851 search results
(0.218 seconds)
- Bouwsma Script by Canada Type,
$24.95Bouwsma Script, based on Philip Bouwsma's own handwriting, was originally released in 1994 and settled for nothing less than being an instant classic. One of Bouwsma's widely used works in the 1990s, Bouwsma Script finds its home now at Canada Type, where it was updated with the Euro symbol and complete support for Turkish, Baltic, and Central and Eastern European languages. It now also comes in all popular font formats, including OpenType. Real, casual, friendly, and loaded with the designer's artistic touch, Bouwsma Script can be seen around the globe on plenty of store signs, book covers, product packaging, promotional posters and a variety of other paraphernalia. - Lancelot Pro by Canada Type,
$39.95When type historians look back on Jim Rimmer, they will consider him the last type designer who just couldn't let go of metal type, even though he was just as proficient in digital type. Lancelot is one definite case in point: A face designed and produced in digital as late in the game as 1999, only to spring onto the new millenium a couple of years later as a metal type cast in three sizes. That was Jim, a time traveler constantly reminding the craft of its origins. This particular time machine was originally designed as a simple set of attractive caps that emphasize the beauty of the variable conventional dialogue between the drawing tool and the intended final form, and the one exchanged within the totality of the forms themselves. Jim designed two weights, with contrast and counterspace being the main difference between them. In 2013, the Lancelot family was remastered and greatly expanded. Lancelot Pro is now a wonder of over 840 glyphs per font, including smaller versions of the caps in the minuscule slots, and alternates and ligatures that can transform the historic spirit of the original design into anything from half-uncial to outright gothic. Language support goes beyond the extended Latin stuff, to cover Cyrillic and Greek as well. 20% of the Lancelot Pro family's revenues will be donated to the Canada Type Scholarship Fund, supporting higher typography education in Canada. - Times Eighteen by Linotype,
$29.00In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Europa LT by Linotype,
$29.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten Paneuropean by Linotype,
$92.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Zennat Pro by Latinotype,
$29.00This font is inspired by the compact, high-impact design aesthetic of the 1990s in Chile, which was defined by the use of very heavy fonts to create eye-catching graphic pieces. With this idea in mind, Zennat Pro was born, a “semi-slab serif” that takes advantage of OpenType features which rotate in alternate characters to best fit the design. Zennat pro comes in 10 weights, and is ideal for magazine design, motion graphics, trademarks, logos, posters, etc. ... - Capital Ideas NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00A new series of eclectic decorative initials, Capital Ideas 1 NF features numbers and uppercase letters rendered in nixietube displays, along with a whimsical walk through the alphabet patterned after Milton Glaser's Hologram. Capital Ideas 2 NF features K. H. Schaefer's eponynmous Versalien for Schriftguss AG in 1927, and Walter Haettenschweiler's Breitfette Unziale from 1958, along with a fancy nine-element box border. Dressing up your next projects with these snappy caps is, indeed, a capital idea. - Albyona by SIAS,
$34.90Albyona English Nº 1 is ideal for titlings and headings in novels or fairy tales. It has a sentimental flavour of history, memories and the good-old-days feeling. Suitable for children’s books, fantasy literature, crime novels, natural food packaging and poison labeling, for infancy memories, vanitas kitsch items, dungeon museum bar menu cards, introductions to herbalism and witchcraft manuals. Albyona supports every Euro-Latin language. For the choice of a similar font go to Abendschroth. - Romanica by K-Type,
$20.00ROMANICA is a relaxed humanist sans with subtly curved corners and slightly flared glyphic terminals that are expressively angled where appropriate. Romanica has the authority of the ages without the harshness of many classically inspired typefaces. All eight fonts include a full complement of Latin Extended-A characters, Welsh diacritics, Irish dotted consonants, and additional oldstyle numerals. ROMANICA is available in three packages - • Basic Family (Regular, Italic, Bold & Bold Italic) • Light (Light & Light Italic) • Medium (Medium & Medium Italic) - HU Flatwhite KR by Heummdesign,
$25.00This is a headline typeface for titles with a retro sensibility. The concave first projection of the vowel and the dot shape further add to the retro feel. It is characterized by the dot shape seen in the initial consonants and the thin ending strokes of 'ㄱ', 'ㅅ', and 'ㅈ' to create a flowing curve. Although it is a full module, the inner space created by the large contrast of strokes gives a cool feeling. This font contains KOREAN - DSari by Latinotype,
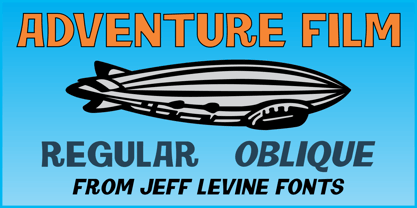
$29.00It is inspired by the friendliness and cordiality of neo-humanist typefaces with a mix of rounded shapes, some apexed characters, and a little bit of black. Although it follows the ductus, D Sari is also a daring font with less pointed shapes, as is the case with regular neo-humanist typefaces. D Sari has 22 variants, which make it a very dynamic typeface. Well-suited for highlighting lettering, magazines, motion graphics, advertising, logotypes, signs, etc. - Adventure Film JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00In most cases, motion pictures with a Western theme have their titles and credits lettered in type styles that reflect the period of the Old West. In 1966, the titles and credits for “Texas Across the River” used casual sans serif lettering more suited to the 1960s than a Western taking place in the 1800s. Nonetheless, the lettering inspired a digital font entitled Adventure Film JNL and it is available in both regular and oblique versions. - Keista Heather by Matra Creative,
$12.00Keista Heather brings her own unique style to every design project. This fantastic script font is best suited for headers of all sizes, and for blocks of text that have maximum and minimum variations. Whether it's for the web, printing, motion pictures, or anything else – Keista Heather would look spectacular. This font is PUA coded which means you can access all the cute glyphs and swashes with ease! It also has many special features including alternate glyphs and ornaments. - Solomon Sans by Fontfabric,
$40.00The new Solomon Sans type family includes 14 unique design styles. The font family is characterized by excellent legibility, well-finished geometric designs, optimized kerning etc. Solomon Sans is most suitable for headlines of all sizes, as well as for text blocks that come in both maximum and minimum variations. The font styles are suitable for any type of graphic design - web, print, motion graphics, etc, and perfect for t-shirts and items like posters and logos. - Contamination by Kenn Munk,
$42.00Vowels produce 'end-characters'. These are used whenever a string of symbols start or end. Consonants make 'middle-characters'. Numerals are zero-width characters. these can be used whenever you feel like it, they will float above and below the string of symbols. Puncuation adds extra spice. Hold down 'shift' and you get the individual symbols mirrored. (very useful with the vowels.) Check my website for a more graphic representation and play, for gods sake, play! - schizophrenia Queue - Unknown license
- Cavello by XdCreative,
$20.00Cavéllo is a bold and clean slab serif font. This original look will appeal to a wide range of crafty ideas, from letterheads and titles, to stationery. Cavéllo the font family contains 3 basic forms: italics, obliques and uprights, Each of which has 4 different weights: light, regular, semi-bold and bold. Cavéllo slab serif font family ideal for the logos as well, t-shirts, the web as well as for print, for motion graphics, It is also great for headings, - Letraflex by Art Grootfontein,
$19.00Letraflex is a bold retro-inspired typeface with a slightly futuristic style. The family is based on old computer lettering and Magnetic Ink Character Recognition, with a little contemporary twist including ink traps. Letraflex layered fonts provide users with a wide range of choices for any design project. This family is an excellent pick for eye-catching designs, including Headline, Poster, Branding, Logos, Concert, and any other heavy design! Take a look at this video to see Letraflex in motion! - FF Providence Sans by FontFont,
$93.99American type designer Guy Jeffrey Nelson created this script FontFont in 1994. The family contains 2 weights: Regular and Bold and is ideally suited for advertising and packaging, festive occasions, poster and billboards as well as web and screen design. FF Providence Sans provides advanced typographical support with features such as ligatures, alternate characters, case-sensitive forms, and stylistic alternates. It comes with proportional lining figures. This FontFont is a member of the FF Providence super family, which also includes FF Providence. - BD Roylac by Typedifferent,
$30.00The BD Roylac typeface has its roots in some lowercase glyphs drawn by Jacques Loison in 1972. Some of these characters are included in the use of stylistic alternates. Filed under a retro-futuristic design the font separates two filled shapes by a thin and curvy line; sometimes following to the path leaning readability and sometimes interfere with it. The font is dedicated to the BD fanboy Monsieur «Eric de Broche des Combes» aka «Roy La Combe» to his fiftieth anniversary. - Braxton by Fontfabric,
$39.00Braxton - brush flavored script font family includes 5 unique font weights. The font family is characterized by excellent legibility in both - web & print design areas, well-finished calligraphic designs, optimized kerning etc. Braxton is most suitable for headlines of all sizes, as well as for text blocks that come in both maximum and minimum variations. The font styles are applicable for any type of graphic design – web, print, motion graphics etc and perfect for t-shirts and other items like posters, logos. - Variera by Kereatype,
$14.00Variera is geometric with a semi-condensed sans serif typeface. It comes in 9 weights ranging from thin to black with matching italics that stand out in headlines and exude a charming personality. Variera is a Utility display type that is flavor in motion. Each part of its system works together to captivate you, combining emotion and usability, allowing you to create attractive and unique designs. Variera is a versatile font system, designed primarily for display uses with a need for visual impact. - Nomad by Coniglio Type,
$20.02NOMAD —Regular is a stand alone font. Nomad -Regular is a clean, interesting revival font. It is a Display font. Nomad, now exclusively in OpenType .oft by Joseph V Coniglio of Coniglio Type. It is a narrow boldfaced font. Its analog source was comprised of an extremely limited die cut, truly generic, craft, peel-and-stick vinyl set of capital letters of ascenders and numbers. It was purchased at a five & dime stores, hardware department from the 1970's. My father owned an original set of characters: Nomad-Regular is nicely expanded to meet the needs of OpenType. The original adhesive labels adhered to the bows of that small boats so fisherman wouldn't get turned away at the Canadian border for not having their vessels tagged and listed with the appropriate license name and numbers, recorded by customs. It was a required serialization of letters and numbers marked on the side of their vessels. On the other hand, most beer and whisky drinking fishers, card players and bait casters would rather not deal with it, but the boat could not cross over the border without them. (Once part of Market LTD from the 1990's, a collection of limited faces, mostly alpha-numeric and some just plain numeric, used primarily in retail and display situations and titling.) Designer: Joseph V Coniglio Author: Coniglio Type - Poster Paint by Canada Type,
$24.95Poster Paint is a fun shocard alphabet which came about from Jim Rimmer’s admiration of Goudy Stout, a design he liked in spite of the fact that Goudy himself claimed to detest it. Extremely eye-catching and humourous to a fault, Poster Paint is an ideal fit for fun environments like theme parks, concession stands, cofee and juice bars, and in print design for children books and fun food packaging. Poster Paint was updated and remastered for the latest technologies in 2012. It comes with a glyphset of over 375 characters, and supports the majority of Latin-based languges. 20% of this font’s revenues will be donated to a GDC scholarship fund, supporting higher typography education in Canada. - 1536 Civilite Manual by GLC,
$42.00This font was created inspired from a handwritten copy of the "Brief story of the second journey in Canada" (1535) by French explorer Jacques Cartier. It is an early "Civilité" manual style, closely looking like the "Civilité" script font carved by Robert Granjon a few years later and still strongly influenced by blackletters forms, clearly visible in the capitals or long s, d, e, f or t forms. (Look at our "1557 Civilite Granjon Pro" and the latest "1638 Civilite Manual"). It is containing Western (including Celtic) and Northern European, Icelandic, Baltic, Eastern, Central European and Turquish diacritics. Historical forms, titling alternates and the numerous lower alternates or ligatures made the font looking like a real various hand. - Silent Drama JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00An ad in the April 19, 1919 edition of Motion Picture News for the (now lost) silent drama "Josselyn's Wife" featured some wonderfully stylized Art Nouveau hand lettering. Primarily a condensed character set with rounded serifs, there are a number of letters that take liberties in both width and character shape. Adding to this, [mostly vertical] parallel lines are cut through the characters to create a "striped' type of "double engraved' effect. Silent Drama JNL is available in both regular and oblique versions. **Uppercase - Fortis by GroupType,
$19.00Formerly named Atlas, Fortis is a 21st century contemporary Latin. Also categorized as a Glyphic, the design was first introduced in the last half of the nineteenth century and is characterized by large, sharp, triangular serifs. Latins were very popular for posters and as a newspaper headline font. Fortis is a Latin with attitude. It is bouncy and much more animated than its predecessors. As a display font, it brings motion and playful personality to a design. Great for party invitations, packaging, headlines, and children's books! - Glaser Stencil by Linotype,
$40.99The renowned American illustrator and graphic designer Milton Glaser designed Glaser Stencil in 1970. Glaser Stencil is a perfect summation of both Modernist proportion and New York-style solidity and self-assurance. An all capitals font, the shapes of the letters are reminiscent of popular sans serif faces of the time, such as Futura and ITC Avant Garde Gothic. Like everything New York-related, Glaser Stencil should be used big, in headlines and display applications, where it can play a bold, proud, and confident role. - Finalist Round Slab Variable by Bülent Yüksel,
$79.00The font was intended primarily to have a stronger body. It has a simple geometrical surface. This font has a strong personality, that makes it perfect for use in headline sizes but means it also works gracefully within text blocks. Finalists Round Slab is carefully crafted and a unique slab serif. Use for websites, print, motion graphics, logo design, packaging design, t-shirts and more. **UPDATES:** -16 Agust 2021: New version 2.0 Variable Font -28 January 2022: Some bug fixes You can enjoy using it. - Coochie Nando NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00Among the many display faces Milton Glaser designed during the heyday of Push Pins Studios was the pattern for this dramatically shadowed face, whose original name—for reasons unexplained—was "Kitchen." Well, whatever the reason, it's definitely "what's cooking," so the Italian word for the latter half of that phrase gives this typeface its name. Equally at home being kookie or spookie. Both versions include the complete Unicode Latin 1252, Central European 1250 and Turkish 1254 character sets, with localization for Moldovan and Romanian. - Gill Floriated Capitals by Monotype,
$29.99Gill Floriated is based on a single character which Eric Gill drew as a decorated initial for use on a specimen setting of his Perpetua type. Although Gill was at first reluctant to produce a full alphabet, Monotype advisor Stanley Morison was able to persuade him to draw a few more characters from which the Type Drawing Office was able to create a full set. Issued in 1937 for display casting, it was revived by Monotype in 1995 for electronic publishing. Best used sparingly as dropped initials. - Sovba by insigne,
$-Sovba is an amiable rounded sans-serif inspired by handwriting. Sovba is useful for a look that is uniquely casual, fresh and smooth. Sovba simplifies character forms down to their basic characteristics, and has a strong, silky smooth forward motion. Sovba includes more traditional optional alternates for a number of characters, including the ëEí and ëF,í OpenType alternate characters, old style figures and small caps. Sovba is a fine choice when you require a versatile upright oblique for logotypes, headlines or short blocks of text. - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer."