9,144 search results
(0.041 seconds)
- Altemus Cuts by Altemus Creative,
$11.00 - Heinemann by Heinemann Collection,
$39.00The Heinemann fonts were initially developed by the in-house design team at Heinemann educational publishing out of the necessity to find the perfect font for use in early primary reading books and literacy products. Basic Heinemann is defined by longer ascenders and descenders which help children to distinguish between letters; rounded edges on all letterforms help focus the reader on the individual letter shape; and modified characters (eg. a, g,) ensure instant recognition of letterforms. Heinemann Special offers further modified characters and kerning pairs ideal for dyslexic or special needs use (eg a, d, b). The Heinemann fonts were developed in partnership with children, literacy advisors, teachers of special needs/dyslexia and primary school teachers, and are now released in response to hundreds of requests from publishers, designers and teachers to purchase them. They have been trialled in schools and learning institutions over an 8 year period, and are a favorite for use in both print and electronic product. The modern, clean aesthetic of the fonts ensures that their use can span beyond educational application. - Heinemann Special by Heinemann Collection,
$39.00The Heinemann fonts were initially developed by the in-house design team at Heinemann educational publishing out of the necessity to find the perfect font for use in early primary reading books and literacy products. Basic Heinemann is defined by longer ascenders and descenders, which help children to distinguish between letters; rounded edges on all letterforms, which help the reader focus on the individual letter shape; and modified characters (eg., a and g), which ensure instant recognition of letterforms. Heinemann Special offers further modified characters and kerning pairs ideal for dyslexic or special-needs use (eg., a, d, and b). The Heinemann fonts were developed in partnership with children, literacy advisors, teachers of special needs/dyslexia, and primary-school teachers and are now available in response to hundreds of requests from publishers, designers, and teachers to purchase them. They have been tested in schools and learning institutions over an 8-year period, and they are a favorite for use in both print and electronic products. The modern, clean aesthetic of the fonts ensures that their use can spread beyond educational applications. - Comenia Serif Pro by Storm Type Foundry,
$69.00Comenia was developed as typographic system for use on all levels of schools and universities. It introduces new aesthetic standards aimed at improving reading and writing skills and the perception of texts for pupils, students, teachers, office and IT staff at schools. It offers a clear, intelligible and universal graphic tool for layout of primers, textbooks, educational texts and materials, for electronic typography and for the information systems. - Pyke by The Northern Block,
$39.95Pyke is a versatile serif typeface inspired by the Didone style of Giambattista Bodoni. After a detailed legibility study, Sofie Beier produced the typeface in three optical sizes; Micro, Text, and Display. The work goes beyond historic revival creating the complexities and subtleties of this classic style fit for users in the modern era. Details include six weights with true italics, specific sizes; Micro for small point sizes of 8 or less, Text for 9–14 points, and Display for larger print sizes, over 530 characters per style with 14 opentype features, and language support for Western, South, and Central Europe. Check out Karlo which is a great pair for Pyke. - Snag by Smith Hands,
$35.00Inspired by a small fragment of sign-written lettering, discovered by accident, Snag is a robust mono-line font with small, pointed tips on its terminations. These embryo serifs are inspired by the legacy of a sign-writers brush, and add an overall texture and character to this, otherwise minimalist, style of lettering. Snag has a warm and traditional feel with a modern clarity. A strong component for a multitude of graphic design functions, including packaging, shop fronts, bar signs, advertising and clothing. Snag features a large glyph set, suitable for Latin-based languages worldwide. - Marketing Strategy JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Marketing Strategy JNL was inspired by some display signage used in an episode of the classic "Alfred Hitchcock Hour". Evoking the early-60s feel of kitchy advertising, this display font has a limited character set and is specifically designed for creating retro ad banners and point-of-sale attention getters as well as period piece signage. For those preferring a blank hexagon for spaces between words, one is located on the equal key. Marketing Strategy JNL is available in both regular (outline) and solid (white letters on black) versions. - Boondock by Canada Type,
$24.95Boondock is another Imre Reiner design resurrected from the ashes of hot metal type for digital use. This wild paint font is a revival of the fascinating Bazaar brush type from 1956. Boondock has some very unique characters that combine to form a statement of casual but loud strength, seriousness and raw primal emotion. Great for short sudden-impact spurts, like book cover titles, single sentence headers, movie posters and music sleeves. Redrawn from original specimen by Patrick Griffin, and expanded with some built-in extras too add to the convenience of this digital version. - Gillcy by Scratch Design,
$9.00Gillcy is a Modern script font with a beautiful shape and natural on each character comes with unique alternative glyphs and has multilingual support. Gillcy it's a very unique font that works great in large sizes with any background colors. Gillcy is perfect for Wedding invitations, Magazine Headlines, Branding Projects, Prints, labels, Price Tags, Clothing & Fashion Branding. Just open your Opentype features while using the script font to use the ligatures and swashes. As you type, your text will look like a natural and authentic script. Features: Stylistic Alternates & Ligatures Numerals & Punctuation Swashes Accented characters Format File: TTF, OTF, Web Multiple Languages Supported - Altemus Games by Altemus Creative,
$11.00Each style is a collection of 174 illustrative game symbol, printer cut designs. - Altemus Sports by Altemus Creative,
$11.00 - Tag Banger by Okaycat,
$12.50TagBanger WADE1 is the first in a short graffiti font series. This series will showcase the hand-styles of various mature street artists that Okaycat is working with. This first release highlights the style of one such graffiti writer, WADE1, who has an eclectic writing style after many years proliferating street art. Long-term graffiti artists develop their own style over their careers, spending as many endless hours honing their letter-forms as any full-time professional typographical artist. Style, individuality, and originality are everything. These attributes are key to the graffiti artist's tao. A writer who copies, or "bites" loses respect -- their work will be painted over or "crossed out" by all other writers. Okaycat's TagBanger series aims to demonstrate just how widely these individual styles can diverge, likely due, at least in part, to the social pressures of a community that ruthlessly punishes copycats. WADE1's tags were transformed into vector format from a generous sampling of their most recent scrawls. Our TagBanger series may not be composed of the most legible or beautiful fonts, but we imagine there are uses for these whenever highly unusual handwriting is needed. TagBanger WADE1 is extended, containing the full West European diacritics & a full set of ligatures, making it suitable for multilingual environments & publications. - Maskule by Invasi Studio,
$15.00Maskule Combo is a vintage combination pairing font that captures the essence of hand-painted signs. It features two fonts: Maskule Regular and Script, which work harmoniously together. With its charming and nostalgic style, it's the perfect choice for creating designs with a vintage theme. Whether you're working on headings, flyers, greeting cards, product packaging, book covers, printed quotes, logotypes, or album covers, Maskule Combo will add a touch of timeless appeal to your projects. - Wildline by Mans Greback,
$59.00Wildline is a fast logotype font, created to help you designing logotype or lettering that looks just like a hand-painted brush logo. Use it for designing signs, packaging, headlines, or a cool typographic print. Wildline has characteristics such as strength and confidence, while being dynamic, readable and very energic. Containing extensive lingual support, it covers all Latin European and Asian scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. - Mont by Fontfabric,
$39.00*Mont Specimen: http://bit.ly/montsp *Scroll down for the FREE DEMO fonts Features: • 744 glyphs in 20 styles; • Extended Latin, Cyrillic and Greek; • Perfect for headlines and logos; • Prominent x-height; • Distinctive pointed triangular bracketed “t”; • Coverage of multiple OpenType features; • Suitable for web, print, motion graphics etc. Mont is a geometric sans serif consisting of 10 weights ranging from Hairline to Black with matching italics. It supports Extended Latin, Cyrillic and Greek — more than 130 languages all together. The balanced characteristic of Mont with unique details, such as the pointed “t” and the prominent x-height makes it perfect for strong headlines and outstanding logos, but also suitable for long text. Mont comes with a range of OpenType features — including tabular figures, advanced typographic features such as ligatures, fractions, case-sensitive forms, superscripts, subscripts etc. The typefaceʼs versatility and merits make it easy to confront any graphic design challenge — web, print, motion graphics etc. Up with Mont to the top and beyond!Mont™ Font Field Guide including best practices, font pairings and alternatives. - Operetta by Synthview,
$34.00Operetta is a neo-didone display font family inspired on Bodoni, Didot (early 18th century) and Walbaum (19th century). Despite of this heritage, Operetta’s design meets contemporary taste and typesetting needs. With five optical sizes, masterfully navigate between contrast and legibility across various dimensions. The range of eight weights, from the weightless Extralight to the robust Extrabold, let you set your tone: from delicate to exuberant. Operetta's generous character set and opentype features let you meet the most demanding layout needs. And don’t forget swashes, arrows and other extra glyphs, seldom included in a didonesque font. The number displayed in the font family name signifies the recommended minimal print size in points. In web design you should double the minimum value for a retina screen, multiply by 4 for a 72dpi screen. Of course its rendering depends on the printing support, screen resolution etc. Therefore, take it as a suggestion or a starting point; make your own trials. And now, the pièce de résistance: Operetta unveils its italics, adding yet another layer of allure and sophistication. - Florati by Proportional Lime,
$19.99Can you imagine the delight that the printers of the Incunabula era would have had if they had such a tool as this font with a hundred and fifty glyphs of decorative capitals. The printers of that era were lucky to have more than a handful such delights. These Decorated initials and drop caps are all based on early period exemplars, dating to prior to 1525, from a wide range of printers such as Thomas de Blavis to Günther Zainer. Every Proportional Lime Font comes equipped with a complete character map. - 1756 Dutch by GLC,
$42.00This family is inspired from the set of two styles, Roman normal and Italic, and the ornaments used by an unknown printer working around East Switzerland, circa 1750's. It is a Dutch style font, slightly bolder than usual Fournier's or Caslon's Roman fonts, with some emphasized serifs and finals parts and special letters as capital "U" for example. A set of initials, fleurons, ornaments and frame elements is joined to the family as a supplement. The two styles, Normal and Italic, are containing standard ligatures, a few alternative characters and titlings (who are more preferable than enlarged capitals). They are "small eye" or "Small x-eight" fonts. The standard characters set is completed with accented or specific characters for Western (Including Celtic) and Central Europe, Baltic, Eastern Europe and Turkish. - Madromit by Dharma Type,
$14.99Madromit(ma-do-ro-mi) is a somewhat nostalgic display font. Do you remember computer advertisements in the 80s and 90s? Yes, it is the most excited period in the history of computer. We call the design in this period Primitive Digital Design. Madromit is, so to speak, the revival or reconstruction of the primitive digital type in the period. The structure and elements of this font are very simple and the key features are geometric shape and simple griddy design with rounded corners, oval bowls, and right‐angled joints which we used to see in the primitive period. In addition to this, Madromit has one more characteristic feature — classic engraving font —. It is called Open Style. Open style is one of the classic method to decorate and emphasize the font. Our aim is the synergy by the mixture of primitive digital design and classic engraving method. This mixture makes new impression we have never seen before. Madromit family consists of 5 styles for stacking color font. Please use Photoshop or Illustrator, or your favorite graphic design apps that can handle layers. Layers are the printing plates of wood type. You should be able to change text color for each layers. Madromit "Standard" style is the base of this font family. You can add open effect by stacking "Fill" layers over the Standard layer. Instruction 1. Type your text as you like. 2. Set font-name "Madromit" and font-style "Standard". 3. Set color of "Standard" layer. 4. Duplicate the "Standard" layer to make "Fill" layer. 5. Set font-style "Half Fill" or "Full Fill" and new color of upper layer. Madromit Standard, Half Open, and Full Open style can be used solely. - 1538 Schwabacher by GLC,
$38.00This 1538 Schwabacher was based on a font used by Georg Rhau in Wittemberg (Germany) to print Des Babsts Hercules [...], a German pamphlet against roman catholicism written by Johannes Kymeus. The original font has a relatively complete set of characters including “long s”, but also the special german types like k, fl or ‰, ˆ, ¸.... A few omissions were remedied, and accented letters were added. A render sheet, enclosed with font files, help to identify them on keyboard. It can be used as web-site titles, posters and fliers, editing ancient texts, menus or greeting cards as a very decorative font... Although this font remains clear and easy to read from 8 or 9 points on screen, it is clearly designed for print works. - 1776 Independence by GLC,
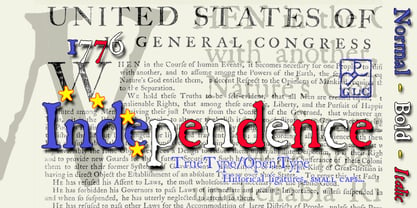
$38.001776 Independence was designed inspired mainly from the Caslon typeface used by John Dunlap in the night of 1776 July 4th in Philadelphia to print the first 200 sheets of the Congress' Declaration of Independence establishing the United States of America. I just added accented letters and a few others, with respect for the original design. A render sheet,enclosed with font file, help to identify them on keyboard. It can be used as web-site titles, posters and fliers, editing ancient texts, menus or greeting cards as a very decorative font... This font supports as easily enlargement or small size, remaining clear and easy to read from 8 or 9 points to 72 and over. It gives a smart look especially to prints. - Ony by Cuda Wianki,
$20.00 - Circuity by Din Studio,
$29.00Circuity is a display font designed in a racing theme which provides a unique yet modern capital letter font. Each stroke shows a firm brave character. Due to its shape and size, it is suitable to apply for a large-sized text such as titles. Enjoy the interesting features to maximize the design projects. Features: Multilingual Supports PUA Encoded Numerals and Punctuation Circuity is definitely proper to use in any design projects such as posters, banners, logos, book covers, headings, printed products, merchandise, social media, and so on. Find out more ways to use this font by taking a look at the font preview. Thanks a lot for purchasing our font. Happy designing. - 1871 Dreamer Script by GLC,
$38.00This script font was inspired from a lot of manuscripts, notes and drafts, written by the famous American poet Walt Whitman. It is a very elegant type, in spite of a few curious ligatures, often concerning the r or z small letters. Notice the very characteristic “th”. It is used as variously as web-site titles, posters and fliers design or greeting cards, all various sorts of presentations, menus, certificates, letters. This font, in spite of its small size, supports very strong enlargements as well as small sizes ( the original size was about 36 to 48 pts ). When printed, it remains perfectly legible and elegant from 9/11 pts even if using an ordinary inkjet printer. - WetPaint - Unknown license
- Petroglifos by John Moore Type Foundry,
$19.00Petroglifos is a dingbats font as a collection of pre-Hispanic petroglyphs of indigenous ethnic Venezuela, most of them are found in signs carved in stone or painted in caves of the pre-Hispanic period, each icon is an accurate representation of these ancestral signs. Forms are very interesting from a visual, anthropological, historical and semiotic point of view. - Times Eighteen by Linotype,
$29.00In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Europa LT by Linotype,
$29.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten Paneuropean by Linotype,
$92.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Altemus Leaves by Altemus Creative,
$11.00 - Altemus Dingbats by Altemus Creative,
$11.00 - Clashed Dinosaurs - 100% free
- ROSETTA STONE - Personal use only
- CROSS STITCH - Personal use only
- Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer."