10,000 search results
(0.044 seconds)
- Studio Five by Lafonts,
$29.00Designed after the sixties neon sign of an arthouse cinema in downtown Zurich, Studio 5 is now a typeface for many applications. The three different styles include old style numbers and alternate characters for titling. All styles have the same metrics. Bold and open styles can be layered for neon sign effects. - ArmWrestler - 100% free
- Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Reverberation JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - PIXymbols Flagman by Page Studio Graphics,
$40.00The numerals and alphabet of the Semaphore Flagging Code, as well as black and white version of the flags and pennants of the International Code of Signals. - Goddess by Device,
$39.00Decadent, baroque and refined. Sinuous curves, ornate swashes and alternates that can be customized to suit your burlesque ball, bodice-ripping romance novel or high-fashion label. The “Swash” version includes swash capitals that can be toggled on or off using the ‘swash’ option in Adobe apps. The “Title” version includes drop-caps that connect with an underline that runs under the regular characters. These again can be toggled on and off using the ‘swash’ option. Also includes optional stylistic alternates and ligatures. - Lectori Salutem Sans by HoboArt,
$10.00Is it royal, or is it dandyish? Either way it's sure to catch the eye. Prepare for titling figures any movie executive would be jealous of using. Do you write sci-fi, fantasy, costume, or cult; or is your announcement for an off-beat wedding? Lectori Salutem Sans offers salutations to the reader, and an edge. Lectori Salutem Sans is the sans serif counterpart of the Lectori Salutem font. A postmodern font with slightly romantic features, cut off at the stem. - Covington Exp - Unknown license
- Covington Cond - Unknown license
- HVD Comic Serif - Unknown license
- Covington SC - Unknown license
- Pickle Sans by Dear Alison,
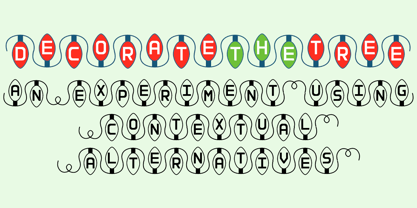
$24.00Discover why Pickle Sans is the font the makers of Comic Sans don't want you to know about! Why not convey a casual professionalism that is a step above the competition? Pickle Sans is a bold, fun, attention getter of a font that is a cleanly readable brush script with a slightly imperfect hand. It speaks to children, retro enthusiasts, and too many others to list. If you've ever had anyone talk to you like a child, you'll understand how the right message can come out wrong. Avoid giving off that message to your audience and approach them in a casual, mature, yet fun manner. Respect your audience, whether younger or older, and convey your message in Pickle Sans. Try it and buy it today! - Decorate The Tree by Ingrimayne Type,
$9.00DecorateTheTree is a festive novelty font family containing two styles designed to be used in layers. Each style has letters on Christmas-tree lights. The regular style has clear bulbs and the bold style has filled bulbs. Some characters are on standing bulbs and others on hanging bulbs and these two sets are made to alternate with the OpenType contextual alternatives (calt) feature. To use only one set of bulbs, this feature must be turned off and character spacing adjusted, though why anyone would want to use only one set is a mystery. These fonts are monospaced. They are useful to display a holiday message not just in words but in the lettering itself. (The characters on the bulbs are derived from the font SansduskiMono.) - SG Noxvile by Studio Gulden,
$24.00Unleash the power of typography with Noxvile, a revolutionary font that demands attention and exudes confidence. Crafted with precision and designed to make a statement, Noxvile brings a whole new level of intensity to your words. Ignite your creativity and let your message roar with Noxvile's super bold style and captivating all-caps specimen. Whether you're designing eye-catching headlines, striking logos, or empowering social media posts, this font will make your words leap off the page and leave a lasting impression. Stand tall among the rest with Noxvile's commanding presence. Embrace its sharp edges, powerful curves, and unparalleled strength to create a visual experience that is truly unforgettable. Let your message shine brighter than ever before, cutting through the noise and leaving your audience captivated. - Hypercreepos by Bisou,
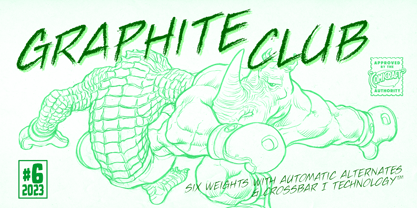
$15.00Hypercreepos is a sweet and creepy hyper-bold font inspired by the horror comic books of the 60s. Handmade in La Chaux-de-Fonds (Switzerland) on lined A4 papers, the letter's shape is conscientiously designed to give a punchos impact on the reader. The unique and vibrant contours are drawn on an improvised backlit table inherited from Bisou's mother. Definitely contemporary, the overall feeling given off by Hypercreepos is profound and human, evoking the graphite smell of the comic's workshops. Exclusively made for titles, this impactos font will suite with delight the text of posters, signs of comics bookstore, gaming bar, horror movie theater or film festival. That said, the designer is not responsible for the use of Hypercreepos and wish it will serve beyond all expectation. - Graphite Club by Comicraft,
$19.00The eight rules of Graphite Club: You do not talk about Graphite Club… You do NOT talk about Graphite Club. If someone types "Stop" taps out “Limp,” the Graphite is over. Only two -- Waitasecond! EVERYBODY wants to talk about Graphite Club! It's the font for rough and tough typesetting that looks as etchy and sketchy, sleek and sexy as Brad Pitt on an off day. It's Light as a featherweight, it's as Regular as wetwork and as Bold as Brass Knuckles. And don't let anyone tell you this font is not special. It's as beautiful and unique as a snowflake. And so are you. Features six weights with alternate uppercase alphabets, language support for Western & Central Europe, Automatic alternates, Stylistic Alternates & Crossbar I Technology™ - Bulkr by Hackberry Font Foundry,
$24.95Over the years, I've used Impact a lot. But, not because I liked it—rather because it was the only font I could find with the bulk I needed for a given title or whatever. I finally decided to make my own. It was originally built off Librum Sans Bold, but I quickly made a mask of Impact for the widths, bumped the x-height way up, made the horizontals much heavier, and on and on. You know how it is when you start designing. The result is a black sans with the bulk of Impact and much more interesting character shapes. I suspect I'll use it a lot. My hope is that you like it as much as I do. Have fun! - Teleprinter - Unknown license
- Silkscreen - Unknown license
- CROWD PERSONAL USE - Unknown license
- Sixties Pin Buttons JNL by Jeff Levine,
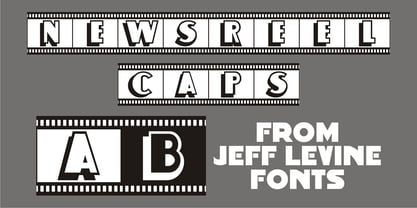
$29.00During the turbulent era of the 1960s, the youth of America found various ways to protest against "The Establishment". Whether it was campus unrest, protest songs, sit-ins or other methods, the message was the counter-culture movement. Arising from this disenchantment with traditional social standards, a small but effective means of protest arose that made no sound, yet spoke volumes - the pin button. Statements against the war in Vietnam, free love, drug use and other messages popped up on little metal discs pinned to tee shirts, suspenders, head band and hats. Sixties Pin Buttons JNL recreates twenty-six of these messages in both white on black (upper case keys) and black on white (lower case keys). Blank buttons in both white and black are found on the parenthesis keys. - Newsreel Caps JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Newsreel Caps JNL is a novelty caps-only outline letter with cast shadow set inside film frames. Although the design idea itself is not new, this version is based on lettering from a vintage piece of sheet music for a song featured in the movie "Fox Movietone Follies". The font is a wink and nod to Fox's long-running newsreel series called "Fox Movietone News". The upper case keys have black letters on a white frame, while the lower case keys have white letters on a black frame. A blank white frame is on the period key; a blank black frame is on the comma key. Use this font for individual initials, set the characters loose for effect or set them tight (as provided) for a continuous film strip. - Elektronik - Personal use only
- Oldbrothers - Personal Use - Personal use only
- Megalito Slab ExtCond - Personal use only
- Space Age - Unknown license
- JUSTICE LEAGUE - Personal use only
- BjorkFont - Unknown license
- Barbarian - 100% free
- ‘DragonForcE’ - 100% free
- The Black Box - Personal use only
- Candy Pop! - Personal use only
- STR - 100% free
- FellFel - Personal use only