10,000 search results
(0.038 seconds)
- PF Tempesta Seven - Unknown license
- Aron Grotesque - Personal use only
- SF Espresso Shack - Unknown license
- Action Man - Unknown license
- SF Planetary Orbiter - Unknown license
- SF Burlington Script - Unknown license
- SF Groove Machine - Unknown license
- SF Port McKenzie - Unknown license
- SF Zero Gravity - Unknown license
- SF Synthonic Pop - Unknown license
- SF Willamette Extended - Unknown license
- TypographerGotisch Schmuck - Unknown license
- SF Wasabi Condensed - Unknown license
- SF Chromium 24 - Unknown license
- SF Cosmic Age - Unknown license
- Engebrechtre Expanded - Unknown license
- Musika by Lurinzu Studios,
$12.75Musika" is a serene and elegant display typeface that is inspired by the vibe of soft jazz. Serene, elegant, soothing, somewhat sensual and at the same time feels like a warm hug. This typeface is made with the intention to be used in both titles and body text. The bold weight (even the light weight could also be used as a title card) holds really well as a title while the lighter weights (regular and light) can be used in body text. *This font includes letters, numbers, multi-language, and all essential marks needed. * Three (3) weights are currently available. (Light, Regular and Bold) - Kathmandu by Volcano Type,
$19.00Kathmandu, the Nepalese capital in the foothills of the Himalayas, is not like any other city. That's why Kathmandu Bold is not like any other font going by the name of a town, either: This font is not as digital as Chicago but not as solid as Aachen. Kathmandu Bold's capital letters are slightly irregular, giving the font its unique character, which is extended and more black than bold. Everyone who has hitherto regarded "naïve" and "cool" as being an oppositional pair should check out this font by Ingo Juergens. For special needs, such as foreign languages, there is a host of special characters. - SF Buttacup Lettering - Unknown license
- Times New Roman Windows compatible by Monotype,In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Times New Roman World Version is an extension of the original Times New Roman with several other scripts like with the Helvetica World fonts. It is part of the Windows Vista system. The following code pages are supported:1250 Latin 2: Eastern European 1251 Cyrillic 1253 Greek 1254 Turkish 1255 Hebrew 1256 Arabic Note: The Roman and Bold versions include the arabic scripts but they are not part in the corresponding italic versions. 1257 Windows Baltic 1258 Windows Vietnamese
- Amherst by Linotype,
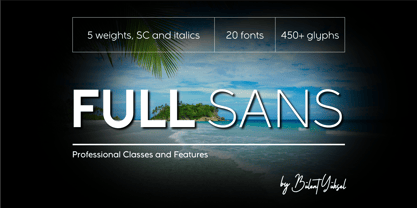
$29.99Amherst is a family of blackletter-inspired typefaces. This family, created by British designer Richard Yeend in 2002, is unique in that it mains the feel of blackletter/medieval type without relying directly on historical forms. Amherst is split into two different sub-families, Amherst and Amherst Gothic. Amherst is very geometric interpretation of Fraktur. Fraktur was a style of German type very popular in central Europe from 1517 until the early 20th Century. Its letters appear "broken" at certain angles and joints. Still, we recommend using it primarily for display purposes. Amherst is available in three weights: Regular, Bold, and Heavy. Amherst Gothic is very loosely inspired by late medieval letterforms, often called Texturas or Gothics. However, the letterforms of Amherst Gothic seem just as inspired by the Art Deco movements of the 1920s and by contemporary sans serif type design as anything else. Nevertheless, certain letters in this typeface do appear more "gothic" than others, especially A, D, M, Y, d, r, and x. Amherst Gothic is made up of three fonts, Amherst Gothic Split, Amherst Gothic Split Alternate, and Amherst Gothic Italic. Amherst Gothic Split has in-lined characters, and appears very ornamented. The alternate characters in Amherst Gothic Split Alternate are quite medieval in their appearance. Amherst Gothic Italic is the least medieval-looking of the set; its characters are very round, and more geometric. All six styles of the Amherst Family are OpenType format fonts, and include old style figures. - Full Sans by Bülent Yüksel,
$19.00Full Sans is a geometric sans in the tradition of Futura, Avant Garde and the like. It has a modern streak which is the result of a harmonization of width and height especially in the lowercase letters to support legibility. Full Sans is the younger brother of original Full Neue, Full Slab and Full Tools. Ideally suited for advertising and packaging, editorial and publishing, logo, branding and creative industries, poster and billboards, small text, wayfinding and signage as well as web and screen design. Full Sans provides advanced typographical support for Latin-based languages. An extended character set, supporting Central, Western and Eastern European languages, rounds up the family. The designation “Full Sans LC 50 Book” forms the central point. The first figure of the number describes the stroke thickness: 10 Thin to 90 Bold. Full Sans LC comes 5 weights and italics also Full Sans SC comes 5 weights and italics total 20 types. The family contains a set of 485 characters. Case-Sensitive Forms, Classes and Features, Small Caps from Letter Cases, Fractions, Superior, Inferior, Denominator, Numerator, Old Style Figures just one touch easy In all graphic programs. Full Sans is the perfect font for web use. You can enjoy using it. UPDATE: 08 March 2019 - Fixed extension of glyhps "y" and "g". - "LineGap" error has been fixed. - Fixed bug in "onum", "pnum", "tnum" and "tnum" software in OpenType feature. - Ritalin - Unknown license
- Adagio - Unknown license
- Grantham - Unknown license
- GranthamCondensed - Unknown license
- Classica Pro by URW Type Foundry,
$35.99Classica Pro by Bernd Möllenstädt A real alternative for letterpress printing A masterpiece It was only after many years, shortly before the end of his life, Bernd Möllenstädt brought out these early drafts of his Classica Light and Light Italic from his drawer, and asked me to produce for him on the computer a Bold and Bold Italic, from which we later wanted to interpolate further cuts like Regular and so on. The boldening of letters with an oblique axis and with hairlines which should not grow to the same extent as the general line widths, is hard to cope with perfectly, even for the smartest computer program, and even more so, when it concerns an as complicated set of data as those conceived by Bernd. The automatically generated result could therefore only be a first step that had to be improved manually later. This was about the stage that we had reached when Bernd died in March 2013, leaving me behind with comprehensive corrections on proofs of this automatically generated Bold. Although I was aware that it would mean a lot of work to complete the project, I did not want to leave it unfinished and decided to finalize and publish the Classica, also in Bernd‘s honor. In the course of the two years that I worked on this font family it somewhat naturally became also my own. New details were added and some of the existing changed. A book typeface requires the supreme and forgives rarely, it represents a true masterpiece. My intention and my ambition were to create a real alternative for letterpress printing, with a font family that contains all the typographic options for an excellent typesetting, and is better readable and has a better appearance than other existing typefaces. Whether this was achieved, the reader may decide. Volker Schnebel, Hamburg, december 2014 - Times Eighteen by Linotype,
$29.00In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Europa LT by Linotype,
$29.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times Ten Paneuropean by Linotype,
$92.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Times by Linotype,
$40.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times™, Times™ Europa, and Times New Roman™ are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times™ is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times™ Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times™ Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer. Times™ Europa is the Walter Tracy re-design of 1972, its sturdier characters and open counterspaces maintain readability in rougher printing conditions. Times New Roman™ is the historic font version first drawn by Victor Lardent and Stanley Morison for the Monotype hot metal caster." - Savour Pro by profonts,
$51.99 - Carabelle by Typejockeys,
$25.00 - Fatso - Unknown license
- Zephyrine by Muksal Creatives,
$10.00 - Milyuna by Suby Studio,
$10.00Milyuna is classic and stylish serif with high contrast. We made two different styles Regular and Italic which is suitable any purpose, such as heading, bussines card, quotes, or invitations. Includes: Milyuna Reguler Milyuna Italic Features Lowercase & Uppercase Numerals & Punctuations Multilingual characters (ÀÁÂÃÄÅÆÇÐĐÈÉÊËÌÍÎÏŁÑÒÓÔÕÖØŒŠÙÚÛÜŸÝŽ) - Pamors by Alit Design,
$18.00PAMORS typeface is a bold and daring blackletter font that exudes a sense of strength and power. The mix of regular and italic styles provides versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of design applications. With 799 characters, Pamors typeface offers extensive multilingual support and includes PUA unicode for easy access to special characters. One of the standout features of this font is its use of ligatures and swashes, which add an extra touch of elegance and sophistication to any project. Whether used in headlines, logos, or body text, Pamors typeface is sure to make a bold statement that commands attention. Language Support : Latin, Basic, Western European, Central European, South European,Vietnamese. In order to use the beautiful swashes, you need a program that supports OpenType features such as Adobe Illustrator CS, Adobe Photoshop CC, Adobe Indesign and Corel Draw. but if your software doesn’t have Glyphs panel, you can install additional swashes font files. - Mantika News by Linotype,
$67.99Mantika News™, from German designer Jürgen Weltin, was designed to expand the Mantika super family with text and display typefaces for setting newspapers and periodicals. The suite of typefaces is comprised of regular and bold designs, with italic counterparts, for setting continuous text, and light and extra bold versions for setting larger sizes in headlines, sub heads, pull quotes and decks. The typefaces intended for text copy were designed with shared character widths, so that changes can be made in typeface choice without disrupting line endings or column length. The display designs have a slightly smaller x-height and shorter ascenders creating a more elegant demeanor while ensuring compact multi-line display copy. In addition, fonts of Mantika News have a large Monotype W1G (World Glyph Set 1) character set enabling the setting of Greek, Cyrillic and over 20 Eastern and Western European Latin-based languages. Proportional figures are available, in the OpenType® fonts, as an alternative to the tabular designs. - Hastafi by Mans Greback,
$49.00Hastafi is a classy serif typeface. It is naturally bold, with contrasting, hairline thin horizontal strokes, and a confident character. Use it for any project that needs that extra bit of elegance and personality, without losing the thoughtfulness and authenticity of a serious serif font. The Hastafi family consists of eight beautiful styles: The Regular, for a medium and normal variety, and the flowing Italic version. It also contains a swash style for decorative additions to the letters, and each of the styles as an emphasized Bold. The font is built with advanced OpenType functionality and has a guaranteed top-notch quality, containing stylistic and contextual alternates, ligatures and more features; all to give you full control and customizability. It has extensive lingual support, covering all Latin-based languages, from North Europe to South Africa, from America to South-East Asia. It contains all characters and symbols you'll ever need, including all punctuation and numbers.