10,000 search results
(0.061 seconds)
- Quat by Ani Dimitrova,
$29.00Quat is a sans serif type family designed by Ani Dimitrova. The family comes in 22 weights, ranging from Hairline to Black with extra drawn italics and small caps versions, and each style contains more than 700 glyphs. The Regular and Medium weights are perfect for body text while the extra drawn Italic gives an interesting texture to the text. The lightest weights work well in subtle headlines while the heaviest ones are perfect for posters, short texts, web, branding and screen design. All weights contain ligatures, proportional figures, tabular figures, old style figure, numerals and arrows, matching currency symbols and fraction. The range of styles give a good flexibility to this family. - Robertson by BA Graphics,
$45.00A great overall Text and Headline face, with its matching drawn Italic it has unlimited possibilites. Even as a stand alone, the Italic will work in just about any design. - Basic Stencil JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00 - FF Engine by FontFont,
$47.99Dutch type designer Alex Scholing created this display and sans FontFont in 1995. The family has 6 weights, ranging from Light to Bold (including italics) and is ideally suited for book text, editorial and publishing as well as software and gaming. FF Engine provides advanced typographical support with features such as small capitals, alternate characters, case-sensitive forms, fractions, super- and subscript characters, and stylistic alternates. It comes with a complete range of figure set options – oldstyle and lining figures, each in tabular and proportional widths. - Bad Rascal by Mans Greback,
$69.00Bad Rascal is a script typeface. This flowing brush font in a fat style gives any project the attention it deserves. Use it for a bold logotype or headline to give your work that extra-bold look. Use underscore _ to make a swash underline. Example: Powers_ Use multiple underscores to make a swashes of different lengths. Example: Baddest_______ (Download required.) The Bad Rascal family consists of the fonts Regular and Italic. The font is built with advanced OpenType functionality and has a guaranteed top-notch quality, containing stylistic and contextual alternates, ligatures and more features; all to give you full control and customizability. It has extensive lingual support, covering all Latin-based languages, from Northern Europe to South Africa, from America to South-East Asia. It contains all characters and symbols you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers. - Dekomia by Keristyper Studio,
$14.00Dekomia is a modern blackletter font that combines the traditional style of Gothic calligraphy with contemporary design elements. Its bold and sharp letterforms give it a strong and edgy appearance, making it perfect for branding, headlines, logos, and more. Featured: Standard Uppercase & Lowercase Numeral & Punctuation Multilingual : ä ö ü Ä Ö Ü ß ¿ ¡ Alternate & Ligature PUA encoded We recommend programs that support the Open Type feature and the Glyphs panel such as Adobe applications or Corel Draw, so you can use all the variations of the glyphs. Hope you enjoy our fonts! - Black Metal G - Unknown license
- Fiolex Mephisto - 100% free
- Twilight - Unknown license
- Louvaine - Unknown license
- Conrad Veidt - 100% free
- Dead Letter Office - Unknown license
- Wicked Queen BB - Personal use only
- Wazoo Outline - Unknown license
- Malloy by Supfonts,
$22.00Introducing the elegant new Malloy Calligraphy Font! For those of you who are needing a touch of elegance and modernity for your designs, this font was created for you! Malloy was built with OpenType features and includes beginning and ending swashes, alternate swash characters for most lowercase letters, numbers, punctuation, alternates, ligatures and it also supports all latin languages :) What's Included Malloy TTF Malloy OTF Multilingual support all Latin languages Accessing the swashes / opentype features / glyphs: If you have opentype capable software such as Illustrator or Photoshop CC, you can access the alternate letters and ligatures via the character/opentype panel and glyphs panel. Or You can use Character Map (win) / FontBook (mac) to copy-paste required symbol into your text editor. Check out my blog: www.instagram.com/youthlettering pinterest.com/dmitriychirkov7 Thanks so much for checking out my shop! All the best, Dmitrii - Aeris by Linotype,
$29.99Aeris™ typeface is a contemporary book face created by the American designer Tom Grace. It combines the proportions and rhythm of a sans serif font with the high contrasts and flexed strokes of script faces, while the open counters also ensure optimal legibility. Tom Grace focuses on providing subtle differentiations in his cuts and, as a consequence, this font family has its own individual structure: there are A and B variants of the basic forms regular, italic, bold and bold italic, and a display version for use in titles that also comes in A and B variants. It is advisable to use the A variant for larger font sizes, while the slightly more emphasized B variant can be recommended for smaller font sizes. Where the basic forms are to be mixed together in a work, it is important to use the corresponding A/B variants throughout as their designs have been carefully coordinated. Aeris is available in the OpenType Pro format and thus includes a wide range of different glyphs. The font family can be used in various environments, such as books, magazines, advertisements and promotional materials, but it is also the perfect choice for printed corporate documentation. - Etnyca by Ahmad Jamaludin,
$17.00Presenting new our font, Etnyca Etnyca - fearless and stylish typeface perfect for headlines for print and web. It's modern, bold, and playful. Perfect if you want to add character to your project. Etnyca fits perfectly too into those nostalgic mood boards and vintage logos. It comes with Italic style, unique lower and uppercase plus numbers, punctuation & multilingual letters File Included : Unique letterforms Works on PC & Mac Simple Installations Accessible in Adobe Illustrator, Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft Word even work on Canva! PUA Encoded Characters Fully accessible without additional design software. Come and say hello over on Instagram! https://www.instagram.com/dharmas.studio/ Dharmas Studio - Cholens by Mevstory Studio,
$20.00Cholens is a bold, rounded script typeface in a modern and classy style. OpenType features include old style figures and ligatures. Cholens is ideal for headlines, headers, logos, labels, packaging, postcards, presentations, magazines, invitations, and more. Features: Basic latin alphabet A-Z Ligatures & Alternates Accented characters Numbers, Punctuation, Currency, Symbols, Math symbols & Diacritics Old style figures - Sabon by Linotype,
$45.99In the early 1960s, the German Master Printers’ Association requested that a new typeface be designed and produced in identical form on both Linotype and Monotype machines so that text and technical composition would match. Walter Cunz at Stempel responded by commissioning Jan Tschichold to design a new version of Claude Garamond’s serene and classical Roman. Its bold, and particularly its italic styles are limited by the requirements of Linotype casting machines, forcing the character widths of a given letter to match between styles, giving the italic its characteristic narrow f. The family’s name is taken from Jacques Sabon, who introduced Garamond’s Romans to Frankfurt. Sabon has long been a favorite of typographers for setting book text, due to its smooth texture, and in large part because Tschichold’s book typography remains world famous. - Pamors by Alit Design,
$18.00PAMORS typeface is a bold and daring blackletter font that exudes a sense of strength and power. The mix of regular and italic styles provides versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of design applications. With 799 characters, Pamors typeface offers extensive multilingual support and includes PUA unicode for easy access to special characters. One of the standout features of this font is its use of ligatures and swashes, which add an extra touch of elegance and sophistication to any project. Whether used in headlines, logos, or body text, Pamors typeface is sure to make a bold statement that commands attention. Language Support : Latin, Basic, Western European, Central European, South European,Vietnamese. In order to use the beautiful swashes, you need a program that supports OpenType features such as Adobe Illustrator CS, Adobe Photoshop CC, Adobe Indesign and Corel Draw. but if your software doesn’t have Glyphs panel, you can install additional swashes font files. - Luteous Maximus - Unknown license
- Lichtspiele by Typocalypse,
$29.00Cinemas from the early 20th century are called “Lichtspiele” in Germany. “Lichtspiele” transports you back to a time where neon lights and marquee letters decorated cinema façades. Of the five styles, three have two versions of italics — the left-leaning italic evokes looking up from lower-left, the right-leaning italic is as if we are looking from lower-right. Display is the basic style, while Neon is inspired by the old neon letters found outside cinemas. Try placing Neon Outline on top of Display or Neon to add another layer to your artwork. Neon 3D is a extruded version of Neon. The Screen Credits style is based on the notes — producers, cast, crew and so on — on movie posters. Get more out of life, go out to a movie. - Mariage by Linotype,
$40.99Morris Fuller Benton, the principal designer of the American Type Founders, designed Mariage in 1901. Mariage, which has been sold under a plethora of different names during the last century, is a blackletter typeface belonging to the Old English category. The term blackletter refers to typefaces that stem out of the historical printing traditions of northern Europe. These letters, called gebrochene Schriften, or "broken type" in German, are normally elaborately bent and distorted. Their forms often print large amounts of ink upon the page, creating text that leaves a heavy, black impression. The Old English style is a subset of blackletter type that dates back to 1498, when Wynken de Worde introduced textura style printing to England. Continental printers had been printing with textura style letters since Gutenberg's invention of the printing press fifty years earlier. Italian printers stopped using them around 1470. For northern Europeans, texturas remained the most popular form of typeface design until the invention of the fraktur style in Nuremberg. Mariage is heavily classicized sort of Old English type. During the Victorian era, designers admired the Middle Ages for its chivalric, community-based values and its pre-industrial lifestyle. Yet they also found the basic medieval textura letterform too difficult to read by present standards. They desired to modernize this old style. Today, this sort of update is often referred to not as "modernization" but as classicism. Benton's design for ATF builds upon earlier Victorian classicist interpretations of Old English/textura letters. For an example of what these Victorian designs looked like, check out the popular 1990 revival of the genre, Old English . Old English style types often appear drastically different from other blackletters. For contrast, compare Mariage to a classical German fraktur design, Fette Fraktur , a schwabacher style face, or the popular early 20th Century calligraphic gothic from Linotype, Wilhelm Klingspor Gotisch . Especially in the United States, classicist Old English typefaces are thought to espouse tradition and journalistic integrity. These features, together with the inherent, complex beauty of Mariage's forms, make this typeface a perfect choice for certificates, awards, and newsletter mastheads. - Bodrum Style by Bülent Yüksel,
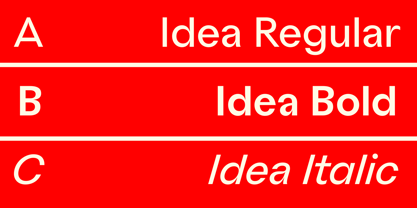
$19.00"Bodrum Style" is a serif Style family designed by Bülent Yüksel in 20018/19. The font, influenced by serif styles that were popular in the 1920s and 30s, is based on optically corrected geometric forms for a better readability. "Bodrum Style" is not purely geometric; it has vertical strokes that are thicker than the horizontals, an “o” that is not a perfect circle, and shortened ascenders. These nuances help the legibility and give "Bodrum Style" an harmonious and sensible appearance for both texts and headlines. Bodrum Style provides advanced typographical support for Latin-based languages. An extended character set - supporting Central, Western and Eastern European language - rounds up the family. “Bodrum Style 14 Regular” forms the central point. "Bodrum Style" is available in 10 weights (Hair, Thin, Extra-Light, Light, Regular, Medium, Bold, Extra-Bold, Heavy and Black) and 10 matching italics. The family contains a set of 650+ characters. Case-Sensitive Forms, Classes and Features, Small Caps from Letter Cases, Fractions, Superior, Inferior, Denominator, Numerator, Old Style Figures just one touch easy In all graphic programs. Bodrum Style is the perfect font for web use. Enjoy using it. - ABC Idea by Alphabets by Chileans (A.B.C.),
$18.00ABC Idea is a contemporary geometric sans full of opentype features in Regular, Bold and very "fast" Italic. The design is an experimental fusion or mix between Humanist, Geometric and Grotesque models. The fine drawing in all letters and signs has precise ink traps to highlight contrast jus like lettering and calligraphy does, then ABC Idea re-creates this exquisite graphic details into the digital world. Designed by Miguel H. Montoya Fonts in Use Images by letargo.cl Magazine. Art Direction by studioprado.cl - Hockeynight Sans by XTOPH,
$20.00Hockeynight Sans with its round corners is the smoothest sports-font you will find. Its the helvetica under the college fonts. Spice it up and mix some of the alternative glyphs in! Hockeynight comes in 7 Weights and each one available as an Italic. Use it big and bold on your sports-poster, space it up to get that dirty look or use some alternate glyphs for your logodesign. Look out for the Brush Versions and the Slab Version of Hockeynight - Bloery by Runsell Type,
$20.00Bloery is a neo grotesque font modified with extended proportion. Comes with a modern look, this font suitable for display and body text. Bloery is a good choice for editorial design, branding, app design and web design. Comes with 7 weights from Thin to Bold with each matching Italic. Contain several OpenType features: Stylistic Alternates and Figures Variation (fraction, tabular lining, numerator, denominator). Each style includes 540+ glyphs supporting all western, eastern and central european languages (over 200 languages supported). - Cleargothic Pro by SoftMaker,
$15.99Morris Fuller Benton designed the serifed Clearface typeface for ATF in 1907. He liked the design so much that he also created a flare-serif variation, Clearface Gothic, soon after. It is a great typeface for headlines. SoftMaker created an updated version, Cleargothic Pro, in 2012. SoftMaker’s Cleargothic Pro typeface family contains OpenType layout tables for sophisticated typography. It also comes with a huge character set that covers not only Western European languages, but also includes Central European, Baltic, Croatian, Slovene, Romanian, and Turkish characters. Case-sensitive punctuation signs for all-caps titles are included as well as many fractions, an extensive set of ligatures, and separate sets of tabular and proportional digits. - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Brotherland by Dikas Studio,
$12.00 - Kwaliteit by Fabulous Rice,
$20.00Kwaliteit is the result of a love story. The love story between a font designer and an old embossing label machine. The big bold letters produced by such machines are wonderful to convey a big bold message (big bold messages are fun!), but sometimes you just can't walk around with one of those antique label machines… That's why this font can come in handy! Its uses are numerous… be the boss of emboss! - Beckinslade by Greater Albion Typefounders,
$15.95Beckinslade is a lovely elaborate blackletter face, released just in time for Christmas, but useable at any time of the year. It is in the best traditions of Victorian Gothic revival, drawing inspiration from a range of sources and marrying them into one homogenous whole. The emphasis is on aesthetics rather than historical accuracy. Great fun though for anywhere ‘ye olde’ look is desired. - K-Block by HiH,
$10.00K-Block was inspired by a hand-lettered sign by a young lady by the name of Kristina Lee. It captures a light-hearted, youthful feeling and is not intended to be taken too seriously. It was drawn for fun and is fun to use. Its very inconsistency insists on being casual and relaxed. Probably better for a birthday party announcement than a bank letterhead. Can you imagine a Just-For-Fun National Bank? K-Block Solid compliments K-Block and provides a stronger presence when required. For two-color work, K-Block can be layered on top of K-Block Solid to provide a different color outline for a very effective presentation. Full Western European character set plus alternate g and y, as well as a Th ligature. If you have a drawing program like Corel Draw, you can easily convert the alternate g and y to curves and stretch out the tails to underline an entire word. The zip package of each font includes two versions. There is an OTF version which is in Open PS (Post Script Type 1) format and a TTF version which is in Open TT (True Type)format. Use whichever works best for your applications. K-Block and K-Block Solid are sold separately. - Dime Museum by Solotype,
$19.95This idea of "wrong way weights" was originally called French Clarendon by the Americans, Italienne by the French, and American by the Italians. Sounds like nobody wanted to own up to it. When it was revived by ATF in 1933, it was given the name P. T. Barnum. Many variations have appeared. Dime Museum is an old wood type.