724 search results
(0.218 seconds)
- Hello My Love Pro by Debi Sementelli Type Foundry,
$39.00“Hello My Love” is a font love story. Inspired by my own long and happy marriage of 35 years, it was created to celebrate love! A classic hand-lettered script with a modern and fresh feel, it fits beautifully with current designs and yet is sure to stand the test of time. Made with invitation designers in mind, the Hello My Love Pro script font includes a total of 1985 glyphs plus a BONUS FONT, Hello My Love Ornaments! It has 91 hand illustrations including frames, florals and design elements. As a result, you will be able to create a variety of designs to highlight your special project. It’s especially well-suited for invitations for branding weddings and other special occasions! And it supports 129 languages! The font is loaded with features: Stylistic and Contextual Alternates, Swash Caps, Standard and Discretionary Ligatures, Beginning Swashes for lower case letters, Cross-less t and f that can be combined with a flourished letter to avoid clashing plus 3 ampersands, small word art "and" & "No.", Roman Numerals, Ordinals and Fractions. This font was created to make designing easy. Need to convert upper case letters into Roman numerals throughout a guest list? Just turn on contextual alternates in Open Type capable programs and presto, the caps become Roman! Want a variety of letter choices? There are 215 stylistic alternate upper cases and 259 stylistic alternate lower cases as well as 69 ligatures to give you plenty of options. You can choose from swashes in 4 different styles and 3 different lengths resulting in unique beginning lower case letters. Works for Cutting Machines! No special software is required to use Hello My Love. All of my fonts have been specially coded for PUA (Private Use Area) so you can access all of the swashes and alternates using Character Map (PC) or Character Viewer (Mac) or with any number of apps including PopChar. If you would like to purchase PopChar at a special discount email me and I will send you the link. For Microsoft Word users, you can easily access the Stylistic and Contextual Alternates and the Roman Numerals through the Typography feature. (Microsoft Word 2010 and later) For more details about how to use my fonts, check out my video tutorials on my YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/Letteringartstudio/videos - An Electronic Display LED LCD LED7 Seg dots 2 by Fortune Fonts Ltd.,
$15.00* For when you need the most realistic looking electronic display. * See User Manuals Main advantages: - Spacing between characters does not change when entering a decimal point or colon between them. - Custom characters can be produced by selecting any combination of segments to be displayed. Low cost electronic displays have a fixed number of segments that can be turned on or off to represent different symbols. A digital watch would be the most common example. Fonts typically available for depicting electronic displays are often in the artistic style of these common LED or LCD displays. They provide the look-and-feel, but fall short when technical accuracy is required. Failure to represent an accurate and consistent representation of the real thing can be a cringe-worthy experience for the product design and marketing team, or even the hobbyist for that matter. To solve this problem, Fortune Fonts has released a range of fonts that accurately depict the displays typically found on low cost electronic devices: watches, answering machines, car stereos, alarm clocks, microwaves and toys. These fonts come with numbers, letters and symbols predefined. However, they also allow you to create your own segment combinations for the custom symbols you need. When producing manuals, marketing material and user interfaces, accuracy is an all-or-nothing concept. Instructions in the user manual describe how to turn these fonts into realistic displays according to your own design, in the manner of the images above. If you cannot see a license option for your specific application, such a license may be purchased from here. By purchasing &/or using &/or distributing the fonts the buyer user and distributor (including Monotype Imaging Inc. & Monotype Imaging Hong Kong) agree to (1) indemnify & hold harmless the foundry, for any consequential, incidental, punitive or other damages of any kind resulting from the use of the deliverables including, but not limited to, loss of revenues, profits, goodwill, savings, due to; including, but not limited to, failure of the deliverables to perform it’s described function, or the deliverable’s infringement of patents, copyrights, trademarks, design rights, contract claims, trade secrets, or other proprietary rights of the foundry, distributor, buyer or other parties (2) not use the fonts to assist in design of, or be incorporated into, non-software displays - An Electronic Display LED LCD LED7 Seg dots1 by Fortune Fonts Ltd.,
$15.00* For when you need the most realistic looking electronic display. * See User Manuals Main advantages: - Spacing between characters does not change when entering a decimal point or colon between them. - Custom characters can be produced by selecting any combination of segments to be displayed. Low cost electronic displays have a fixed number of segments that can be turned on or off to represent different symbols. A digital watch would be the most common example. Fonts typically available for depicting electronic displays are often in the artistic style of these common LED or LCD displays. They provide the look-and-feel, but fall short when technical accuracy is required. Failure to represent an accurate and consistent representation of the real thing can be a cringe-worthy experience for the product design and marketing team, or even the hobbyist for that matter. To solve this problem, Fortune Fonts has released a range of fonts that accurately depict the displays typically found on low cost electronic devices: watches, answering machines, car stereos, alarm clocks, microwaves and toys. These fonts come with numbers, letters and symbols predefined. However, they also allow you to create your own segment combinations for the custom symbols you need. When producing manuals, marketing material and user interfaces, accuracy is an all-or-nothing concept. Instructions in the user manual describe how to turn these fonts into realistic displays according to your own design, in the manner of the images above. If you cannot see a license option for your specific application, such a license may be purchased from here. By purchasing &/or using &/or distributing the fonts the buyer user and distributor (including Monotype Imaging Inc. & Monotype Imaging Hong Kong) agree to (1) indemnify & hold harmless the foundry, for any consequential, incidental, punitive or other damages of any kind resulting from the use of the deliverables including, but not limited to, loss of revenues, profits, goodwill, savings, due to; including, but not limited to, failure of the deliverables to perform it’s described function, or the deliverable’s infringement of patents, copyrights, trademarks, design rights, contract claims, trade secrets, or other proprietary rights of the foundry, distributor, buyer or other parties (2) not use the fonts to assist in design of, or be incorporated into, non-software displays. - An Electronic Display LED LCD LED14 Seg 1 by Fortune Fonts Ltd.,
$15.00* For when you need the most realistic looking electronic display. * See User Manuals Main advantages: - Spacing between characters does not change when entering a decimal point or colon between them. - Custom characters can be produced by selecting any combination of segments to be displayed. Low cost electronic displays have a fixed number of segments that can be turned on or off to represent different symbols. A digital watch would be the most common example. Fonts typically available for depicting electronic displays are often in the artistic style of these common LED or LCD displays. They provide the look-and-feel, but fall short when technical accuracy is required. Failure to represent an accurate and consistent representation of the real thing can be a cringe-worthy experience for the product design and marketing team, or even the hobbyist for that matter. To solve this problem, Fortune Fonts has released a range of fonts that accurately depict the displays typically found on low cost electronic devices: watches, answering machines, car stereos, alarm clocks, microwaves and toys. These fonts come with numbers, letters and symbols predefined. However, they also allow you to create your own segment combinations for the custom symbols you need. When producing manuals, marketing material and user interfaces, accuracy is an all-or-nothing concept. Instructions in the user manual describe how to turn these fonts into realistic displays according to your own design, in the manner of the images above. If you cannot see a license option for your specific application, such a license may be purchased from here. By purchasing &/or using &/or distributing the fonts the buyer user and distributor (including Monotype Imaging Inc. & Monotype Imaging Hong Kong) agree to (1) indemnify & hold harmless the foundry, for any consequential, incidental, punitive or other damages of any kind resulting from the use of the deliverables including, but not limited to, loss of revenues, profits, goodwill, savings, due to; including, but not limited to, failure of the deliverables to perform it’s described function, or the deliverable’s infringement of patents, copyrights, trademarks, design rights, contract claims, trade secrets, or other proprietary rights of the foundry, distributor, buyer or other parties (2) not use the fonts to assist in design of, or be incorporated into, non-software displays - AF LED7Seg 1 by Fortune Fonts Ltd.,
$15.00* For when you need the most realistic looking electronic display. * See User Manuals Main advantages: - Spacing between characters does not change when entering a decimal point or colon between them. - Custom characters can be produced by selecting any combination of segments to be displayed. Low cost electronic displays have a fixed number of segments that can be turned on or off to represent different symbols. A digital watch would be the most common example. Fonts typically available for depicting electronic displays are often in the artistic style of these common LED or LCD displays. They provide the look-and-feel, but fall short when technical accuracy is required. Failure to represent an accurate and consistent representation of the real thing can be a cringe-worthy experience for the product design and marketing team, or even the hobbyist for that matter. To solve this problem, Fortune Fonts has released a range of fonts that accurately depict the displays typically found on low cost electronic devices: watches, answering machines, car stereos, alarm clocks, microwaves and toys. These fonts come with numbers, letters and symbols predefined. However, they also allow you to create your own segment combinations for the custom symbols you need. When producing manuals, marketing material and user interfaces, accuracy is an all-or-nothing concept. Instructions in the user manual describe how to turn these fonts into realistic displays according to your own design, in the manner of the images above. If you cannot see a license option for your specific application, such a license may be purchased from here. By purchasing and/or using and/or distributing the font, the buyer, user and distributor (including Monotype Imaging Inc. & Monotype Imaging Hong Kong) agrees to (1) indemnify and hold harmless the font foundry and neither the font foundry nor distributor is responsible to the buyer or user or any other party for any consequential, incidental, special, punitive or other damages of any kind resulting from the use of the deliverables including, but not limited to, loss of revenues, profits, goodwill, savings or expected savings, due to; including, but not limited to, failure of the deliverables to perform it’s described function, or the deliverable’s infringement of patents, copyrights, trademarks, design rights, contract claims, trade secrets, or other proprietary rights of the foundry, distributor, buyer or other parties, (2) not use the fonts to assist in design of, or be incorporated into, non-software displays. - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Typewriter 1950 Tech Mono by TypoGraphicDesign,
$29.00The typeface Typewriter 1950 Tech Mono is designed for the Typo Graphic Design font foundry in 2017 by Manuel Viergutz. A display slab serif type for headlines. Based on an old typewriter machine from 1950. Plus state-of-the-art OpenType-features like contextual alternates (calt), decorative ligatures e. g. type the word “LOVE” for ❤ and the word “SMILE” for ☺ and Versal Eszett (German Capital Sharp S). For use in magazines, posters, headlines and advertisement, plus as webfont for decorative headlines. Character Set: Latin Extended (Adobe Latin 3). 1490 glyphs with 5× A–Z, 5× a–z, 5× 0–9 and 290+ extra icons like arrows, dingbats, symbols, geomatric shapes, catchwords and many alternative letters. Have fun with this font & use the DEMO-FONT (with reduced glyph-set) FOR FREE! How To Use – OpenType-Features ■ In Adobe Photoshop and Adobe InDesign, font feature controls are within the Character panel sub-menu → OpenType → Discretionary Ligatures … Checked features are applied/on. Unchecked features are off. ■ In Adobe Illustrator, font feature controls are within the OpenType panel. Icons at the bottom of the panel are button controls. Darker ‘pressed’ buttons are applied/on. ■ Additionally in Adobe InDesign and Adobe Illustrator, alternate glyphs can manually be inserted into a text frame by using the glyphs panel. The panel can be opened by selecting Window from the menu bar → Type → Glyphs. Or use sign-overview of your operating system. ■ For a overview of OpenType-Feature compatibility for common applications, follow the myfonts-help http://www.myfonts.com/help/#looks-different ■ Font Name: Typewriter 1950 Tech Mono ■ Font Weights: Regular + Negative + Black + Mono + Icons + DEMO (with reduced glyph-set) ■ Font Category: Slab Serif Display for Headline Size ■ Font Format:.otf (OpenType Font for Mac + Win) + .ttf (TrueType Font) ■ Glyph Set: 1490 glyphs ■ Language Support: 28+ for Latin Extended (Adobe Latin 3). Afrikaans, Albanian, Catalan, Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Hungarian, Icelandic, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Norwegian, Polish, Portugese, Romanian, Slovak, Slovenian, Spanisch, Swedish, Turkish, Zulu ■ Specials: 290+ decorative extras like icons for arrows, dingbats, emojis, symbols, geometric shapes, catchwords + German Capital Eszett. ■ Open Type Features: Kerning (kern), Stylistic Set 1 (ss01) … Stylistic Set 6 (ss06), Ornaments (ornm), Titling (titl), Localized Forms (locl), Subscript (subs) Superscript (sups), Ordinals (ordn), Oldstyle Figures (onum), Lining Figures (lnum), Fractions (frac), Denominators (dnom), Numerators (numr), Standard Ligatures (liga), Contextual Alternates (calt) e. g. Stylistic Set-Loop and Decorative Ligatures (dlig) e. g. type the word “LOVE” for ❤ or “SMILE” for ☺ ■ Design Date: 2017–2018 ■ Type Designer: Manuel Viergutz - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Sagittarius by Hoefler & Co.,
$51.99A typeface with lightly-worn futurism, Sagittarius is equally at home among the beauty and wellness aisles, or the coils of the warp core. The Sagittarius typeface was designed by Jonathan Hoefler in 2021. A decorative adaptation of Hoefler’s Peristyle typeface (2017), Sagittarius’s rounded corners and streamlined shapes recall the digital aesthetic of the first alphabets designed for machine reading, a style that survives as a cheeky Space Age invocation of futurism. Sagittarius was created for The Historical Dictionary of Science Fiction, where it first appeared in 2021. From the desk of the designer: Typeface designers spend a lot of time chasing down strange valences. We try to figure out what’s producing that whiff of Art Deco, or that vaguely militaristic air, or what’s making a once solemn typeface suddenly feel tongue-in-cheek. If we can identify the source of these qualities, we can cultivate them, and change the direction of the design; more often, we just extinguish them without mercy. Sometimes, we get the chance to follow a third path, which is how we arrived at Sagittarius. During the development of Peristyle, our family of compact, high-contrast sans serifs, I often found myself unwittingly humming space-age pop songs. Nothing about Peristyle’s chic and elegant letterforms suggested the deadpan romp of “The Planet Plan” by United Future Organization, let alone “Music To Watch Space Girls By” from the ill-advised (but delicious) Leonard Nimoy Presents Mr. Spock’s Music from Outer Space, but there they were. Something in the fonts was provoking an afterimage of the otherworldly, as if the typeface was sliding in and out of a parallel universe of high-tech spycraft and low-tech brawls with rubber-masked aliens. It might have had something to do with a new eyeglass prescription. But I liked the effect, and started thinking about creating an alternate, space-age version of the typeface, one with a little more funk, and a lot more fun. I wondered if softer edges, a measured dose of seventies retrofuturism, and some proper draftsmanship might produce a typeface not only suitable for sci-fi potboilers, but for more serious projects, too: why not a line of skin care products, a fitness system, a high-end digital camera, or a music festival? I put a pin in the idea, wondering if there’d ever be a project that called for equal parts sobriety and fantasy. And almost immediately, exactly such a project appeared. The Historical Dictionary of Science Fiction Jesse Sheidlower is a lexicographer, a former Editor at Large for the Oxford English Dictionary, and a longtime friend. He’s someone who takes equal pleasure in the words ‘usufructuary’ and ‘megaboss,’ and therefore a welcome collaborator for the typeface designer whose love of the Flemish baroque is matched by a fondness for alphabets made of logs. Jesse was preparing to launch The Historical Dictionary of Science Fiction, a comprehensive online resource dedicated to the terminology of the genre, whose combination of scholarship and joy was a perfect fit for the typeface I imagined. For linguists, there’d be well-researched citations to explain how the hitherto uninvented ‘force field’ and ‘warp speed’ came to enter the lexicon. For science fiction fans, there’d be definitive (and sometimes surprising) histories of the argot of Stars both Trek and Wars. And for everyone, there’d be the pleasure of discovering science fiction’s less enduring contributions, from ‘saucerman’ to ‘braintape,’ each ripe for a comeback. A moderated, crowdsourced project, the dictionary is now online and growing every day. You’ll find it dressed in three font families from H&Co: Whitney ScreenSmart for its text, Decimal for its navigational icons, and Sagittarius for its headlines — with some of the font’s more fantastical alternate characters turned on. The New Typeface Sagittarius is a typeface whose rounded corners and streamlined forms give it a romantically scientific voice. In the interest of versatility, its letterforms make only oblique references to specific technologies, helping the typeface remain open to interpretation. But for projects that need the full-throated voice of science fiction, a few sets of digital accessories are included, which designers can introduce at their own discretion. There are alternate letters with futuristic pedigrees, from the barless A popularized by Danne & Blackburn’s 1975 ‘worm’ logo for NASA, to a disconnected K recalling the 1968 RCA logo by Lippincott & Margulies. A collection of digitally-inspired symbols are included for decorative use, from the evocative MICR symbols of electronic banking, to the obligatory barcodes that forever haunt human–machine interactions. More widely applicable are the font’s arrows and manicules, and the automatic substitutions that resolve thirty-four awkward combinations of letters with streamlined ligatures. About the Name Sagittarius is one of thirteen constellations of the zodiac, and home to some of astronomy’s most inspiring discoveries. In 1977, a powerful radio signal originating in the Sagittarius constellation was considered by many to be the most compelling recorded evidence of extraterrestrial life. Thanks to an astronomer’s enthusiastically penned comment, the 72-second transmission became known as the Wow! signal, and it galvanized support for one of science’s most affecting projects, the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). More recently, Sagittarius has been identified as the location of a staggering celestial discovery: a supermassive black hole, some 44 million kilometers in diameter, in the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. < - The "Ming" typeface, designed by Keith Bates, is an evocative fusion of cultural elements and typographic innovation. This font is a homage to the Ming Dynasty, which ruled China from 1368 to 1644 an...
- Times Eighteen by Linotype,
$29.00In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Europa LT by Linotype,
$29.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten Paneuropean by Linotype,
$92.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Korataki by Typodermic,
$11.95Discover the mesmerizing power of Korataki—the ultimate contemporary font that pays tribute to the iconic ultramodern style of the 1970s classic, China/Chimes. With its simplistic yet striking industrial design, Korataki captures the essence of a bygone era while simultaneously bringing it into the modern age. The beauty of this font lies in its ability to communicate with unparalleled clarity and precision, evoking a sense of wonder and intrigue in the mind of the beholder. Whether you’re looking to make a bold statement or convey a subtle message, Korataki has got you covered. With seven distinct weights and accompanying italics, as well as OpenType alternates for A, G, Q, and 4, this font is fully customizable to suit your every need. Let Korataki guide you on a journey of creativity and self-expression. With its wide industrial design and timeless aesthetic, it’s sure to make a lasting impression on anyone who beholds it. Most Latin-based European, and some Cyrillic-based writing systems are supported, including the following languages. A Afaan Oromo, Afar, Afrikaans, Albanian, Alsatian, Aromanian, Aymara, Bashkir (Latin), Basque, Belarusian (Latin), Bemba, Bikol, Bosnian, Breton, Bulgarian, Cape Verdean, Creole, Catalan, Cebuano, Chamorro, Chavacano, Chichewa, Crimean Tatar (Latin), Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dawan, Dholuo, Dutch, English, Estonian, Faroese, Fijian, Filipino, Finnish, French, Frisian, Friulian, Gagauz (Latin), Galician, Ganda, Genoese, German, Greenlandic, Guadeloupean Creole, Haitian Creole, Hawaiian, Hiligaynon, Hungarian, Icelandic, Ilocano, Indonesian, Irish, Italian, Jamaican, Kaqchikel, Karakalpak (Latin), Kashubian, Kikongo, Kinyarwanda, Kirundi, Komi-Permyak, Kurdish (Latin), Latvian, Lithuanian, Lombard, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, Maasai, Macedonian, Makhuwa, Malay, Maltese, Māori, Moldovan, Montenegrin, Ndebele, Neapolitan, Norwegian, Novial, Occitan, Ossetian, Ossetian (Latin), Papiamento, Piedmontese, Polish, Portuguese, Quechua, Rarotongan, Romanian, Romansh, Russian, Sami, Sango, Saramaccan, Sardinian, Scottish Gaelic, Serbian, Serbian (Latin), Shona, Sicilian, Silesian, Slovak, Slovenian, Somali, Sorbian, Sotho, Spanish, Swahili, Swazi, Swedish, Tagalog, Tahitian, Tetum, Tongan, Tshiluba, Tsonga, Tswana, Tumbuka, Turkish, Turkmen (Latin), Tuvaluan, Ukrainian, Uzbek (Latin), Venetian, Vepsian, Võro, Walloon, Waray-Waray, Wayuu, Welsh, Wolof, Xhosa, Yapese, Zapotec Zulu and Zuni. - Ah, the Edo font by Vic Fieger, you say? Imagine if a brush, after a night out drinking with its inky pals, decided to take a stroll across the canvas, leaving behind a trail filled with personality,...
- Anonymous Pro - 100% free
- Classic Grotesque by Monotype,
$40.99Classic Grotesque by Rod McDonald: a traditional font with a modern face. The growing popularity of grotesque typefaces meant that many new sans serif analogues were published in the early 20th century. Setting machines were not compatible with each other but all foundries wanted to offer up-to-date fonts, and as a result numerous different typeface families appeared that seem almost identical at first glance and yet go their separate ways with regard to details. One of the first fonts created with automatic typesetting in mind was Monotype Grotesque®. Although this typeface that was designed and published by Frank Hinman Pierpont in 1926 has since been digitalised, it has never achieved the status of other grotesque fonts of this period. But Monotype Grotesque was always one of designer Rod McDonald’s favourites, and he was overjoyed when he finally got the go-ahead from Monotype in 2008 to update this “hidden treasure”. The design process lasted four years, with regular interruptions due to the need to complete projects for other clients. In retrospect, McDonald admits that he had no idea at the beginning of just how challenging and complex a task it would be to create Classic Grotesque™. It took him considerable time before he found the right approach. In his initial drafts, he tried to develop Monotype Grotesque only to find that the result was almost identical with Arial®, a typeface that is also derived in many respects from Monotype Grotesque. It was only when he went back a stage, and incorporated elements of Bauer Font’s Venus™ and Ideal Grotesk by the Julius Klinkhardt foundry into the design process, that he found the way forward. Both these typefaces had served as the original inspiration for Monotype Grotesque. The name says it all: Classic Grotesque has all the attributes of the early grotesque fonts of the 20th century: The slightly artificial nature gives the characters a formal appearance. There are very few and only minor variations in line width. The tittles of the ‘i’ and ‘j’, the umlaut diacritic and other diacritic marks are rectangular. Interestingly, it is among the uppercase letters that certain variations from the standard pattern can be found, and it is these that enliven the typeface. Hence the horizontal bars of the “E”, “F” and “L” have bevelled terminals. The chamfered terminal of the bow of the “J” has a particular flamboyance, while the slightly curved descender of the “Q” provides for additional dynamism. The character alternatives available through the OpenType option provide the designer with a wealth of opportunities. These include a closed “a”, a double-counter “g” and an “e” in which the transverse bar deviates slightly from the horizontal. The seven different weights also extend the scope of uses of Classic Grotesque. These range from the delicate Light to the super thick Extrabold. There are genuine italic versions of each weight; these are not only slightly narrower than their counterparts, but also have variant shapes. The “a” is closed, the “f” has a semi-descender while the “e” is rounded. Its neutral appearance and excellent features mean that Classic Grotesque is suitable for use in nearly all imaginable applications. Even during the design phase, McDonald used his new font to set books and in promotional projects. However, he would be pleased to learn of possible applications that he himself has not yet considered. Classic Grotesque, which has its own individual character despite its neutral and restrained appearance, is the ideal partner for your print and web project. - Burgues Script by Sudtipos,
$99.00Burgues Script is an ode to the late 19th century American calligrapher Louis Madarasz, whose legendary pen has inspired schools of penmanship for over 100 years. His talent has caused some people to call him “the most skillful penman the world has ever known.” I use the word ‘ode’ in a colloquially ambitious manner. If I was an actual poet, my words would be about things I desire but cannot attain, objects of utter beauty that make me wallow in humility, or people of enormous talent who look down at me from the clouds of genius. But I don’t write poems. My work consists of letters drawn to fit together, that become an element of someone’s visual poetry. I am the poet’s assistant, so to speak. Once in a while, the assistant persists on what the subject of the poem will be. And occasionally, the poet gives in to the persistence. I hope you, visual poet, find my persistence justified in this case. The two main sources for Burgues were the calligraphy examples shown in Zaner Bloser’s The Secret of the Skill of Madarasz: His Philosophy and Penmanship Masterpieces, and C. W. Jones’s Lessons in Advanced Engraver’s Script Penmanship by L. Madarasz. These two references were the cornerstone for the concept I was trying to work with. I did have to change many of the letters in order to be able to produce digital calligraphy that can flow flexibly and offered the user a variety of options, while maintaining its attractive appearance. To this end, many ligatures and swashes were made, as well as full flourished sets of letters for use at the beginnings or endings of words and sentences. All of this has been tied together with OpenType and tested thoroughly within today’s standard design and desktop publishing software. After working with digital scripts for so long, at one point I thought that Burgues Script would become a bit of a chore to complete. I also thought that, like with most other scripts, the process would regularize itself after a while and be reduced to a mechanical habit. Surprisingly, and fortunately for me, this did not happen. The past holds as many surprises as the future. Madarasz’s method of penmanship was fascinating and challenging to translate into the strict, mathematically oriented language of the computer. It seems that the extremely high contrast of the forms, coupled with the required flow and connectivity of such lettering, will always be hard work for any visual artist to produce, even with the aide of a powerful machine. I can only imagine what steady nerves and discipline Madarasz must have had to be able to produce fully flourished and sublimely connected words and sentences on a whim. When I think of Madarasz producing a flourished calligraphic logotype in a few seconds, and try to reconcile that with the timelines of my or my colleagues’ work in identity and packaging design, the mind reels. Such blinding talent from over a hundred years ago. Burgues is the Spanish word for Bourgeois. In the end, I hope Burgues Script will serve you well when a flourished word or sentence is required for a design project. One of the wonders of the computer age is the ability to visually conjure up the past, serving both the present and the future. With Burgues, you have a piece of “the most skillful penman the world has ever known,” at your service. Burgues received important awards such as a Certificate of Excellence TDC2 2008 and a Certificate of Excellence at the Bienal Tipos Latinos 2008. - Piel Script by Sudtipos,
$89.00Over the past couple of years I received quite a number of unusual and surprising requests to modify my type designs to suit projects of personal nature, but none top the ones that asked me to typeset and modify tattoos using Burgues Script or Adios. At first the whole idea was amusing to me, kind of like an inside joke. I had worked in corporate branding for a few years before becoming a type designer, and suddenly I was being asked to get involved in personal branding, as literally “personal” and “branding” as the expression can get. After a few such requests I began pondering the whole thing from a professional perspective. It was typography, after all, no matter how unusual the method or medium. A very personal kind of typography, too. The messages being typeset were commemorating friends, family, births, deaths, loves, principles, and things that influenced people in a deep and direct way, so much so that they chose to etch that influence on their bodies and wear it forever. And when you decide to wear something forever, style is of the essence. After digging into the tattooing scene, I have a whole new respect for tattoo artists. Wielding that machine is not easy, and driving pigment into people’s skin is an enormous responsibility. Not to mention that they're some of the very few who still use a crafty, hands-on process that is all but obsolete in other ornamentation methods. Some artists go the extra mile and take the time to develop their own lettering for tattooing purposes, and some are inventive enough to create letters based on the tattoo’s concept. But they are not the norm. Generally speaking, most tattoo artists use generic type designs to typeset words. Even the popular blackletter designs have become quite generic over the past few decades. I still cringe when I see something like Bank Script embedded into people’s skin, turning them into breathing, walking shareholder invitations or government bonds. There’s been quite a few attempts at making fonts out of whatever original tattoo designer typefaces can be found out there - wavy pseudo-comical letters, or rough thick brush scripts, but as far as I could tell a stylish skin script was never attempted in the digital age. And that’s why I decided to design Piel Script. Piel is Spanish for skin. In a way, Piel Script is a removed cousin of Burgues Script. Although the initial sketches were infused with some 1930s showcard lettering ideas (particularly those of B. Boley, whose amazing work was shown in Sign of the Times magazine), most of the important decisions about letter shapes and connectivity were reached by observing whatever strengths and weaknesses can be seen in tattoos using Burgues. Tattoos using Adios also provided some minor input. In retrospect, I suppose Affair exercised some influence as well, albeit in a minor way. I guess what I'm trying to say is there is as much of me in Piel Script as there is in any of the other major scripts I designed, even though the driving vision for it is entirely different from anything else I have ever done. I hope you like Piel Script. If you decide it to use it on your skin, I'll be very flattered. If you decide to use it on your skateboard or book cover, I'll be just as happy. Scripts can't get any more personal than this. Piel Script received the Letter2 award, where they selected the best 53 typefaces of the last decade, organised by ATypI. - FF Fago Monospaced by FontFont,
$67.99FF Fago Thanks to his many years of involvement in major corporate type projects, Ole Schäfer had the necessary resources from which to construct his FF Fago™. The result is an extended family that provides comprehensive typographic support and whose qualities come to the fore in all relevant contexts ? from print to office through internet and wayfinding systems. FF Fago The sizable x-height together with the generous and open design of the characters ensure that the sans serif Fago remains clearly legible even in small point sizes or in potentially difficult situations, such as on wayfinding systems. A subtle contrast in line weight and letter forms that are reminiscent of those of an antiqua typeface provide the font with a restrained yet friendly and lively tone. Available in five weights, each with three different kerning widths and matching genuine italic variants, FF Fago is equipped for practically every situation. There are also small caps, oldstyle and lining figures, a selection of ligatures and geometric symbols. The range of potential applications of this universal font is almost inexhaustible ? it can be used in packaging design, on signs, posters and even for setting longer text sections. Fago is the ideal partner for those working on major corporate projects! FF Fago Correspondence Sans und Correspondence SerifThe Correspondence versions of Fago have been optimized for use in the business environment and in office communication. The carefully modified characters have a particularly robust feel, so that the clear, easily differentiated glyphs allow for straightforward communication even on screen. With these aims in mind, Schäfer has not only adjusted the x-height, but has provided certain letters in the sans variant ? such as the lowercase "i", the "r" and the uppercase "I" ? with serifs. Correspondence Serif, on the other hand, has been conceived as a slab serif throughout and in appearance has the look of the letters produced by the old office typewriting machines. An individual note has been added by providing a few unusual serif forms, as for example in the case of the "m", the "v" and the "y". Both Correspondence Sans and Serif are available in two weights with complementary italic versions and thus are ideally suited for use with standard office programs. This is all rounded off with a selection of office symbols. FF Fago Monospaced The use of a few typographic tricks is necessary to ensure that the letters of the alphabet appear to have the same width. Narrow letters such as "r" and "i" have been made to seem more expansive by using prominent serifs while the broader letters ? a good example is the "m" ? have the forms seen in a condensed font. And it is thanks to this design strategy that Fago Monospaced has the character of old typewriter text. What was once unavoidable because of the technology of the time is now a welcome alternative that can be used for the purposes of emphasis. As an additional supplement to the Fago superfamily, Fago Monospaced can be used, for example, to set short notes or draw attention to special text passages. There are three weights, in their original form without italic variants or small caps, but offering an alternative, technical form of the "0" with a crossbar. - Varidox by insigne,
$35.00Varidox, a variable typeface design, allows users to connect with specific design combinations with slightly varied differences in style. These variations in design enable the user to reach a wider scope of audiences. As the name suggests, Varidox is a paradox of sorts--that is, a combination of two disparate forms with two major driving influences. In the case of type design, the conflict lies in the age-old conundrum of artistic expression versus marketplace demand. Should the focus center primarily on functionality for the customer or err on the side of advancing creativity? If both are required, where does the proper balance lie? Viewed as an art, type design selections are often guided by the pulse of the industry, usually emphasizing unique and contemporary shapes. Critics are often leading indicators of where the marketplace will move. Currently, many design mavens have an eye favoring reverse stress. However, these forms have largely failed to penetrate the marketplace, another major driving factor influencing the font world. Clients now (as well as presumably for the foreseeable future) demand the more conservative forms of monoline sans serifs. Typeface designers are left with a predicament. Variable typefaces hand a great deal of creative control to the consumers of type. The demands of type design critics, personal influences of the typeface designer and the demands of the marketplace can all now be inserted into a single font and adjusted to best suit the end user. Varidox tries to blend the extremes of critical feature demands and the bleeding edge of fashionable type with perceptive usability on a scalable spectrum. The consumer of the typeface can choose a number between one and one-thousand. Using a more conservative style would mean staying between zero and five hundred, while gradually moving higher toward one thousand at the high end of the spectrum would produce increasingly contemporary results. Essentially, variable fonts offer the ability to satisfy the needs of the many versus the needs of the few along an axis with a thousand articulations, stabilizing this delicate balance with a single number that represents a specific form between the two masters, a form specifically targeted towards the end user. Practically, a user in some cases may wish to use more conservative slab form of Varidox for a more conservative clientele. Alternatively, the same user may then choose an intermediate instance much closer to the other extreme in order to make a more emphatic statement with a non-traditional form. Parametric type offers a new options for both designers and the end users of type. In the future, type will be able to morph to target the reader, based on factors including demographics, mood or cultural influences. In the future, the ability to adjust parameters will be common. With Varidox, the level of experimentality can be gauged and then entered into the typeface. In the future, machine learning, for example, could determine the mood of an individual, their level of experimentality or their interest and then adjust the typeface to meet these calculated parameters. This ability to customize and tailor the experience exists for both for the designer and the reader. With the advent of new marketing technologies, typefaces could adjust themselves on web pages to target consumers and their desires. A large conglomerate brand could shift and adapt to appeal to a specific target customer. A typeface facing a consumer would be more friendly and approachable, whereas a typeface facing a business to business (B2B) customer would be more businesslike in its appearance. Through both experience, however, the type would still be recognizable as belonging to the conglomerate brand. The font industry has only begun to realize such potential of variable fonts beyond simple visual appearance. As variable font continues to target the user, the technology will continue to reveal new capabilities, which allow identities and layouts to adjust to the ultimate user of type: the reader. - Juvenis by Storm Type Foundry,
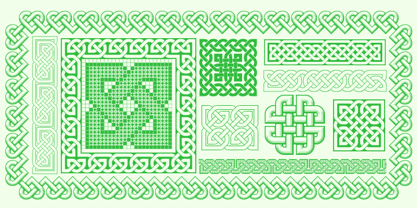
$32.00Designs of characters that are almost forty years old can be already restored like a historical alphabet – by transferring them exactly into the computer with all their details. But, of course, it would not be Josef Tyfa, if he did not redesign the entire alphabet, and to such an extent that all that has remained from the original was practically the name. Tyfa published a sans-serif alphabet under the title Juvenis already in the second half of the past century. The type face had a large x-height of lower-case letters, a rather economizing design and one-sided serifs which were very daring for their time. In 1979 Tyfa returned to the idea of Juvenis, modified the letter “g” into a one-storey form, narrowed the design of the characters even further and added a bold and an inclined variant. This type face also shows the influence of Jaroslav Benda, evident in the open forms of the crotches of the diagonal strokes. Towards the end of 2001 the author presented a pile of tracing paper with dozens of variants of letter forms, but mainly with a new, more contemporary approach: the design is more open, the details softer, the figures and non-alphabetical characters in the entire set are more integral. The original intention to create a type face for printing children’s books thus became even more emphasized. Nevertheless, Juvenis with its new proportions far exceeds its original purpose. In the summer of 2002 we inserted all of this “into the machine” and designed new italics. The final computer form was completed in November 2002. All the twelve designs are divided into six variants of differing boldness with the corresponding italics. The darkness of the individual sizes does not increase linearly, but follows a curve which rises more steeply towards the boldest extreme. The human eye, on the contrary, perceives the darkening as a more fluent process, and the neighbouring designs are better graded. The x-height of lower-case letters is extraordinarily large, so that the printed type face in the size of nine points is perceived rather as “ten points” and at the same time the line spacing is not too dense. A further ingenious optical trick of Josef Tyfa is the figures, which are designed as moderately non-aligning ones. Thus an imaginary third horizontal is created in the proportional scheme of the entire type face family, which supports legibility and suitably supplements the original intention to create a children’s type face with elements of playfulness. The same applies to the overall soft expression of the alphabet. The serifs are varied; their balancing, however, is well-considered: the ascender of the lower-case “d” has no serif and the letter appears poor, while, for example, the letter “y”, or “x”, looks complicated. The only serif to be found in upper-case letters is in “J”, where it is used exclusively for the purpose of balancing the rounded descender. These anomalies, however, fit perfectly into the structure of any smoothly running text and shift Juvenis towards an original, contemporary expression. Tyfa also offers three alternative lower-case letters *. In the case of the letter “g” the designer follows the one-storey form he had contemplated in the eighties, while in “k” he returns to the Benda inspiration and in “u” adds a lower serif as a reminder of the calligraphic principle. It is above all the italics that are faithful to the tradition of handwritten lettering. The fairly complicated “k” is probably the strongest characteristic feature of Juvenis; all the diagonals in “z”, “v”, “w”, “y” are slightly flamboyant, and this also applies to the upper-case letters A, V, W, Y. Juvenis blends excellently with drawn illustrations, for it itself is modelled in a very creative way. Due to its unmistakable optical effect, however, it will find application not only in children’s literature, but also in orientation systems, on posters, in magazines and long short-stories. - Celtic Knots by Clanbadge,
$20.00While it is obvious that this is an ornamental style font, it is more than that: it is a Celtic Knotwork design tool! Irish, Scottish, Welsh, even Norse and Viking cultures have used knotwork designs for millenia. These ancient traditional interwoven designs are experiencing a revival as Celtic culture gains exposure in the modern world. Intricate Celtic knots are featured everywhere from jewelry to tattoos. While many enjoy them simply for their beauty and fascinating twists, they can also be used to add an air of myth, magic and mystery to any project. The interlaced lines make them perfect for wedding invitations, borders, dividers and rules, web graphics, and logos. I began using Celtic knotwork designs in my own work as part of my knifemaking and jewelry making hobbies. I read all of the books I could find about Celtic knots and at first I drew them by hand with pencil and paper. Then as I realized how nice it would be to have "undos" I switched over to using Corel Draw. Draw proved to be a natural for this type of artwork with tools like contour and the trim function. But even with these great tools, it was still tedious to create these designs. I noticed that I was able to reuse a lot of parts in repetitive sections. I developed a small library of reusable bits and chunks of Celtic designs. I found them so useful and fun to work with that I began thinking about ways to market my Celtic design kit. I thought about CDR and EPS formats, but then I thought of creating this toolset as a True Type Font. That way anyone with ANY program that uses fonts could easily create Celtic knotwork designs. Word processors, embroidery programs, engraving programs, jewelry design programs, CAD/CAM programs...almost every program can use fonts. I was also interested in CNC work and thought that this font would work well for applications such as laser etching, vinyl signs, and machining. With that in mind, I designed each character of the font with extremes of accuracy. If one character from the font is used at one inch tall, every control point will be placed to an accuracy of better than 0.0001 inch. I wanted every piece to meet exactly with the next, with no possibility for misalignment. The different styles are all very carefully created to fit accurately with each other. So the Filled Style fits exactly into the Outline Style, and the Inverse Style fits precisely around the Outline Style so as to make up the background behind the knotwork. Combining the styles allows you to have complete creative control. By assembling the nearly 200 pieces it is quite easy to produce very complex designs. It is actually a bit like playing with a puzzle and many people really enjoy putting the pieces together to make designs. In fact, I have had many customers tell me of how they love playing with this font and making knots into the wee hours of morning. If you like puzzles then you will absolutely love this font! And creating the patterns is just the beginning of the fun! If you apply your favorite Photoshop tricks on them you can make anything from dazzling chrome knotwork to carved stone. Photoshop plug-ins like SuperBladePro are great for converting knotwork text into corroded bronze or rusted iron. Use your knotwork to add texture to a virtual landscape, or add them as surface embelishments on architecture and furniture. You can also make round knotwork by using this font with "WordArt" (WordArt is included with every copy of Microsoft Word. See http://clanbadge.com/round_knots.htm for a tutorial on how to make round knotwork). For Crafters there are limitless uses for this font. It has been used for embroidery, jewelry, leatherwork, stencils, stained glass, quilting, painting, pyrography, woodcarving and lots more. We have even sold copies to monks for use in decorating handmade books! - LT Soul - 100% free
- Temporarium - 100% free
- Averia Serif - 100% free
- LT Hoop - 100% free
- Old Standard TT - 100% free
- Pecita - 100% free
- News Cycle - 100% free
- Pfennig - 100% free
- nineveh - 100% free
- Gentium - 100% free