1,562 search results
(0.08 seconds)
- Shangri La NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00An unusual handlettered alphabet from the 1922 chapbook Modern Show Card Writing, by Joseph Bertram Jowitt, provided the pattern for this whimsical face. Its letterforms, as well as its name, conjure up visions of faraway places, and is sure to add a unique charm to your next project. This font contains the complete Latin language character set (Unicode 1252) plus support for Central European (Unicode 1250) languages as well. - Durable JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00The front page of a late-1940s sales catalog for the [now defunct] Duro Decal Company of Chicago had its company name hand-lettered in a tall, condensed chamfered sans serif type design. Although chamfered lettering had been popular for decades, the way the "R" was shaped gave the letters a bit of an Art Deco influence, and this influence was carried through in the creation of Durable JNL. - Haute Couture JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00A style of die-cut cardboard letters and numbers used for signs, displays and show cards was the basis for Haute Couture JNL, an Art-Deco flavored typeface from Jeff Levine. A direct cousin to Signboard JNL, this font shares some similar characteristics in letterforms. Both styles of die-cut lettering were manufactured by a number of companies, and were most popular from the 1940s through the mid-1960s. - Koliba JY by JY&A,
$39.00Inspired by architecture and hand-lettered posters of the 1940s, JY Koliba makes a statement that is very 21st century. With an ultra-light weight plus an elegant book and bold, Koliba was designed to be flexible. Fine-tuned with a full Latin glyph complement, and Windows kerning support for designer Jure Stojan’s Slovenian mother tongue, Koliba is set to be one of the foundry’s best-loved sans serifs. - Mezz by Adobe,
$29.00Clarinetist Milton ?Mezz? Mezzrow (1899-1972) was a remarkable jazz musician, as becomes evident upon reading his autobiography Really the Blues. His sharp tone and serpentine lines inspired English lettering artist and jazz lover Michael Harvey to create a condensed, oblique display typeface with the look of a chiseled alphabet in the musician's honor. Vertical formats such as book jackets and posters will be invigorated by Mezz as the display face. - Dance Number JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Vintage sheet music for the song "Just Once for All Time" (from the United Artists release "Congress Dances") provided the bold sans that served as the model for Dance Number JNL. This 1932 film was the English language version of the German comedy "Der Kongrefl tanzt" The movie's plot is based around the Congress of Vienna. There, an Austrian commoner is mistakenly thought to be the Tsar of Russia. - Rummy Tall by Bunny Dojo,
$23.00Rummy, the stout, scrappy font inspired by sports branding and 1940s film, has grown up and is ready to take on new responsibilities. The result: Rummy Tall. Still powerful, precise, and packed with personality, Rummy Tall's added height brings with it even more versatile charm. Track Rummy Tall tightly for a sturdy foundation, or give Rummy Tall some breathing room for an unexpected air of nobility. Reach new heights! - 1906 Fantasio Auriol by GLC,
$38.00We have created this family inspired from the set of well known Auriol fonts used by the French popular "cheerful" satirical magazine Fantasio (1906-1948). The present version contains Normal, Italic, Bold and Bold Italic styles, in use for texts, plus narrow titlings and normal outlined with upper and lower case, both in use for titles. This family may be used together with 1906 French News, 1906 Titrage and 1890 Notice. - School Activities JNL by Jeff Levine,
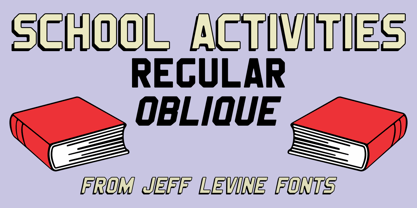
$29.00An image spotted in an online auction online of a 1940 Milton Bradley child's activity set consisting of wooden letters formed the basis for School Activities JNL, which is available in both regular and oblique versions. Although the basic characters feature chamfered corners, the nature of bending the steel rule dies to form the letters to be cut from the wood provided rounded edges as well, creating their unique look. - Egg Farm JNL by Jeff Levine,
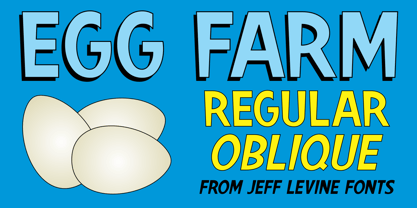
$29.00The opening titles and credits of the 1947 film comedy “The Egg and I” were done in a hand lettered casual sans serif typeface which inspired the digital font Egg Farm JNL; available in both regular and oblique versions. “The Egg and I” introduced audiences to Ma and Pa Kettle as portrayed by Marjorie Main and Percy Kilbride, who went on to do a number of additional films as those characters. - Humpty Dumpling NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00This rollicking romp through the alphabet is based on an offering from the irrepressible M. Draim, seen in La Lettre dans le Décor & la Publicité Modernes, published by Monrocq Frères of Paris in 1932. Its animated and friendly demeanor will add personality to any headline it graces. Both versions of this font contain the Unicode 1252 (Latin) and Unicode 1250 (Central European) character sets, with localization for Romanian and Moldovan. - Tinseltown NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00Suitable for headlines, subheads and short copy blocks, this decidedly Deco number is based on Willard T. Sniffin’s Hollywood, designed for American Type Founders in 1932. A few of the fussier details have been modified from the original to render a clean, streamlined and sophisticated face. All versions of this font include the Unicode 1250 Central European character set in addition to the standard Unicode 1252 Latin set. - ITC Blaze by ITC,
$29.00ITC Blaze was designed by Patty King in 1995. It is a typeface which looks as though it were written by hand with a broad tipped pen on rough paper. The pointed ends of the characters and the leaning to the right give the font a dynamic, energetic feel. Blaze shows the influence of the late 1940s and is best suited for headlines and short to middle length texts. - Lazurski by ParaType,
$30.00Designed at Polygraphmash type design bureau in 1984 by Vladimir Yefimov, with the addition of demi and demi italic. Based on a hot-metal typeface (1962) by Moscow book designer Vadim Lazurski (1909–1994), inspired by the early 16th century typefaces of Italian Renaissance. The typeface is useful for text and display composition, in fiction and art books. An 'expert set' was added by ParaType (ParaGraph) in 1997. - Gavotte by Linotype,
$29.99Linotype Gavotte was designed by Rudo Spemann in 1940. His style was unmistakable, marked by original ideas and completely new forms. His tendency toward the unusual and adventurous resulted in unique, decorative characters. When he wrote, the tip of his pen flew across the page, leaving behind rows of letters which displayed an almost unbelievable regularity of form and flow. Gavotte is a perfect example of the best of Spemann’s calligraphy. - Deco Revisited JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Inspired by a retro Art Deco poster as well as many of the true classic Art Deco type designs of the 1930s and 1940s, Deco Revisited JNL is a bold, black, stencil-influenced design with no counters. Although being a contemporary design, its use in any retro project will truly evoke a feeling for the “streamline” era. Deco Revisited JNL is available in both regular and oblique versions. - Horizon by Bitstream,
$29.99Horizon was inspired by the style of the lettering used in the original Star Trek TV series. Quite fittingly, this font was used 21 years later in the film Star Trek: Into Darkness. In keeping with the digital experimentation of the 90s, Horizon has a space-age look—with sharp, unexpected angles that were achieved sharply with digital tools. It was designed in 1992 by Bitstream staff designers. - Numancia NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00This elegant and somewhat edgy typeface is a faithful revival of Numantina, designed by Carl Winkow amd released by Madrid's Fundición Tipográfica Nacional in the 1940s. The lowercase letters take their design cues from medieval Spanish uncial lettering, making this face a natural choice for intriguing headlines and subheads. Both versions feature the complete Latin 1252, Central European 1250 and Turskish 1254 character sets, with localization for Lithuanian, Moldovan and Romanian. - Wellness JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00The Federal Art Project of the WPA (Works Progress Administration) employed artists to create posters for various subjects including health, tourism, safety, patriotism, theater and the arts during the Great Depression years of the 1930s on through the early 1940s. One health-related poster had the word “against” in a thin Art Deco monoline which served as the basis for Wellness JNL, which is available in regular and oblique versions. - VLNL DBXLZX by VetteLetters,
$9.00DBXLZX was inspired by the logo of the ZX Spectrum home computer, released in 1982 by Sinclair Research. For many designers the 8-bit pixel grid of the ZX Spectrum was one of the first steps into the realm of digital design. DBXLZX was initially developed by DBXL into a three weight family for use on the Armind record label of world famous trance deejay Armin van Buuren. - Guadalajara JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Hand lettered, the title on the sheet music for a 1940s hit song "Ti-Pi-Tin" inspired Guadalajara JNL. The melody and original Spanish lyrics were written by Maria Grever, one of Mexico's first successful female composers, with English lyrics supplied by Raymond Leveen. This decorative and fun type face brings to mind fiestas South of the border, and emanates the charm of Mexico's music, dance and colorful costumes. - Lansere by omtype,
$37.00Lansere is an art-deco typeface inspired by lettering of Russian graphic artist, painter and sculptor Evgeniy Lansere (1875–1946). A strongly geometric lettering style of his late book covers and an elegance of early ones has been combined in a modern typeface . This all-caps font has two versions for each letter and more than 60 discretionary ligatures (both Latin and Cyrillic). The initial graphic idea by Denis Bashev. - Headliner No. 45 by KC Fonts,
$34.00Headliner No. 45 is an ode to the 1940’s-era news headline. The Headliner No. 45 Family is simply two fonts: Regular & Italic. Headliner No. 45 has a very classic look to its features; worn out by a touch of grunge. This font will work with any of your design needs! For a customized look, switch between uppercase and lowercase for a change of erosion on the letters. - PiS Koernig by PiS,
$38.00PiS Koernig is inspired by handwritten alphabets from Max Körner's book „Das Neue Schriftenbuch“ from 1949 featuring bold and decorative display type for use in sign painting and advertising. It features clean and readable glyphs as well as quirky deco alternate letters in Max Körner's original style to add some 1950ies flavour to your projects. Be sure to use E and F caps + alternates for some labyrinth-esque patterns! - Island Time JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Island Time JNL is based on the hand-lettered title from a piece of 1940s sheet music called "An Island Melody". This Art Deco typeface is perfect for projects where a clean, yet attractive headline font is needed. The font's name is based on the euphamism popular amongst Caribbean Islanders that when someone is excessively late for an appointment, date or event they are running on "island time". - Kiddie Stencil JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00At one time, the Hampton Publishing Company of New York specialized in producing reading and activity books for children. The “Letters and Numbers Stencil Book” (probably from the late 1940s or early 1950s) was the basis for Kiddie Stencil JNL. This bold sans serif type style replicates the handmade steel rule dies used for cutting the stencil pages of the book, and is available in both regular and oblique versions. - Romeo by Font Bureau,
$40.00David Berlow drew Romeo Medium Condensed during winter of 1990, basing the design on the Estrecha Fina weight of Electra, a spectacular art deco sanserif with an unusually fine condensed series. Carlos Winkow designed it circa 1940 for the Nacional typefoundry of Madrid, the leading typefoundry in Spain. Jill Pichotta drew the ultra-light Skinny Condensed, a digital tour de force released with Medium Condensed; FB 1990–91 - Drafting Class JNL by Jeff Levine,
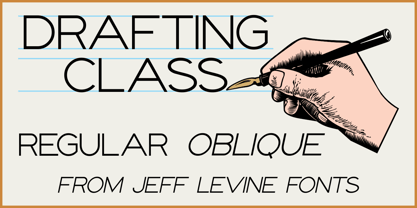
$29.00Within the pages of “The Essentials of Lettering” by Thomas E. French and Robert Meiklejohn (circa 1912) is an example for creating a sans serif alphabet and numerals. The lesson plate is entitled “Upright Single-Stroke Gothic”; a basic monoline font most useful for architectural and drafting plans because of its easy-to-read properties. This type design is now available as Drafting Class JNL, in both regular and oblique versions. - Kymmera Deco NF by Nick's Fonts,
$10.00The dreams that you dare to dream really can come true when you perk up your headlines with this re-imagining of Saul Bass's 1982 glitzy Deco classic, Rainbow Bass. For best results at large sizes, choose the TrueType version, rendered at a full 2,048 UPM. Both versions include the complete Latin 1252, Central European 1250 and Turkish 1254 character sets, as well as localization for Moldovan and Romanian. - Sunshine Susie JNL by Jeff Levine,
$29.00Sheet music for the song "Today I Feel So Happy" from the 1932 motion picture "Sunshine Susie" provided both the visual model and the name for Sunshine Susie JNL, available in both regular and oblique versions. The lettering is a bold Art Deco thick-and-thin design, and comes not from the song's title, but the hand lettered name of the movie as it appeared on the cover the song folio. - Times New Roman PS Cyrillic by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Seven by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman WGL by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman Small Text by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS Greek by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Times New Roman PS by Monotype,
$67.99In 1931, The Times of London commissioned a new text type design from Stanley Morison and the Monotype Corporation, after Morison had written an article criticizing The Times for being badly printed and typographically behind the times. The new design was supervised by Stanley Morison and drawn by Victor Lardent, an artist from the advertising department of The Times. Morison used an older typeface, Plantin, as the basis for his design, but made revisions for legibility and economy of space (always important concerns for newspapers). As the old type used by the newspaper had been called Times Old Roman," Morison's revision became "Times New Roman." The Times of London debuted the new typeface in October 1932, and after one year the design was released for commercial sale. The Linotype version, called simply "Times," was optimized for line-casting technology, though the differences in the basic design are subtle. The typeface was very successful for the Times of London, which used a higher grade of newsprint than most newspapers. The better, whiter paper enhanced the new typeface's high degree of contrast and sharp serifs, and created a sparkling, modern look. In 1972, Walter Tracy designed Times Europa for The Times of London. This was a sturdier version, and it was needed to hold up to the newest demands of newspaper printing: faster presses and cheaper paper. In the United States, the Times font family has enjoyed popularity as a magazine and book type since the 1940s. Times continues to be very popular around the world because of its versatility and readability. And because it is a standard font on most computers and digital printers, it has become universally familiar as the office workhorse. Times?, Times? Europa, and Times New Roman? are sure bets for proposals, annual reports, office correspondence, magazines, and newspapers. Linotype offers many versions of this font: Times? is the universal version of Times, used formerly as the matrices for the Linotype hot metal line-casting machines. The basic four weights of roman, italic, bold and bold italic are standard fonts on most printers. There are also small caps, Old style Figures, phonetic characters, and Central European characters. Times? Ten is the version specially designed for smaller text (12 point and below); its characters are wider and the hairlines are a little stronger. Times Ten has many weights for Latin typography, as well as several weights for Central European, Cyrillic, and Greek typesetting. Times? Eighteen is the headline version, ideal for point sizes of 18 and larger. The characters are subtly condensed and the hairlines are finer." - Heidorn Hill - Unknown license
- The MonospaceTypewriter font, crafted by the renowned typeface designer Manfred Klein, is a digital throwback to the era of mechanical typewriters. This font embodies the quintessential characteristi...
- Stoehr numbers - Personal use only