5,892 search results
(0.038 seconds)
- Radhen Retro by Letterfreshstudio,
$20.00Radhen Retro Font is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular/Extrude/ Thankyou - Sonya Script by Letterfreshstudio,
$15.00Sonya Retro Font is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular/Extrude/Outline Thankyou - Mackless Script by Sibelumpagi,
$12.00Mackless is a clean script font inspired by hand-lettering, bold script, brush script, and logotype. It comes with an extra extruded font for a good combination on your design need, and includes OpenType features with PUA encoded such as alternates and ligatures. Mackless would be good for branding, logotype, poster, badge, book cover, invitation, t-shirt design, packaging and many more. - Pradis Retro by Letterfreshstudio,
$16.00Pradis Retro Font is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular/Extrude/ Thankyou - Bigland Retro by Letterfreshstudio,
$21.00Vintage Retro - Bigland is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular/Extrude/ Thankyou - Brudy Retro by Letterfreshstudio,
$20.00Vintage Retro - Brudy is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular/Extrude/ Thankyou - La Vintage Script by Letterfreshstudio,
$20.00La Vintage Font is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular Thankyou - Spring Magic by Letterfreshstudio,
$19.00Spring Magic Font is an urban retro font with the style like a logotype lettering. was created to help you designing logotype or lettering style for your Brand or your clients. it has an extensive lingual support, covering European and Asian Latin scripts. The font contains all characters you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. Multilingual Support Alternates, Regular/Extrude/ Thankyou - Alea Weiqsaw by Sitintahitam,
$25.00Alea Weiqsaw inspired from victorian era, art neuveau, psychedelic art and music. This font comes with unique trippy style, it will be interesting to make a headlines, packaging design and vintage style logotype like a cover album, sign logotype, vintage headline. Alea Weiqsaw also bring some alternative glyph and unique ornament. This combination allows you to easily develop awesome designs. - Eknaton by T4 Foundry,
$21.00The powerful Eknaton comes with slanted slabserifs, a new way to add some spring to the old Egyptian slabs. Eknaton echoes the tradition that started with Napoleon's Egyptian campaign 1798, and the simultaneous looting of Egyptian art. The imports led to new ladies fashion in Europe, new architecture and new typefaces like Antique (Figgins, 1815) and Egyptian (Caslon, 1816). The Egyptian faces were also the origin of the famous Clarendon (1845) and Ionic No.5 (1925) as well as the rest of "the legibility types". In the 20th century the slabserifs became popular again with Bauhaus incarnations like Memphis (Wolf, 1929) and Beton (Jost, 1931). The Bauhaus movement, otherwise anti-serif, liked the architectural influence in Egyptian slabserifs. The Bo Berndal design of Eknaton puts some speed into the old Sphinx - the cat is back, in better form than ever! Bo Berndal, born 1924, has been designing typefaces for 56 years, for Monotype, Linotype and other foundries. Eknaton comes in five different widths, from Tight to Expanded, and is an OpenType typeface for both PC and Mac. Swedish type foundry T4 premiere new fonts every month. Eknaton is our eleventh introduction. - Sabon Next by Linotype,
$57.99The design of Sabon® Next by Jean François Porchez, a revival of a revival, was a double challenge: to try to discern Jan Tschichold´s own schema for the original Sabon, and to interpret the complexity of a design originally made in two versions for different typecasting systems. The first was designed for use on Linotype and Monotype machines, and the second for Stempel hand composition. Because the Stempel version does not have the constraints necessary for types intended for machine composition, it seems closer to a pure interpretation of its Garamond ancestor. Naturally Porchez based Sabon Next on this second version and also referred to original Garamond models, carefully improving the proportions of the existing digital Sabon while matching its alignments. The new family is large and versatile - with Roman and italic in 6 weights from regular to black. Most weights also have small caps, Old style Figures, alternates (swashes, ligatures, etc); and there is one ornament font with many lovely fleurons. The standard versions include revised lining figures that are intentionally designed to be a little smaller than capitals. Featured in: Best Fonts for Resumes, Best Fonts for Websites, Best Fonts for PowerPoints - Yuli by Hanoded,
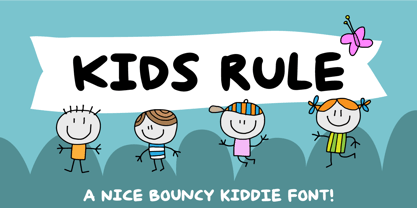
$15.00Yuli is my daughter - she was born on February 13th, 2014. I named this font after her, because there are some similarities. Both are bouncy and happy, playful and quirky, funny and happy - and above all: cute and cuddly. Yuli font was loosely based on Bodoni and Spumoni - two typefaces I like a lot. Yuli speaks a lot of languages. - Kids Rule by PizzaDude.dk,
$13.00Sometimes you need a lot of text, and that text needs a little bit extra something. Something sweet for the eye, but still legible and not too funky. Maybe that's where Kids Rule comes in. It's a bouncy, but super-legible handmade comic font. It has a lot of attitude, and I have added 5 different versions of each letter! - Astrology by Monotype,
$40.99Astrology signs that had been designed for newspaper and printers purposed in the hotmetal aera from the Monotype caster. - Curvesta by wearecolt,
$18.00 - Londrina Serif by Tipos Pereira,
$10.00 - Water Brush by TypeSETit,
$24.95 - Savourer by Cititype,
$12.00 - As of my last update in April 2023, I cannot offer a detailed description of a font named "abc" specifically by Fenotype, as it might not exist or hasn't been widely recognized yet in available font ...
- Really No 2 W2G by Linotype,
$124.99Really No. 2 is a redesign and update of Linotype Really, a typeface that Gary Munch first designed in 1999. The new Really No. 2 offers seven weights (Light to Extra Bold), each with an Italic companion. Additionally, Really No. 2 offers significantly expanded language support possibilities. Customers may choose the Really No. 2 W1G fonts, which support a character set that will cover Greek and Cyrillic in addition to virtually all European languages. These are true pan-European fonts, capable of setting texts that will travel between Ireland and Russia, and from Norway to Turkey. Customers who do not require this level of language support may choose from the Really No. 2 Pro fonts (just the Latin script), the Really No. 2 Greek Pro fonts (which include both Latin and Greek), or the Really No. 2 Cyrillic Pro fonts (Latin and Cyrillic). Each weight in the Really No. 2 family includes small capitals and optional oldstyle figures, as well as several other OpenType features. Really No. 2's vertical measurements are slightly different than the old Linotype Really's; customers should not mix fonts from the two families together. As to the design of Really No. 2's letters, like Linotype Really, the characters' moderate-to-strong contrast of its strokes recalls the Transitional and Modern styles of Baskerville and Bodoni. A subtly oblique axis recalls the old-style faces of Caslon. Finally, sturdy serifs complete the typeface's realist sensibility: a clear, readable, no-nonsense text face, whose clean details offer the designer a high-impact selection. - Really No 2 Paneuropean by Linotype,
$103.99Really No. 2 is a redesign and update of Linotype Really, a typeface that Gary Munch first designed in 1999. The new Really No. 2 offers seven weights (Light to Extra Bold), each with an Italic companion. Additionally, Really No. 2 offers significantly expanded language support possibilities. Customers may choose the Really No. 2 W1G fonts, which support a character set that will cover Greek and Cyrillic in addition to virtually all European languages. These are true pan-European fonts, capable of setting texts that will travel between Ireland and Russia, and from Norway to Turkey. Customers who do not require this level of language support may choose from the Really No. 2 Pro fonts (just the Latin script), the Really No. 2 Greek Pro fonts (which include both Latin and Greek), or the Really No. 2 Cyrillic Pro fonts (Latin and Cyrillic). Each weight in the Really No. 2 family includes small capitals and optional oldstyle figures, as well as several other OpenType features. Really No. 2's vertical measurements are slightly different than the old Linotype Really's; customers should not mix fonts from the two families together. As to the design of Really No. 2's letters, like Linotype Really, the characters' moderate-to-strong contrast of its strokes recalls the Transitional and Modern styles of Baskerville and Bodoni. A subtly oblique axis recalls the old-style faces of Caslon. Finally, sturdy serifs complete the typeface's realist sensibility: a clear, readable, no-nonsense text face, whose clean details offer the designer a high-impact selection. - Lomo by Linotype,
$29.99Lomo, PLC is a Russian optical manufacturer, whose cameras have built up an international cult following since 1992. Swiss designer Fidel Peugeot recently tapped into this phenomenon, creating an astounding series of pixel fonts for use in a variety of applications-from websites to mobile phone displays. Now available as a single family from Linotype, Lomo's versatility extends itself across 37 various faces. Whether on screen or online, Lomo's different weights deliver great legibility at low resolutions. Additionally, the amazing breadth of this family allows these pixilated faces to crossover into print, bringing a contemporary technology feeling to your more traditional pieces, too. Worth experimenting with is the Lomo Wall series, of which 14 of the Lomo family's 37 fonts belong to. In graphics applications like Adobe's PhotoShop of Illustrator, the Lomo Wall fonts may be layered over top of one another in various combinations. For example, Lomo Wall Chart 50 could be colored red, and layered behind Lomo Wall Pixel 50. The text in Lomo Wall Pixel 50 would then looked like it had been painted over top of a brick wall. With 14 fonts, and millions of colors in your application's color palette to choose from, the combination possibilities for this layering technique are endless! (If you really like this layering feature, check out what Karin Huschka, another Linotype designer, did with her Chineze Dragon family.) Convinced? Give the unlimited possibilities of Lomo a spin today! The entire Lomo family is part of the Take Type 5 collection, from Linotype." - Really No 2 by Linotype,
$29.99Really No. 2 is a redesign and update of Linotype Really, a typeface that Gary Munch first designed in 1999. The new Really No. 2 offers seven weights (Light to Extra Bold), each with an Italic companion. Additionally, Really No. 2 offers significantly expanded language support possibilities. Customers may choose the Really No. 2 W1G fonts, which support a character set that will cover Greek and Cyrillic in addition to virtually all European languages. These are true pan-European fonts, capable of setting texts that will travel between Ireland and Russia, and from Norway to Turkey. Customers who do not require this level of language support may choose from the Really No. 2 Pro fonts (just the Latin script), the Really No. 2 Greek Pro fonts (which include both Latin and Greek), or the Really No. 2 Cyrillic Pro fonts (Latin and Cyrillic). Each weight in the Really No. 2 family includes small capitals and optional oldstyle figures, as well as several other OpenType features. Really No. 2's vertical measurements are slightly different than the old Linotype Really's; customers should not mix fonts from the two families together. As to the design of Really No. 2's letters, like Linotype Really, the characters' moderate-to-strong contrast of its strokes recalls the Transitional and Modern styles of Baskerville and Bodoni. A subtly oblique axis recalls the old-style faces of Caslon. Finally, sturdy serifs complete the typeface's realist sensibility: a clear, readable, no-nonsense text face, whose clean details offer the designer a high-impact selection. - Bordemile by Letterhend,
$18.00 - Tasci Serif by Abdullah Tasci,
$30.00TASCI SERIF typeface has been derived from TASCI typeface, it is especially designed to use for logotype and display designs. - Late Frost by Gleb Guralnyk,
$13.00 - Roka by Thinkdust,
$10.00 - Frivolous by Typadelic,
$19.00The informal style of Frivolous feature lots of flourishes and swirls that give it a charming and spontaneous handwritten quality. - Chesta by RahagitaType,
$14.00 - Meyer Two by Font Bureau,
$40.00Meyer Two captures the early Hollywood flavor and nostalgia of silent-film intertitles. From 1922 through 1928, Mergenthaler Linotype cut five fonts to Louis B. Meyer’s personal specifications. Meyer Two, drawn in 1926, curiously combines Cleland’s ATF Della Robbia capitals of 1902 with lowercase and figures from ATF Post Monotone No. 2, also from the same period. Meyer Two was revived, with a Condensed added, by David Berlow; FB 1994 - Din Condensed by ParaType,
$30.00Designed at ParaType (ParaGraph) in 1997 by Tagir Safayev. Based on a condensed style of DIN type family (Linotype Staff designers). That is a group of sans serif faces made to conform to the German Industrial Standard. Based on geometric style, they vary in width but not in weight. Light style was added in 2014 by Manvel Schmavonyan. Demi Bold style was added in 2020 by Isabella Chaeva. - Gavotte by Linotype,
$29.99Linotype Gavotte was designed by Rudo Spemann in 1940. His style was unmistakable, marked by original ideas and completely new forms. His tendency toward the unusual and adventurous resulted in unique, decorative characters. When he wrote, the tip of his pen flew across the page, leaving behind rows of letters which displayed an almost unbelievable regularity of form and flow. Gavotte is a perfect example of the best of Spemann’s calligraphy. - Rundfunk Antiqua by Linotype,
$29.99Rundfunk-Antiqua was originally designed as a font for small point size and shorter texts. It was presented 1933/35 by Linotype Designstudio but unfortunately never developed as a font family, including only Antiqua roman and sans-serif bold. Such an unusual combination resulted from the font combinations common during that time. The font’s basic forms tend toward the Transitional style but its details come from the influence of Jugendstil. - Macbeth by Linotype,
$29.99Macbeth is a heavy, condensed Art Deco-style typeface from Linotype. Macbeth includes some particularly noteworthy diagonal elements -- these enliven the design and give typeface its overall character. Macbeth should be used for music-oriented applications, or anything that is both reminiscent of the early 20th Century and a bit spooky. The letters in Macbeth are quite similar to display style found on Frankenstein posters, and those of other early films. - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer."