabets from them - is a fascinating calligraphic adventure. Because the set of constructed designs looked nothing like the original signatures, fictitious names were assigned to the new script typefaces. The typeface styles were then showcased in Higgins Ink catalogs. Alejandro Paul and Sudtipos bring the Bluemlein scripts back to life in a set of expanded digital versions, reflecting the demands of today’s designer. Extreme care has been taken to render the original scripts authentically, keeping the fictitious names originally assigned to them by Bluemlein. - Gothic Gothic by Typeco,
$29.00Gothic Gothic is a fusion of old and new that is both Gothic and Gothic. In typography Gothic can refer to German Blackletter or Old English styles. Gothic can also mean block or sans serif style lettering. By combining and balancing the elements from both of these ideas we have created a contemporary extended block letter typeface. The Gothic Gothic family contains 2 companion fonts. Gothic Gothic Text is a more minimal variation that has a more roman looking style while still retaining some Blackletter feel. Gothic Gothic Black is a bolder version designed to tend more toward the Blackletter style of Gothic with more contrast of stroke and a few of the more unusual Blackletter forms thrown in for flavor. Gothic Gothic has been honored with an award of Excellence in Type Design from Association Typographique International (ATypI) in 2001. Typeco has updated this font and has released it as an expanded family. Gothic Gothic is a crepuscular family of 3 fonts - Mr Sandsfort Pro by Sudtipos,
$45.00The Charles Bluemlein Script Collection is an intriguing reminder of the heady days of hand lettering and calligraphy in the United States. From the early 1930s through World War II, there were about 200 professional hand letterers working in New York City alone. This occupation saw its demise with the advent of photo lettering, and after digital typography, became virtually extinct. The odd way in which the Bluemlein scripts were assembled and created - by collecting different signatures and then building complete alphabets from them - is a fascinating calligraphic adventure. Because the set of constructed designs looked nothing like the original signatures, fictitious names were assigned to the new script typefaces. The typeface styles were then showcased in Higgins Ink catalogs. Alejandro Paul and Sudtipos bring the Bluemlein scripts back to life in a set of expanded digital versions, reflecting the demands of today’s designer. Extreme care has been taken to render the original scripts authentically, keeping the fictitious names originally assigned to them by Bluemlein. - Capires by Craft Supply Co,
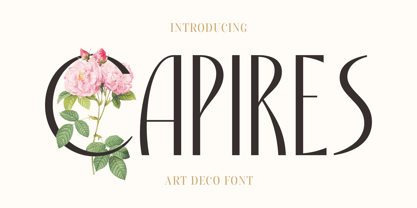
$20.00Capires - Art Deco Font is a captivating fusion of two iconic art movements, Art Deco and Art Nouveau, blended into a contemporary typeface that pays homage to the rich artistic heritage of both styles. This font beautifully combines the geometric precision of Art Deco with the intricate, organic motifs of Art Nouveau, resulting in a harmonious masterpiece of design. Capires is the perfect choice for projects that demand a unique and mesmerizing synthesis of these two influential art movements. Whether you're working on branding, packaging, or editorial design, Capires brings a sense of timeless elegance and artistic richness to your work. With Capires, your designs seamlessly bridge the gap between past and present, making it an exceptional choice for projects that seek to capture the essence of both Art Deco's geometric refinement and Art Nouveau's flowing, ornamental beauty. This font transforms your creations into an elegant and visually captivating experience, where tradition meets modernity in a harmonious embrace.