10,000 search results
(0.027 seconds)
- French Calligraphic JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00French Calligraphic JNL is actually more semi-calligraphic in nature. Its name takes a descriptive liberty because of the sharp, angled pen strokes of the original hand lettered example found in the 1930s publication "100 Alphabets Publicitaires" by M. Moullet. The design is available in both regular and oblique versions. - French Bistro JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Pen Work JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Grounds Crew Stencil JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Parisian Playboy JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Sheet music for the song "My Ideal" (from the 1930 Paramount picture "Playboy of Paris" starring Maurice Chevalier) had the name of the movie hand lettered in an Art Deco, Broadway-influenced type design. This became the inspiration for Parisian Playboy JNL, which is available in both regular and oblique versions. - Drama Deco JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00The movie poster for the 1936 film “Dodsworth” had its title hand lettered in a thin Art Deco sans serif with a mix of both stylized and squared characters. Expanding on this unusual lettering combination, the final results became Drama Deco JNL, which is available in both regular and oblique versions. - Movie Star Deco JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Evening Event JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Outline Sans JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Dance Band JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - Grand Label by Gleb Guralnyk,
$14.00 - LeftheriaPRO by Sea Types,
$29.00LeftheriaPRO has its structure projected from the capitals of the Greek columns of Ionian order, it is a typography condensed with vertical emphasis composed by 5 weights (light, regular, medium, semibold, bold) including ligatures, alternates, smal caps, old styles figures, fractions, superiors, inferiors. | Download Specimen - Haglos by Vultype Co,
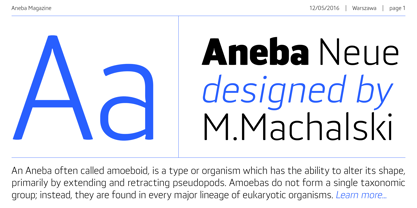
$29.00 - Aneba Neue by Borutta Group,
$27.00 - Heselna by Liartgraphic,
$18.00Hello gaes! How are you guys doing ? i’m sure that’s nice! Meet our newest product, we call this product Heselna font. Heselnas font are serif typeface font Whit a uniqe touch and assertive Heselna font is very nice to use on: fashion magazine, logos, ,and photography, landing page, fliyer, What’s includes - mutilngual support - alternate - ligature Thank you, salutations Ali Sifak Muftari - Hellotropica by Garisman Studio,
$20.00Hellotropica is made with natural hand brushes to give it Summer Vibes. With the unique Opentype and ligature it will add aesthetic value to your design product. Including Hellotropica Swashes which you can unite into an amazing design. Simple installation Works for Windows or MAC Included file OTF, TTF PUA Encoded Open Versatile for poster, logotype, labels, book cover Detailed dry brush - Alyester by Liartgraphic,
$30.00Hello gaes! How are you guys doing ? i’m sure that’s nice! Meet our newest product, we call this product Alyester font. Alyester font are cute typeface font Whit a uniqe touch and assertive Alyester font is very nice to use on: fashion magazine,logos, ,and photography,landing page,fliyer, What’s includes - mutilngual support - alternate - ligature Thank you,salutations Ali Sifak Muftari - Acharnes by Liartgraphic,
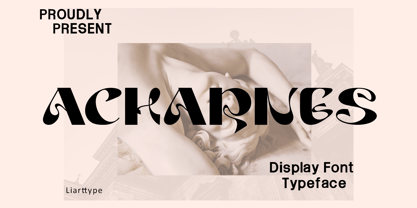
$23.00Hello gaes! How are you guys doing ? i’m sure that’s nice! Meet our newest product, we call this product Archanes font. Archaness font are display typeface font Whit a uniqe touch and assertive Archanes font is very nice to use on: fashion magazine,logos, ,and photography,landing page,fliyer, What’s includes - mutilngual support - alternate - ligature Thank you,salutations Ali Sifak Muftari - Jane Plain NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00Here's a clean, simple architectural-blueprint style, eminently suitable for subheads and text blocks. Inspired by and named for a gentlewoman who gave up a career as an architect in Bolivia to care for the elderly in the United States. All versions of this font include the Unicode 1250 Central European character set in addition to the standard Unicode 1252 Latin set. - Zondrone by Liartgraphic,
$20.00Hello gaes! How are you guys doing ? i’m sure that’s nice! Meet our newest product, we call this product Zondrone font. Zondron font are cute typeface font Whit a uniqe touch and assertive Zondron font is very nice to use on: fashion magazine,logos, ,and photography,landing page,fliyer, What’s includes - mutilngual support - alternate - ligature Thank you,salutations Ali Sifak Muftari - Quantour by TEKNIKE,
$129.00Quantour is a geometric monospaced display sans typeface which has a distinct style and is inspired by the Mid-Century Modern era. The Quantour name is a combination of the Latin 'quantum' meaning "unit of something" and the French 'tour' which means "to turn". Quantour is recommended for luxury brands, logos, fashion, cinema, architecture, invitations, display work, posters and headings. - Side A by bb-bureau,
$60.00 - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Kropotkin Std by sugargliderz,
$30.00This typeface design was influenced by the British Rail corporate type introduced in an old lettering instruction book published in Japan. Of course, the only clue to this typeface is the lettering instruction book at hand. Therefore, this typeface is based on the British Rail corporate type introduced in an old lettering instruction book published in Japan, and I have expanded the design variations. I started with the Bold design first. Then I designed Light, Regular, and Black in that order. Light and Regular are intended to be used as the text type, while Bold and Black are intended to be used as the base for logotypes, headlines, and other eye-catchers. - Astronef Std Super by Typofonderie,
$59.00The Astronef Super borrows from the charm of retro-futuristic universes. Without concessions, and even radical, the Astronef Super, declined in three styles, pushes the weight limits as far as possible systematically while preserving a unique design. Using the Astronef Super in large size is a real pleasure, it is a very identifiable typeface family, recognizable immediately. Undeniably, choosing the Astronef Super in your designs is not insignificant. This typeface used in large sizes will strengthen your graphic identities. Background The Astronef Super could be considered as the “Spin-off” of the Astronef currently being designed, that will offer an important variation of styles. Of course the Astronef, is wiser in his drawing, it places himself in the tradition of the Univers more than the Helvetica. Genesis and the creative process The idea for an Astronef Super comes from an excerpt from a 60s TV show which shows a logo in the background with a very bold S and this super thin in the middle. The Astronef is already modular in its design. The brief then becomes simple for the Super: accentuate the strongest weights of the Astronef by minimizing the counterform that will remain constant for the three styles. It is the mass effect that maintains the overall cohesion of the Astronef Super family. - Atto Serif by Wilton Foundry,
$29.00I set out to design a contemporary font that is condensed with thick and thin strokes. The highly structured forms of this condensed font was made more interesting and softer by giving it a slightly calligraphic tone and by adding round corners. Atto's express purpose is to be both utilitarian, compact and technical but with a friendly face. The name "atto" was adopted since it refers to the measurement of "smallness" or detail. You will no doubt discover all the many pleasant nuances within Atto. Adopted in 1964, "atto" comes from the Danish "atten", meaning eighteen. Atto - (symbol a) a SI prefix to an unit and means that it is 10 to the power- 18 times this unit. Examples are one attosecond or one attometer/attometre. Atto is available in for Mac and Windows in Postscript, Truetype and Opentype. See also the companion font Atto Sans. - Candyful - Personal use only
- Movement - Personal use only
- Dopestyle - Personal use only
- Kick The Font - Personal use only
- LT Funk - 100% free
- Vineyard - 100% free
- FarCry - Personal use only
- NFL Packers - Unknown license